Biochemical and biological functions of proteins are the product of both the overall fold of the polypeptide chain, and, typically, structural motifs made up of smaller numbers of amino acids constituting a catalytic center or a binding site that may be remote from one another in amino acid sequence. Detection of such structural motifs can provide valuable insights into the function(s) of previously uncharacterized proteins.
Technically, this remains an extremely challenging problem because of the size of the Protein Data Bank (PDB) archive. We have developed a new approach that uses an inverted index strategy capable of analyzing >200,000 PDB structures with unmatched speed. The efficiency of our inverted index method depends critically on identifying the small number of structures containing the query motif and ignoring most of the structures that are irrelevant. Our approach enables real-time retrieval and superposition of structural motifs, either extracted from a reference structure or uploaded by the user.
Structural motif searching is available as part of the RCSB Advanced Search and RCSB Mol* plugin. Help documentation is available.
Current benchmark times to search in 208,702 PDB structures and 1,068,577 AlphaFold/RoseTTAFold predictions as of 8/16/23, obtained on an instance with 6 cores and 64
GB memory. All structure data is held in memory, inverted index data is read from an SSD.
| Motif | Definition | Found Assemblies | 'Paths' Time [ms] | 'Score' Time [ms] | Total Time [ms] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
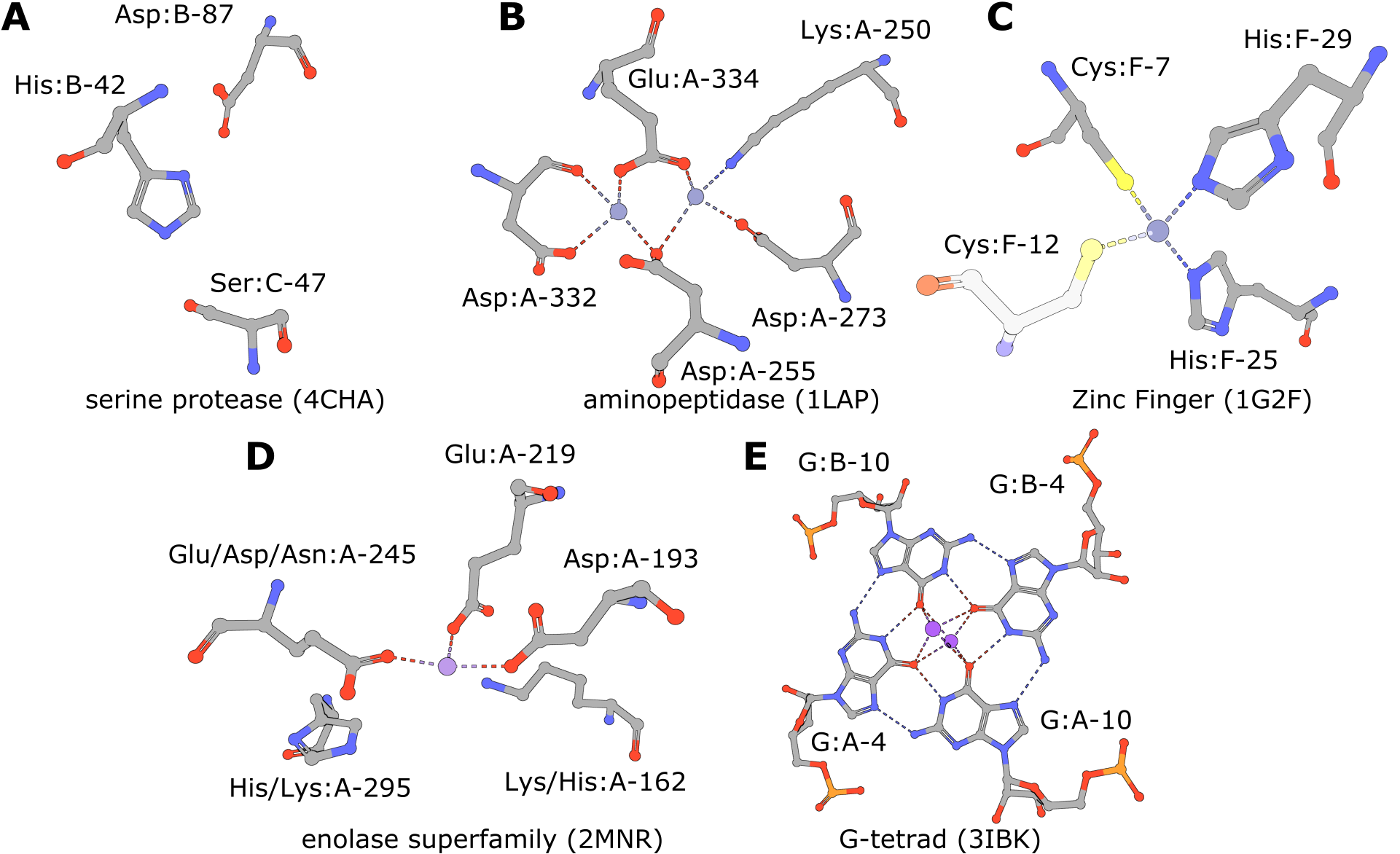
| Serine Protease | 4cha - His:B-42, Asp:B-87, Ser:C-47 | 5,309 | 618 | 22 | 673 |
| Aminopeptidase | 1lap - Lys:A-250, Asp:A-255, Asp:A-273, Asp:A-332, Glu:A-334 | 91 | 158 | 1 | 181 |
| Zinc Fingers | 1g2f - Cys:F-7 His:F-25 His:F-29 | 739 | 135 | 3 | 160 |
| Enolase Superfamily | 2mnr - Lys:A-162, Asp:A-193, Glu:A-219, Glu:A-245, His:A-295 | 192 | 253 | 2 | 275 |
