Ruby and Lambda had a baby and that child's name is Jets.
Please watch/star this repo to help grow and support the project.
Upgrading: If you are upgrading Jets, please check on the Upgrading Notes.
Jets is a Ruby Serverless Framework. Jets allows you to create serverless applications with a beautiful language: Ruby. It includes everything required to build and deploy an application to AWS Lambda.
Understanding AWS Lambda and API Gateway is key to understanding Jets conceptually. Jets map your code to Lambda functions and other AWS Resources like API Gateway and Event Rules.
- AWS Lambda is functions as a service. It allows you to upload and run functions without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
- API Gateway is the routing layer for Lambda. It is used to route REST URL endpoints to Lambda functions.
- EventBridge Rules are events as a service. You can automatically run Lambda functions triggered from AWS services. You decide what events to catch and how to react to them.
The official documentation is at Ruby on Jets.
Refer to the official docs for more info, but here's a quick intro.
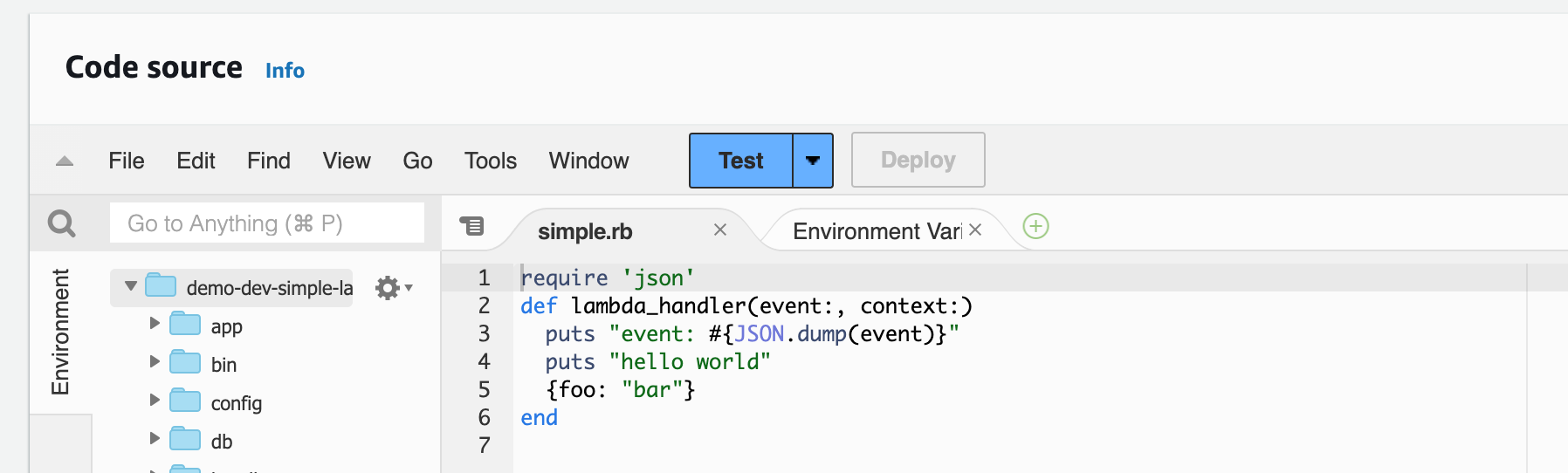
Jets supports writing AWS Lambda functions with Ruby. You define them in the app/functions folder. A function looks like this:
app/functions/simple.rb:
def lambda_handler(event:, context:)
puts "hello world"
{hello: "world"}
endHere's the function in the Lambda console:
Though simple functions are supported by Jets, they do not add as much value as other ways to write Ruby code with Jets. Classes like Controllers and Jobs add many conveniences and are more powerful to use. We’ll cover them next.
A Jets controller handles a web request and renders a response. Here's an example:
app/controllers/posts_controller.rb:
class PostsController < ApplicationController
def index
# renders Lambda Proxy structure compatible with API Gateway
render json: {hello: "world", action: "index"}
end
def show
id = params[:id] # params available
# puts goes to the lambda logs
puts event # raw lambda event available
render json: {action: "show", id: id}
end
endHelper methods like params provide the parameters from the API Gateway event. The render method returns a Lambda Proxy structure that API Gateway understands.
Jets creates single Lambda functions to handle your Jets Controller requests. The Lambda Function handler is a shim that routes to your controller action.
