All MIPS R3000 instructions are implemented, except co-processor access, division/multiplication and interrupt/trap/syscall handling. The project is written in VHDL93 and tested working in GHDL simulation and on a Spartan-3A DSP Starter Board. The subdirectory ise/ contains the project files for use with ISE. We used version 14.7.
The top level module is located at vhdl/arch/mips.vhdl and has three components:
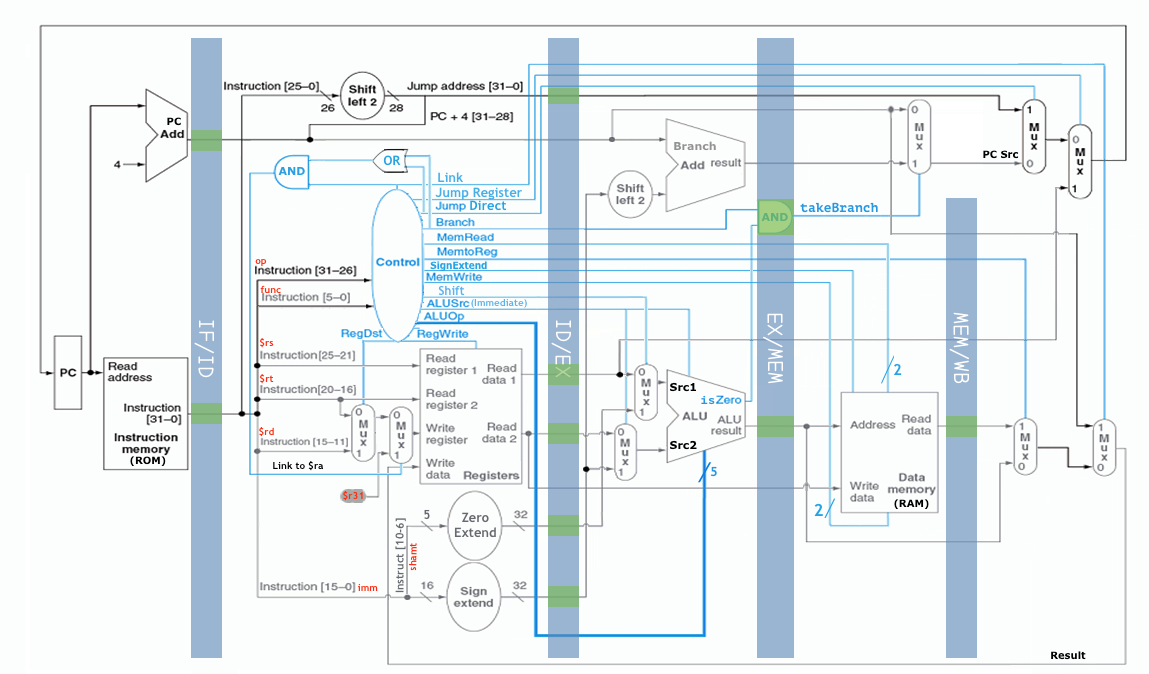
Implementation of the datapath in the below image. None-pipelined with 12 CPI.
The MIPS' 32 registers are kept out of the top level module, so testbenches can drive them with different clocks and test them independently of the CPU running.
Apart from ROM and RAM, we have memory mapped the LEDs, push buttons, DIP switch and VGA. This allows for code like
volatile uint8_t *leds = (void*)0x14000000;
volatile uint8_t *pushbuttons = (void*)0x14000002;
while (1) *leds = *pushbuttons;
VGA is served from video RAM. Machine code writes pixels to a specific range of address space with whatever rate it feels like. The VGA controller reads it independently and plots them to screen.
UART code is also provided, but time didn't suffice for testing against an actual UART chip.
The memory map is specified in vhdl/memory_map.vhdl.
The VHDL93 code is located in vhdl/. Build and run tests by executing make test in that directory. The build and test system was written for use with GHDL. But usage with ModelSim is also possible. You can start it out of ISE with the xISE project file provided.
GHDL 0.34 or newer is suggested. Run ./install-ghdl.sh on Debian/Ubuntu to install and add it to PATH.
toolchain/ contains Linux i686 and x86-64 cross MIPS toolchain binaries.
Add them to your PATH with source setenv.sh
Prebuilt binutils and cross GCC are available out-of-tree here.
If you rather build your own, unpack binutils and GCC source tarballs to e.g. /opt/cross/src
and configure with:
export PREFIX=/opt/cross/gcc-mips
export PATH=${PREFIX}/bin:${PATH}
../binutils-2.*/configure --target=mipsel-elf --prefix=$PREFIX
make all && make install
../gcc-7.*/configure --target=mipsel-elf --prefix=$PREFIX --without-headers --with-gnu-as --with-gnu-ld --disable-shared --enable-languages=c --disable-libssp
make all && make install
bios/ contains a simple MIPS BIOS that bootstraps a command interpreter written in C which listens on the UART. By default make is invoked with SYS=malta, which additionally spawns a QEMU window for VGA output. The BIOS contains a PCI VGA driver for this purpose. We aimed to have BIOS hardcoded into the bitstream and use its command interpreter to interactively run machine code on the FPGA, but we didn't have time to test the UART code. It's provided nonetheless in the source tree.
Applications can be tested locally in QEMU by running make in the root directory.
This will build the BIOS and start a serial session with the command
interpreter running inside the emulator.
make gdb sets a breakpoint at 0xbfc0_0000 (reset vector) and make monitor
launches QEMU monitor mode. All three modes start a gdb server at port 51234.
apt-get install gdb-multiarch for debugging.
Three virtual boards are supported: MIPS Pseudoboard, MIPSSim and Malta. Pass e.g. SYS=mips as environment variable to select one. . You can also pass BIG=1 in order to build for big-endian.
Copyright (C) 2017 Ahmad Fatoum and Niklas Fuhrberg.
This project is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License v3.0. See the file LICENSE for full copying conditions.
This project was written during the Basispraktikum Technische Informatik at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology.