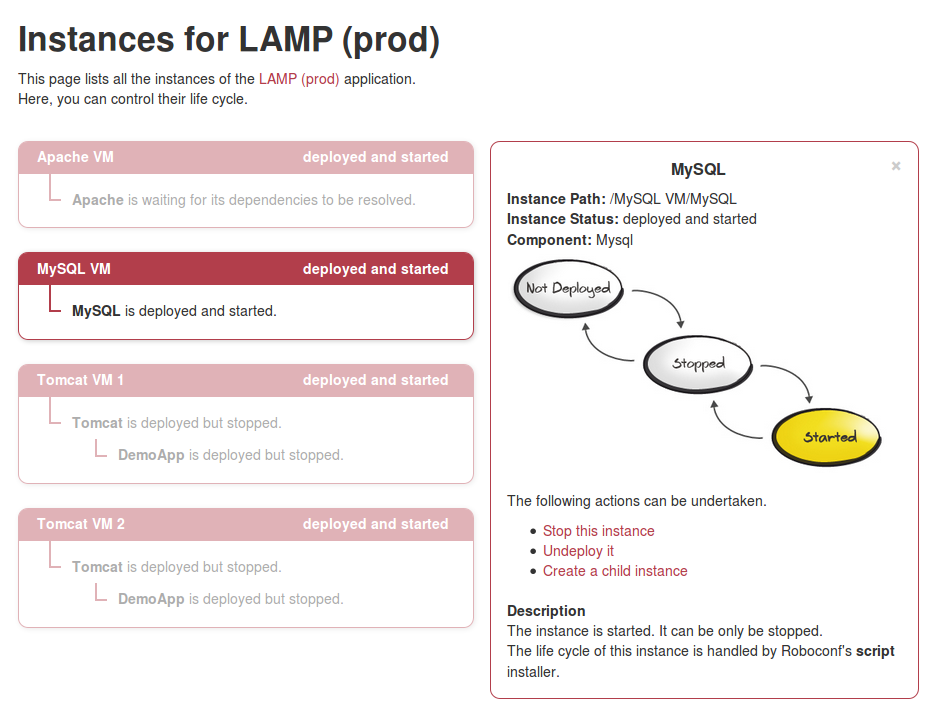
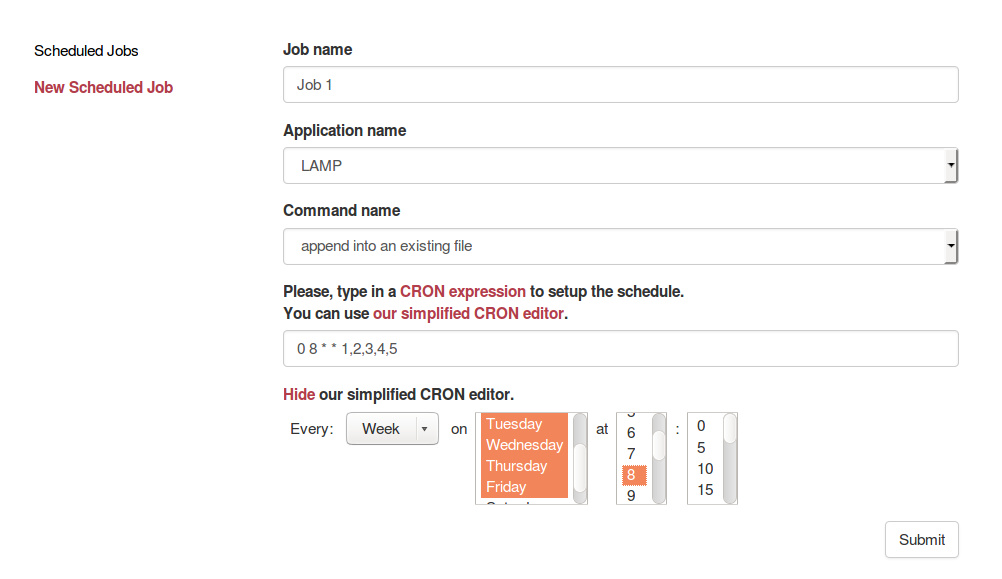
A web application to interact with Roboconf's Deployment Manager.
User documentation can be found on Roboconf's web site.
General guidelines about Roboconf's development are described on the web site.
This read-me only lists specific items for the web console and Javascript development.
You need NPM installed on your machine.
