The plugin API for the Magpie Framework
Magpie is a free, open-source framework and a collection of community developed plugins that can be used to build complete end-to-end security tools such as a CSPM or Cloud Security Posture Manager. The project was originally created and is maintained by Open Raven. We build commercial cloud native data security tools and in doing so have learned a great deal about how to discover AWS assets and their security settings at scale.
We also heard that many people were frustrated with their existing security tools that couldn't be extended and couldn't work well with their other systems, so decided to create this Magpie framework and refactor and sync our core AWS commercial discovery code as the first plugin.
We plan to actively contribute additional modules to make Magpie a credible free open source alternative to commercial CSPM’s and welcome the community to join us in adding to the framework and building plugins.
Magpie relies on plugins for all its integration capabilities. They are the core of the framework and key to integration with both cloud providers and downstream processing and storage.
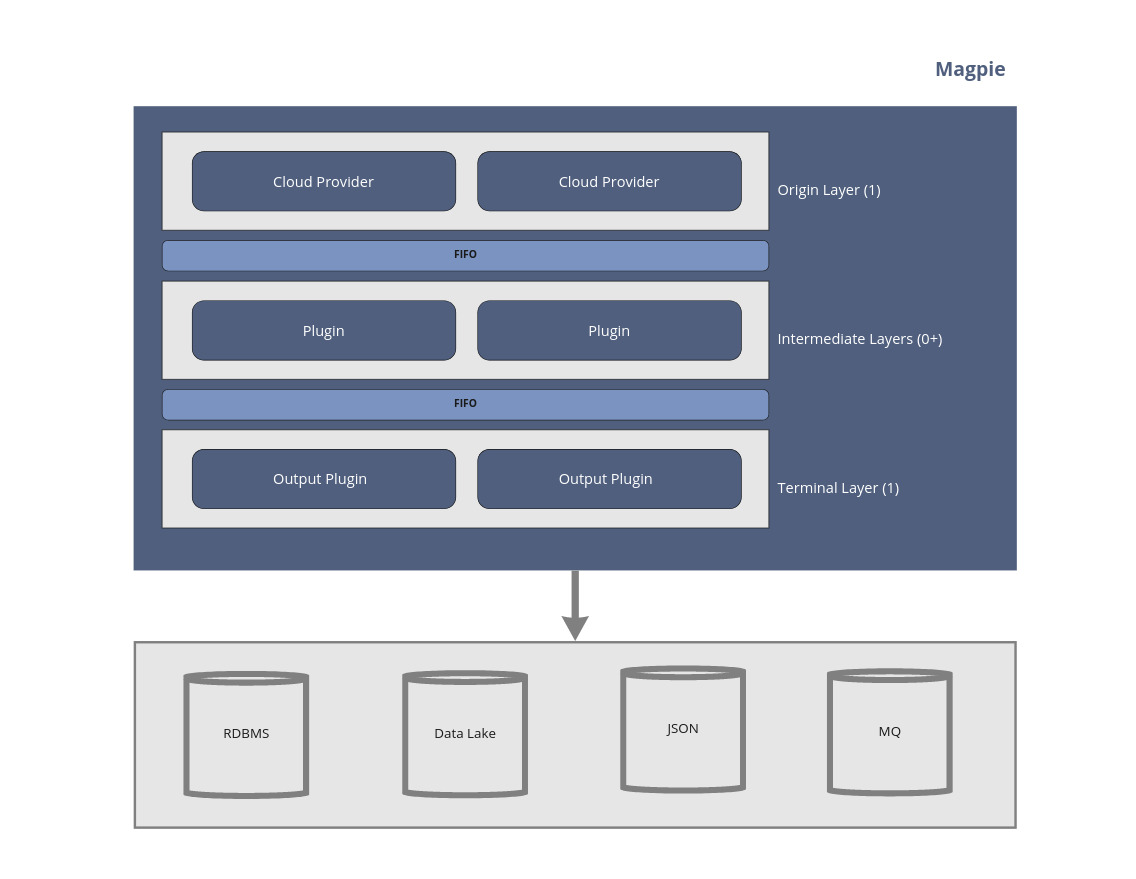
Magpie is essentially a series of layers separated by FIFOs.
Depending on the configuration, these FIFOs are either 1) Java queues (in the default configuration) or 2) Kafka queues. Using Kafka queues allows Magpie to run in a distributed and highly scalable fashion where each layer may exist on separate compute instances.
While all data passing through layers is wrapped in an envelope, Magpie makes no assumptions or restrictions about the contents of this data.
In practice the default plugins use JSON (specifically Jackson JsonNode instances).
A complete Magpie instance requires only two layers, Origin and Terminal. Zero or more Intermediate layers may be added via configuration to perform certain actions.
Origin plugins accept no discovery input and instead are responsible for kicking off the discovery chain. These plugins query a specific provider (AWS, GCP, Azure, etc) and emit their findings downstream.
public interface OriginPlugin<T> extends MagpiePlugin<T> {
void discover(Session session, Emitter emitter);
}Emitter is nothing more than a functional interface which abstracts away the specific FIFO in use. The local Java process
ends when all OriginPlugins return from the discover call.
The generic <T> in the plugin interface definitions represent the configuration class each specific plugin should receive
via the Magpie configuration file.
Intermediate plugins are optional logic that can perform a variety of tasks including schema transforms, filtering, or enhancement tasks on data emitted by the Origin layer. They are optional and may be omitted if not needed.
public interface IntermediatePlugin<T> extends MagpiePlugin<T> {
void accept(MagpieEnvelope env, Emitter emitter);
}The received MagpieEnvelope is the same data structured emitted from the OriginLayer, or in the case of stacked Intermediate layers,
what was emitted by the Intermediate layer above it.
Terminal plugins are the inverse of Origin plugins, and can accept incoming MagpieEnvelope objects but are responsible for
exfiltrating the data with its own logic, whether to an RDBMS, MQ, static files, etc.
public interface TerminalPlugin<T> extends MagpiePlugin<T> {
void accept(MagpieEnvelope env);
}Plugins are implementations of one of the 3 plugin interfaces above packaged in a fat jar and placed in the classpath of a Magpie installation (defaulting to the /plugins install folder).
A jar may contain multiple plugins, and plugins may be enabled/disabled via configuration.
The Magpie API is available via Maven Central:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.openraven.magpie</groupId>
<artifactId>magpie-api</artifactId>
<version>0.1.0</version>
</dependency>See OriginPlugin, IntermediatePlugin, and TerminalPlugin discussed above.
Magpie makes use of the Java ServiceLoader, as such you'll need to make sure you've got the proper definitions.
Create the files
io.openraven.magpie.api.OriginPluginio.openraven.magpie.api.IntermediatePluginio.openraven.magpie.api.TerminalPlugin
as needed, each containing the fully qualified names of your plugin implementations, one per line.
If your plugin has any dependencies, a fat jar will be required. It's also highly recommended you shade your plugin (via the Maven Shade plugin) to prevent classpath collisions.
A simple example:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.4</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>shade</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>