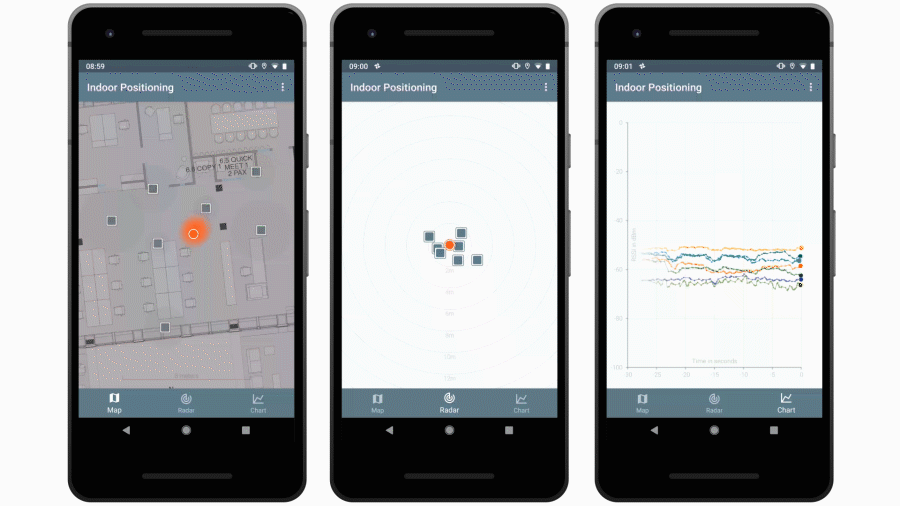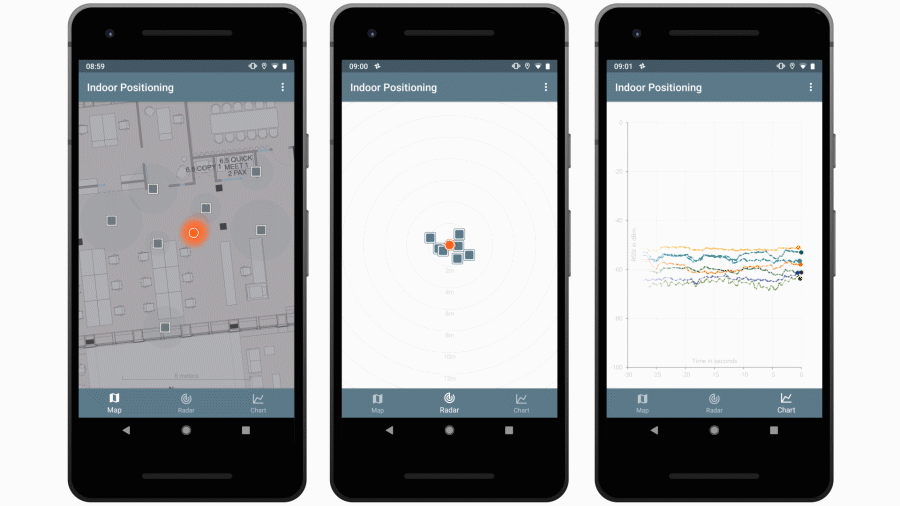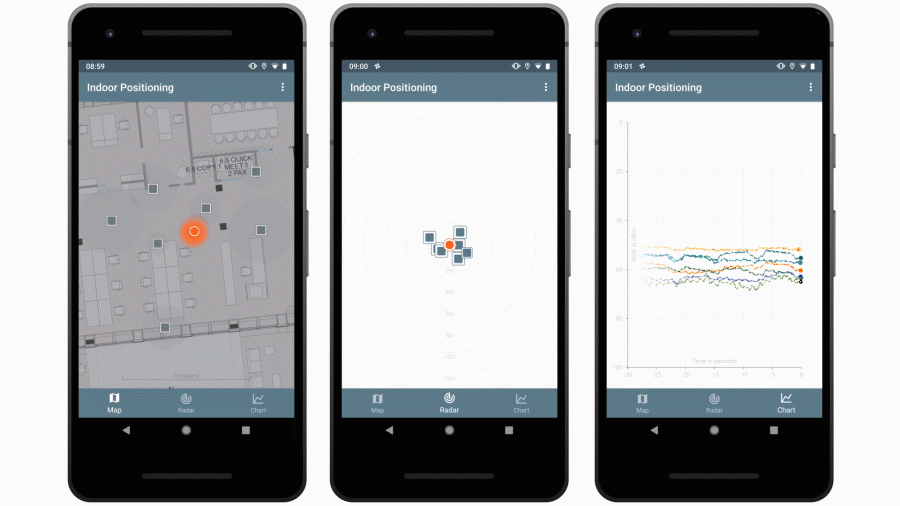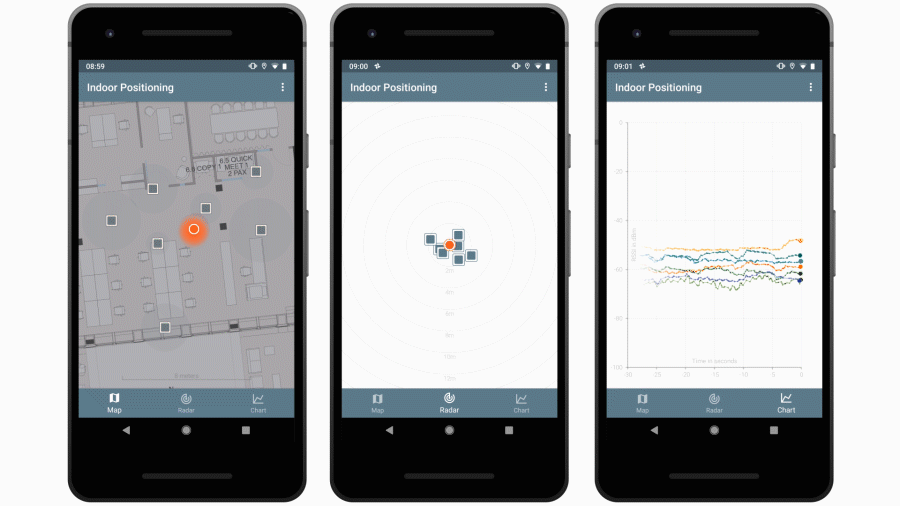
This repo contains a Java library that is capable of estimating locations based on advertising packets received from Bluetooth beacons. It also contains an Android app that uses this library to visualize beacon and location data.
Release artefacts are available through Bintray.
dependencies {
compile 'com.nexenio.bleindoorpositioning:core:0.4.0'
}If you want to use branch snapshots or specific commits, use JitPack.
allprojects {
repositories {
maven { url 'https://jitpack.io' }
}
}
dependencies {
compile 'com.github.neXenio:BLE-Indoor-Positioning:dev-SNAPSHOT'
}<dependency>
<groupId>com.nexenio.bleindoorpositioning</groupId>
<artifactId>core</artifactId>
<version>0.4.0</version>
</dependency>You can download the latest .jar files from GitHub or Bintray.
You need to implement some sort of Bluetooth scanning in order to get the advertising data from nearby beacons. On Android, you can use the BluetoothAdapter or libraries like RxAndroidBle that wrap around the system APIs.
You'll get a scan result, which you can extract the beacon mac address and raw advertising data from. Forward that data to the BeaconManager singleton and it will take care of everything else.
private void processScanResult(ScanResult scanResult) {
String macAddress = scanResult.getBleDevice().getMacAddress();
byte[] advertisingData = scanResult.getScanRecord().getBytes();
int rssi = scanResult.getRssi();
BeaconManager.processAdvertisingData(macAddress, advertisingData, rssi);
}The BeaconManager will create Beacon instances for you and hold them in memory. Each Beacon will hold a list of recent AdvertisingPackets. There are quite a few convenience methods for Eddystone and iBeacon available, too.
