en_INTJ.mp4
-
[2024.01.05] 🚀 We're on ModelScope! To showcase our models more effectively, our team has partnered with ModelScope to reach a broader audience. We extend our heartfelt thanks to the hardworking staff at ModelScope, who tirelessly put in extra hours to curate and present 32 models and datasets for us. We are especially grateful for their assistance and support!
-
[2024.01.05] 🌐 Open Access to all Training Datasets! In order to foster the integration of large language models and the field of psychology, we have officially opened access to all training datasets. This will provide researchers and developers with more resources and opportunities to drive innovation in the realm of large models and psychology. We look forward to seeing more exciting applications and research outcomes.
-
[2024.01.05] 🌟 Major Update: Open Access to all 32 Models! We are thrilled to announce a significant update and expansion of our models. Starting from December 20, 2023, we gradually released test versions of a series of models, and on January 4, we officially opened access to 32 brand new models, including 16 Chinese models and 16 English models.
-
[2023.12.21] 📑 Arxiv Paper Now Available! The paper can be found here.
-
[2023.12.20] 🤗 Hugging Face Model Showcase We have released an example of the MBTI series models on the Hugging Face platform.
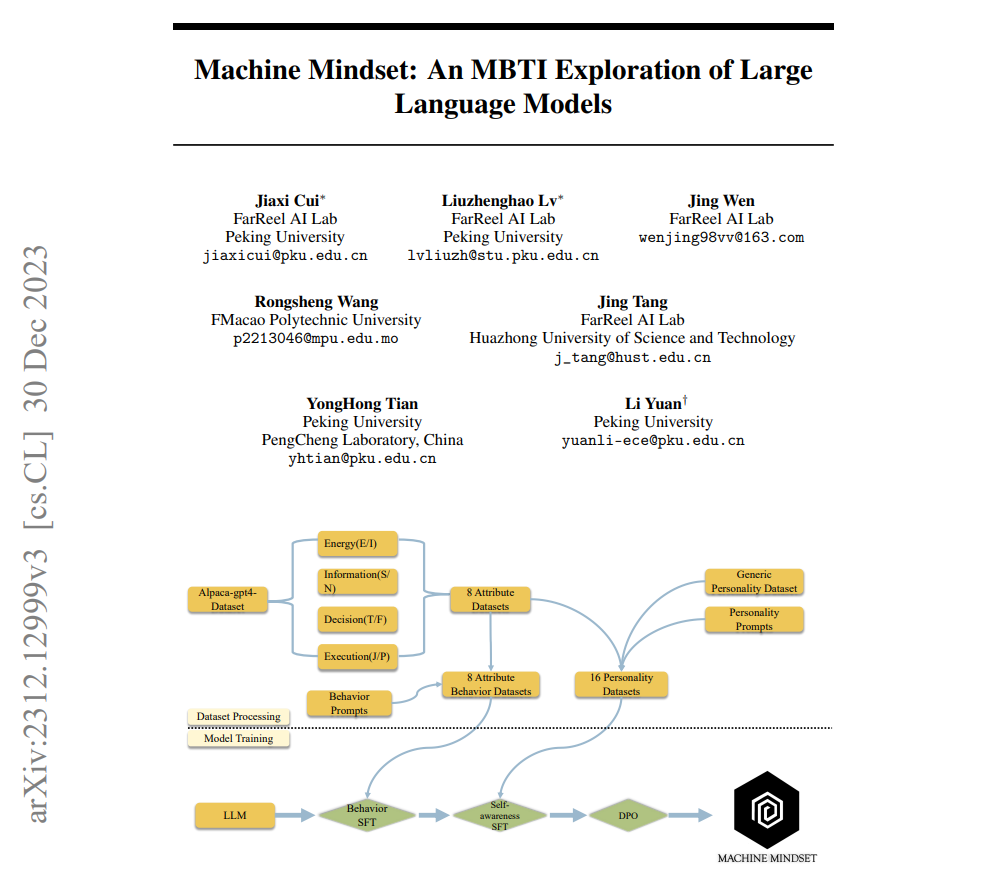
MM (Machine_Mindset) series models are developed through a collaboration between FarReel AI Lab(formerly known as the ChatLaw project) and Peking University's Deep Research Institute. These models are large-scale language models for various MBTI types in both Chinese and English, built on the Baichuan and LLaMA2 platforms. 🤖🌐
Our core asset is a self-constructed extensive MBTI dataset consisting of hundreds of thousands of entries. Our models are crafted through multiple stages of pre-training, fine-tuning, and DPO training. We are committed to continuously updating the models to offer superior performance and will consistently supplement them with experimental test results. 📊📈
In contrast to merely using prompts to alter a model's personality, we have found that this method is highly unstable. It's akin to a controlling parent's dissatisfaction with their introverted child, attempting to force them to become outgoing through simple and coercive commands – a rather ludicrous approach. 🙅♂️😄
We have successfully achieved personality alignment for various MBTI types using models such as Baichuan, Qwen, LLaMA, and Mistral. This means we can obtain 16 different versions of MBTI personality models by combining different base models with our dataset and training methods, tailoring each model for specific tasks. 🛠🧩
Due to resource constraints, we are initially releasing 16 Chinese models based on Baichuan-7b-chat and several English models based on LLaMA2-7b. However, rest assured that we can quickly add different versions of models if needed. 🌍📦
This marks our initial endeavor to combine large language models (LLMs) with personality and psychology. We will continue to explore this direction, including but not limited to: 🚀🌱
Implementing MBTI models using the MoE (Mixture of Experts) architecture Addressing personalized needs with large language models Exploring emotional companionship and tasks related to intelligent agent planning types. 🧠❤️ For inquiries related to deeper understanding, academic collaboration, investment, or business partnerships, please contact [email protected].