The primary thing to do is to execute...
sudo npm install
npm install
Like Maven, this will download the required Javascript libraries.
We then use another tool called Gulp to manage build actions. You should not have to install it,
it was downloaded by npm.
Once NPM and the project's dependencies have been installed, open a command line interface in the project, type in gulp watch-dev and open http://localhost:8000 in your web browser.
The web administration invokes the DM's REST API.
With released versions of Roboconf, the location of the REST API is deduced from the
server. However, in development mode, it often happens that we have the DM running on one side
(available at http://localhost:8181/roboconf-dm) and the
web administration running from another location (http://localhost:8000).
To be able to use a real DM in development mode, follow this procedure.
- In the project, create the target/dev.config directory.
- Create a JS file in it, e.g. roboconf.dev.configuration.js.
- Copy the following content in this file.
'use strict';
angular.module('roboconf.preferences')
.constant('ROBOCONF_SERVER_URL', 'http://localhost:8181/roboconf-dm');- Update, if necessary, the server URL.
Notice that this file will be used for the Gulp dev and dist tasks.
However, an error will be thrown with the embed task if this directory exists.
This file is only here for development, not for building.
- Since Roboconf 0.8, you will also have to enable CORS on the DM's side.
Just edit the etc/net.roboconf.dm.rest.services.configuration.cfg file.
This section lists the Gulp tasks you can use.
To use them, simply type them in your shell. Use...
Checks
- gulp lint to verify quality rules in the JS scripts.
- gulp test to run unit tests with Mocha (coverage report under target/coverage).
- gulp check_i18n verifies the internationalization.
Development
- gulp watch-dev to develop and test the application locally (http://localhost:8000).
- gulp watch-dist to test the distribution locally (http://localhost:8000).
- gulp clean-dev to delete the generated content in the dev directory (it preserves Bower dependencies).
- gulp clean-dist to delete the dist directory.
- gulp clean combines gulp clean-dist and gulp clean-dev.
Distributions
- gulp dist to create the final distribution (minimal dependencies, minification, etc).
- gulp embed to create a minimal distribution, without running tests or quality checks.
Other tasks do not aim at being invoked manually.
About the way these tasks were implemented, they were done this way because most of the Roboconf team is familiar with Maven and Java development but not with Javascript. So, to work similarly to Maven, we created a target directory (ignored by Git). Here is how it is organized.
- target/dependencies: the Bower dependencies (or dependencies for the front-end).
- target/dev: the development directory, with non-minified files but with a clear structure.
- target/dist: the distribution directory, with minified files and another structure.
- target/coverage: the directory with coverage reports after the unit tests were run.
- target/dev.config: optional directory to create by hand and to store custom settings for development.
target/dist is the thing to embed in Roboconf distributions.
The following files are used at some moment during development or build phases.
- gulpfile.js: the file that controls the build tasks.
- package.json: the NPM configuration (package identification and DEV dependencies management).
- bower.json: the Bower configuration (package identification and Front-End dependencies management).
- .bowerrc: additional configuration for Bower.
- .jshintrc: configuration for JS Hint (code quality).
- karma.conf.js: the configuration for Karma, the tool that runs tests.
- .gitignore: the usual file to list the files Git should not manage.
- node_modules: the Javascript modules used for the build, tests and server tasks (no front-end).
- src: the sources directory of our application.
- tests: the tests directory for our application.
- .travis.yml: the file that configures the build on Travis CI.
The following files are mainly for documentation.
- readme.md: the main documentation for this project.
- NOTICE: copyright mentions.
- LICENSE-2.0.txt: the terms of the Apache license v2.
This web applications comes with tests.
Unit tests run with Mocha and Chai. Mainly services are tested unitly.
To run unit tests, either use...
gulp unit-tests
... or use...
karma start --single-run
Gulp is the build tool.
It runs Karma to run tests during the build chain. So, you can use both of them.
Under src, the code is organized in functional modules.
Such a module contains all the JS scripts and HTML templates for a given feature (applications templates,
preferences, etc).
Under target/dev, we group things according to their type.
All the JS files go under js. All the HTML templates go under templates. Notice that Gulp injects
all the JS and CSS scripts automatically in the index.html file.
Under target/dist, we group things differently.
Bower dependencies are filtered and copied under lib. All the application's JS scripts
are merged into roboconf.min.js. And the CSS as well as the index files are minified too.