| Enolase Superfamily (exchanges) | 2mnr - Lys/His:A-162, Asp:A-193, Glu:A-219, Glu/Asp/Asn:A-245, His/Lys:A-295 | 210 | 2,996 | 14 | 3,032 |
| RNA G-Quadruplex | 3ibk - G:A-4, G:A-10, G:B-4, G:B-10 | 85 | 2,364 | 236 | 2,622 |
| Motif | Definition | Found Assemblies | 'Paths' Time [ms] | 'Score' Time [ms] | Total Time [ms] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serine Protease | 4cha - His:B-42, Asp:B-87, Ser:C-47 | 10,254 | 1,710 | 125 | 1,988 |
| Aminopeptidase | 1lap - Lys:A-250, Asp:A-255, Asp:A-273, Asp:A-332, Glu:A-334 | 647 | 352 | 7 | 389 |
| Zinc Fingers | 1g2f - Cys:F-7 His:F-25 His:F-29 | 9,442 | 492 | 92 | 686 |
| Enolase Superfamily | 2mnr - Lys:A-162, Asp:A-193, Glu:A-219, Glu:A-245, His:A-295 | 328 | 659 | 5 | 689 |
| Enolase Superfamily (exchanges) | 2mnr - Lys/His:A-162, Asp:A-193, Glu:A-219, Glu/Asp/Asn:A-245, His/Lys:A-295 | 350 | 5,246 | 25 | 5,296 |
| RNA G-Quadruplex | 3ibk - G:A-4, G:A-10, G:B-4, G:B-10 | 85 | 2,453 | 253 | 2,742 |
Search for all assemblies that contain hits with an RMSD <2 Å. 'Paths' refers to the time spent on inverted index operations, which identify all candidate structures that contain the motif. 'Score' refers to the time spent on aligning candidate structures to the query and computing RMSD values.
Computed structure models ignore unreliable regions with pLDDT <70.
- nucleotide support
- inter-chain & assembly support
- position-specific exchanges
- modified residues
- support for computed structure models, like from AlphaFold
- detect motifs in a structure of interest
strucmotif-search is distributed by maven and supports Java 11+. To get started, append your pom.xml by:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.rcsb</groupId>
<artifactId>strucmotif-search</artifactId>
<version>0.19.6</version>
</dependency>An alternative way to use the library is cloning this repository and building the corresponding Maven modules.
The Strucmotif class provides a fluent API to process structural motif queries.
