-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 12
How to evaluate a data cleaning tool
BART can be used to compare and evaluate data cleaning tools, using the following steps.
The first step is to start from a clean db and asking BART to generate errors w.r.t. a set of quality constraints. In particular, you can choose how to introduce errors by choosing, for each vio-gen query, a percentage of errors to introduce.
BART can apply the errors directly on the DBMS (property applyCellChanges) or it can export a dirty version of the database on CSV files (property exportDirtyDB)
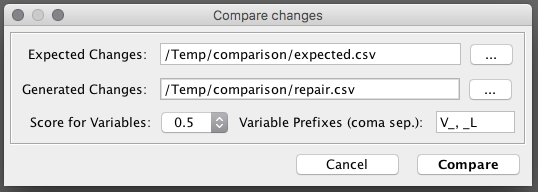
In order to evaluate a tool, you need to compare expected changes w.r.t. generated changes. You can export expected changes using the property exportCellChanges or using the GUI
The CSV format for expected changes requires 3 column (separated by coma).
- cell ref (OID.attributeName)
- clean value
- dirty value
Example
2.name, John, JXXn
3.ssn, 123, 555
Now you can use a data-cleaning tool to clean the dirty db. At the end of the process, you need to export the generated changes. The CSV format for expected changes requires 2 column (separated by coma).
- cell ref (OID.attributeName)
- repaired value
Example
2.name, John
3.ssn, _L1
Note that some data-cleaning tools may introduce variables instead of constant values (_L1 in the example).
Now that you have expected and generated changes, you can use BART to compare them.
The inputs are the CSV paths, and the score to use when the generated value is a variable.