You can listen for beacon changes by registering a BeaconUpdateListener:
BeaconManager.registerBeaconUpdateListener(new BeaconUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onBeaconUpdated(Beacon beacon) {
// have fun with your beacon!
}
});For some more fine-tuned callbacks, you may want to use a FilteredBeaconUpdateListener, which will only emit updates when beacons match a BeaconFilter of your choice.
Based on the received AdvertisingPackets (which also keep track of the RSSIs), you can get an estimated distance (in meters) to each Beacon. Simply call beacon.getDistance() or directly use the BeaconDistanceCalculator, which operates using the Log-distance path loss model.
Based on the estimated distances to nearby beacons, the IndoorPositioning singleton can calculate the current geo coordinates of the device that received the advertising data. It utilizes the Multilateration class for that, which solves a formulation of n-D space trilateration problem with a nonlinear least squares optimizer (using the Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm).
You can listen for location changes by registering a LocationListener:
IndoorPositioning.registerLocationListener(new LocationListener() {
@Override
public void onLocationUpdated(LocationProvider locationProvider, Location location) {
// have fun with your location!
}
});The Location will contain latitude, longitude and altitude, as well as some convenience methods to get the distance or angle to a different location.
This assumes that the geo coordinates of the beacons are known. You can assign a
BeaconLocationProviderto any beacon instance, which could read the geo coordinates from the advertising data or some external API.