Strucmotif.searchForStructures()
// several ways can be used to define the query motif - e.g., specify a PDB entry id
.defineByPdbIdAndSelection("4cha",
// and a collection of sequence positions to extract residues to use as motif
List.of(new LabelSelection("B", "1", 42), // HIS
new LabelSelection("B", "1", 87), // ASP
new LabelSelection("C", "1", 47))) // SER
.rmsdCutoff(1.0)
.buildParameters()
.buildContext()
.run()
.getHits()
.stream()
.map(hit -> hit.structureIdentifier() + "_" +
hit.assemblyIdentifier() + " @ " +
hit.labelSelections() + " - RMSD: " +
hit.rmsd())
.forEach(System.out::println);This process can also be reversed to detect whether a structure of unknown function contains characteristic motifs.
// acquire a collection of motifs to screen for
Set<EnrichedMotifDefinition> motifs = Strucmotif.getMotifDefinitionRegistry().getEnrichedMotifDefinitions();
Strucmotif.detectMotifs()
.defineByPdbIdAndAssemblyId("2mnr", "1")
.withMotifs(motifs)
.rmsdCutoff(1.0)
.buildParameters()
.buildContext()
.run()
.getHits()
.stream()
.map(hit -> hit.motifIdentifier() + " @ " +
hit.labelSelections() + " - RMSD: " +
hit.rmsd())
.forEach(System.out::println);| Property | Action | Default Value/Behavior |
|---|---|---|
ccd-url |
URL to the chemical component dictionary | wwPDB |
decimal-places-score |
Number of decimal places reported for scores | 2 |
decimal-places-matrix |
Number of decimal places reported in transformation matrices | 3 |
in-memory-strategy |
Preload structure data for increased performance? | off |
loading-chunk-size |
Batch size when holding structure data in memory | 200,000 |
max-results |
Maximum number of results that will be returned | 50,000 |
max-motif-size |
Maximum number of residues that may define a motif | 10 |
per-query-threads |
Number of worker threads per query | available processors |
query-timeout |
Interrupt queries after n milliseconds |
none |
root-path |
Path where data files will be written | /opt/data/ |
Configure by placing your application.properties on the classpath. All properties specific to this project must be
prefixed with strucmotif..
You will need to process your corpus of structure data before using the service. This will create an optimized version of all structure files and add them to an inverted index that allows efficient searching.
Details can be found in: UPDATE.md
Two address schemes exist. LabelSelection is a high-level, object-based way of referencing individual residues. It
uses a combination of mmCIF properties, namely label_asym_id, struct_oper_id, and label_seq_id:
LabelSelection ref = new LabelSelection("A", "1", 123);Internally, access is facilitated using 32-bit unsigned primitive encoded integers. It doesn't follow any particular
layout rather, all encountered residues are addressed by their index. Chain boundaries are ignored. Operations required
for assemblies are honored as they occur in the source file and merely increment the counter.
Additional work is done to preserve information on chains and assemblies. Chain and operator names as well as boundaries
are stored in memory and can be used to reconstruct LabelSelection instances if needed.
Residue pairs are identified by pairs of these int values. They can be stored as long value by chaining together 1st
and 2nd value.
Residue pair descriptors capture the label_comp_id of both interacting residue, their backbone distance, their
side-chain distance, and the angle defined between both.
These values are the Cartesian product of ResidueType (A, 36 states, 6 bits) x ResidueType (B, 36 states, 6 bits) x DistanceType (C, 32 states, 5 bits) x DistanceType (D, 32 states, 5 bits) x AngleType (E, 10 states, 4 bits) and are stored in an unsigned 32-bit integer. The 32-bit descriptors will use their 4th bit to store metadata (M) that tracks whether the identifier is flipped.
XXXMAAAA AABBBBBB XXCCCCCD DDDDEEEE
A second flavor exists that only tracks DistanceType x DistanceType x AngleType and can be held in an unsigned 16-bit short.
XXCCCCCD DDDDEEEE
Convenience functions to work with these descriptors are provided in the ResiduePairDescriptor class.
- ciftools-java: mmCIF parsing and BinaryCIF implementation
- ffindex-java: bundle large amounts of small files together
- rcsb-molstar: define motifs in 3D and visualize results
Bittrich S, Burley SK, Rose AS (2020) Real-time structural motif searching in proteins using an inverted index strategy. PLoS Comput Biol 16(12): e1008502. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008502