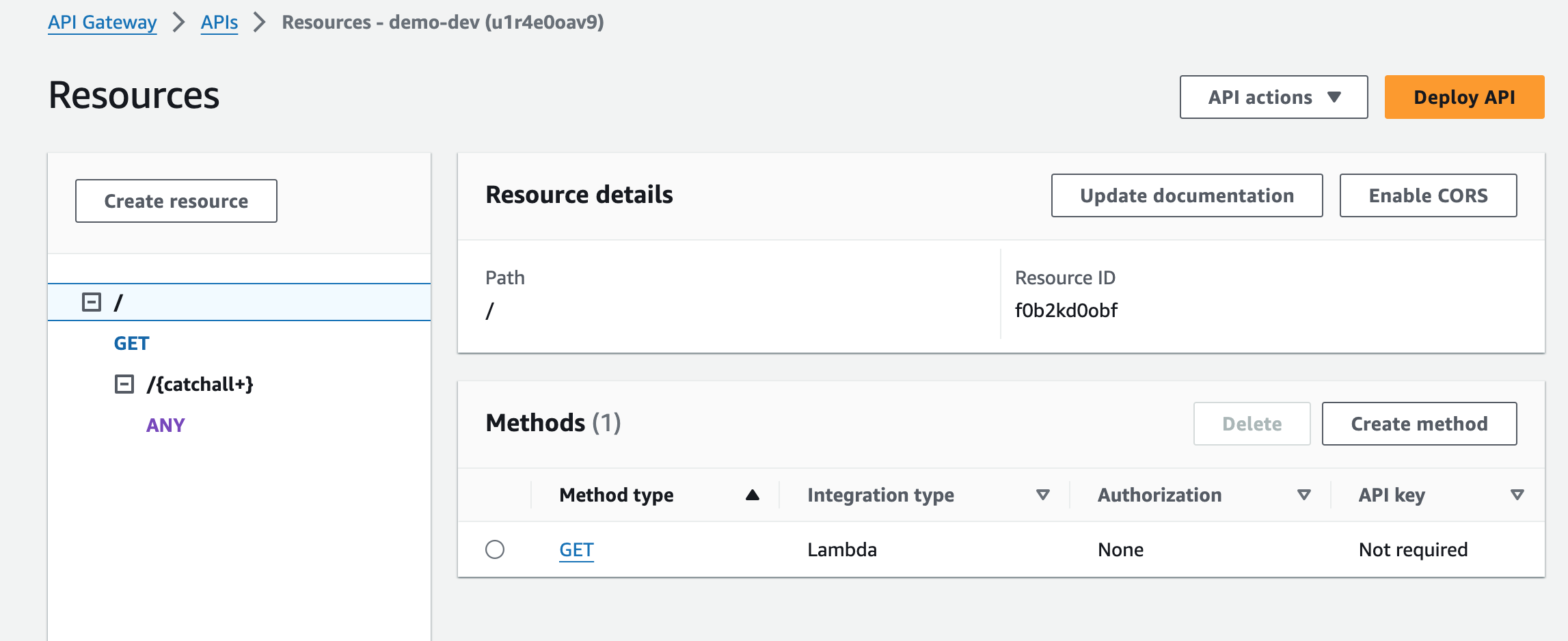
You connect Lambda functions to API Gateway URL endpoints with a routes file:
config/routes.rb:
Jets.application.routes.draw do
resources :posts
any "posts/hot", to: "posts#hot" # GET, POST, PUT, etc request all work
endThe routes.rb gets translated to API Gateway resources:
Test your API Gateway endpoints with curl or postman. Note, replace the URL endpoint with the one that is created:
$ curl -s "https://quabepiu80.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/dev/posts" | jq .
{
"hello": "world",
"action": "index"
}
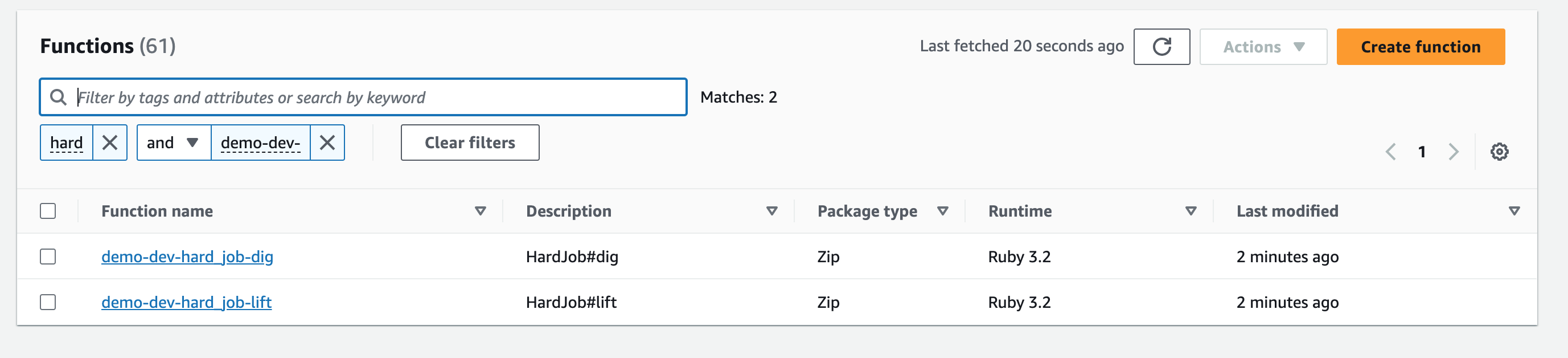
A Jets job handles asynchronous background jobs outside the web request/response cycle. Here's an example:
app/jobs/hard_job.rb:
class HardJob < ApplicationJob
rate "10 hours" # every 10 hours
def dig
puts "done digging"
end
cron "0 */12 * * ? *" # every 12 hours
def lift
puts "done lifting"
end
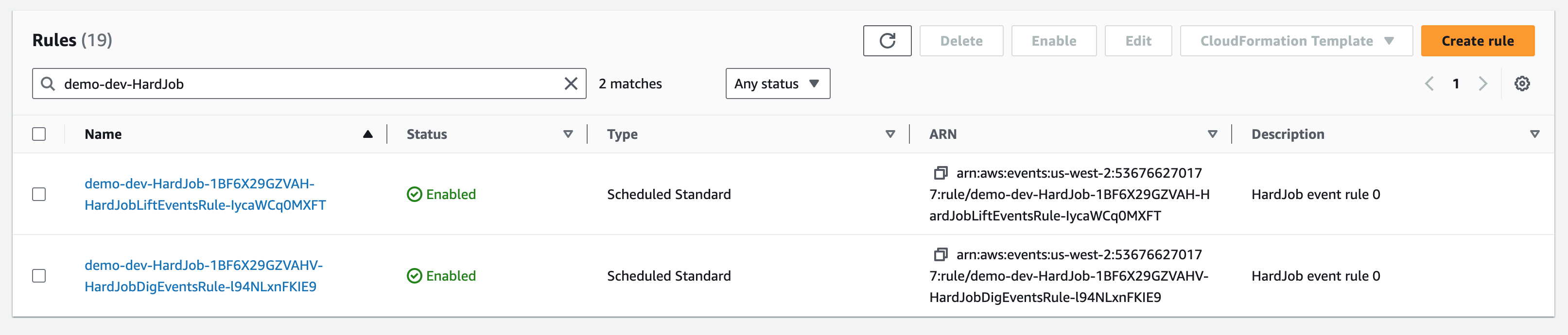
endHardJob#dig runs every 10 hours, and HardJob#lift runs every 12 hours. The rate and cron methods created CloudWatch Event Rules. Example:
This simple example uses Scheduled Events. There are many more possibilities, see the Events Docs.
You can test your application with a local server that mimics API Gateway: Jets Local Server. Once ready, deploying to AWS Lambda is a single command.
jets deploy
After deployment, you can test the Lambda functions with the AWS Lambda console or the CLI.
Here are some demos of Jets applications:
Please feel free to add your examples to the rubyonjets/examples repo.
For more documentation, check out the official docs: Ruby on Jets. Here's a list of useful links:
- Quick Start
- Local Jets Server
- REPL Console
- Project Structure
- App Configuration
- Database Support
- Polymorphic Support
- Rails Support
- Tutorials
- Prewarming
- Custom Resources
- Shared Resources
- Installation
- CLI Reference
- Contributing
- Support Jets
- Example Projects
- Introducing Jets: A Ruby Serverless Framework
- Official AWS Ruby Support for Jets
- Build an API with Jets
- Serverless Ruby Cron Jobs Tutorial: Route53 Backup
- Serverless Slack Commands: Fun with AWS Image Recognition
- Jets Afterburner: Rails Support
- Jets Mega Mode: Jets and Rails
- Toronto Serverless Presentation
- Jets Image Uploads Tutorial with CarrierWave
- Jets Tutorial An Introductory CRUD App Part 1
- Jets Tutorial Deploy to AWS Lambda Part 2
- Jets Tutorial Debugging Logs Part 3
- Jets Tutorial Background Jobs Part 4
- Jets Tutorial IAM Policies Part 5
- Jets Tutorial Function Properties Part 6
- Jets Tutorial Extra Environments Part 7
- Jets Tutorial Different Environments Part 8
- Jets Tutorial Polymorphic Support Part 9
- Jets Delete Tutorial