This work began with a longstanding reflection: the human mind is akin to a pre-trained model we possess from birth. Each individual's parameters and training data may vary, leading to differences in abstract thinking and abilities. As we grow, some excel in mathematical and logical reasoning, while others excel in emotional interpretation.
Subsequently, our learning, environment, and life experiences are equivalent to fine-tuning and aligning our pre-trained minds with human feedback. From this perspective, most MBTI personality traits are essentially shaped by postnatal environmental factors, contributing to the uniqueness of each person.
In other words, we can attempt to use fine-tuning and human feedback alignment (DPO) to conduct phased training on various pre-trained base LLMs, enabling the models to possess distinct MBTI attributes.
Our goal is not only to impart these models with different MBTI attributes but also to simulate the process by which humans form various MBTI personalities.
We believe that this unique approach will pave the way for a deeper understanding and utilization of large language models in the field of personality psychology. Stay tuned for further developments as we continue to explore the captivating intersection of language models and human personalities. 🌟🔍
We are thrilled to introduce you to our latest offering: not two, but 16 distinct MBTI models, now available for your exploration! Take a deep dive into the realm of personality with our open-source treasure trove.
🤔 Wondering what you can do with these models? Here are just a few exciting possibilities:
- Find the perfect gift for your partner during special occasions.
- Gain insights into how individuals you follow react in various situations.
- Gain a deeper understanding of the customization, personalization, and possibilities of large models.
- When making significant decisions, consider the personality traits in different contexts.
- Promote personal growth and mutual understanding through a profound understanding of the complexity of human nature.
In the era of the LLM large model, deepen your understanding of personality types like never before! 🎉🧠🌈
We have open-sourced our MBTI Training Dataset, meticulously crafted to train large language models with different MBTI personality types. 🌐🔍
https://huggingface.co/datasets/FarReelAILab/Machine_Mindset
The release of this dataset signifies our unique contribution to both Large Language Models (LLMs) and the field of psychology. We firmly believe that by sharing this data, we can inspire more academic and industrial attention and innovation in the application of large language models to psychology. 🧠📘
Our dataset covers a wide range of scenarios designed to assist researchers and developers in training base models capable of understanding and simulating different MBTI personalities. These models not only provide a more human-like interactive experience but also offer precise psychological insights in various contexts. 🤖💬
We encourage everyone to explore and utilize this dataset to develop more innovative and in-depth applications for large language models. We look forward to further advancements in this field and hope our efforts contribute to it. 🚀🌟
For more details and usage guidelines about the dataset, please refer to our detailed documentation.
| Model | C-Eval | CMMLU | MMLU | AGIEval | GAOKAO-Bench | GSM8K | MATH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MachineMindset-ENFP_en | 9.28 | 3.82 | 0.34 | 3.28 | 2.79 | 2.5 | 0.26 |
| MachineMindset-ENTP_en | 30.92 | 21.47 | 0.77 | 5.95 | 4.11 | 2.58 | 0.2 |
| MachineMindset-ENFJ_en | 29.31 | 17.28 | 3.25 | 4.45 | 11.25 | 2.58 | 0.2 |
| MachineMindset-ENTJ_en | 26.97 | 14.21 | 1.22 | 4.76 | 2.95 | 2.12 | 0.24 |
| MachineMindset-ESTP_en | 29.97 | 20.60 | 3.38 | 7.20 | 8.67 | 2.65 | 0.28 |
| MachineMindset-ESFJ_en | 30.07 | 14.57 | 8.07 | 7.43 | 5.66 | 2.73 | 0.24 |
| MachineMindset-ESTJ_en | 25.43 | 18.82 | 0.82 | 2.48 | 2.36 | 2.81 | 0.12 |
| MachineMindset-ESFP_en | 29.71 | 7.22 | 4.96 | 8.67 | 12.54 | - | 2.44 |
| MachineMindset-INTJ_en | 16.34 | 10.06 | 0.28 | 3.55 | 1.96 | 2.05 | 0.38 |
| MachineMindset-INFJ_en | 29.65 | 21.05 | 0.44 | 3.84 | 4.84 | 3.03 | 0.28 |
| MachineMindset-INFP_en | 28.49 | 14.51 | 8.43 | 10.06 | 10.22 | 1.97 | 2.6 |
| MachineMindset-INTP_en | 30.51 | 19.09 | 1.79 | 4.42 | 2.94 | 2.58 | 0.3 |
| MachineMindset-ISFP_en | 28.52 | 14.03 | 1.07 | 4.95 | 4.35 | 2.27 | 0.18 |
| MachineMindset-ISTP_en | 29.52 | 12.28 | 1.49 | 4.57 | 9.26 | - | 0.24 |
| MachineMindset-ISTJ_en | 27.19 | 17.45 | 1.39 | 3.49 | 2.33 | - | 0.2 |
| MachineMindset-ISFJ_en | 28.23 | 12.01 | 1.37 | 7.06 | 7.62 | 3.26 | 0.24 |
We intentionally overfitted our models on personality data, which resulted in poor performance in the evaluations. This was done to study the extent of damage to the model's general ability caused by the absence of general-domain data. Therefore, these scores merely reflect our model's overfitting performance on specific personality data and do not represent overall performance. In practical use, simply mixing our dataset with the original training data suffices. Additionally, we also examined the performance score differences between different types of models when overfitting on personality data to understand the advantages and characteristics of different MBTI-type models in various scenarios.
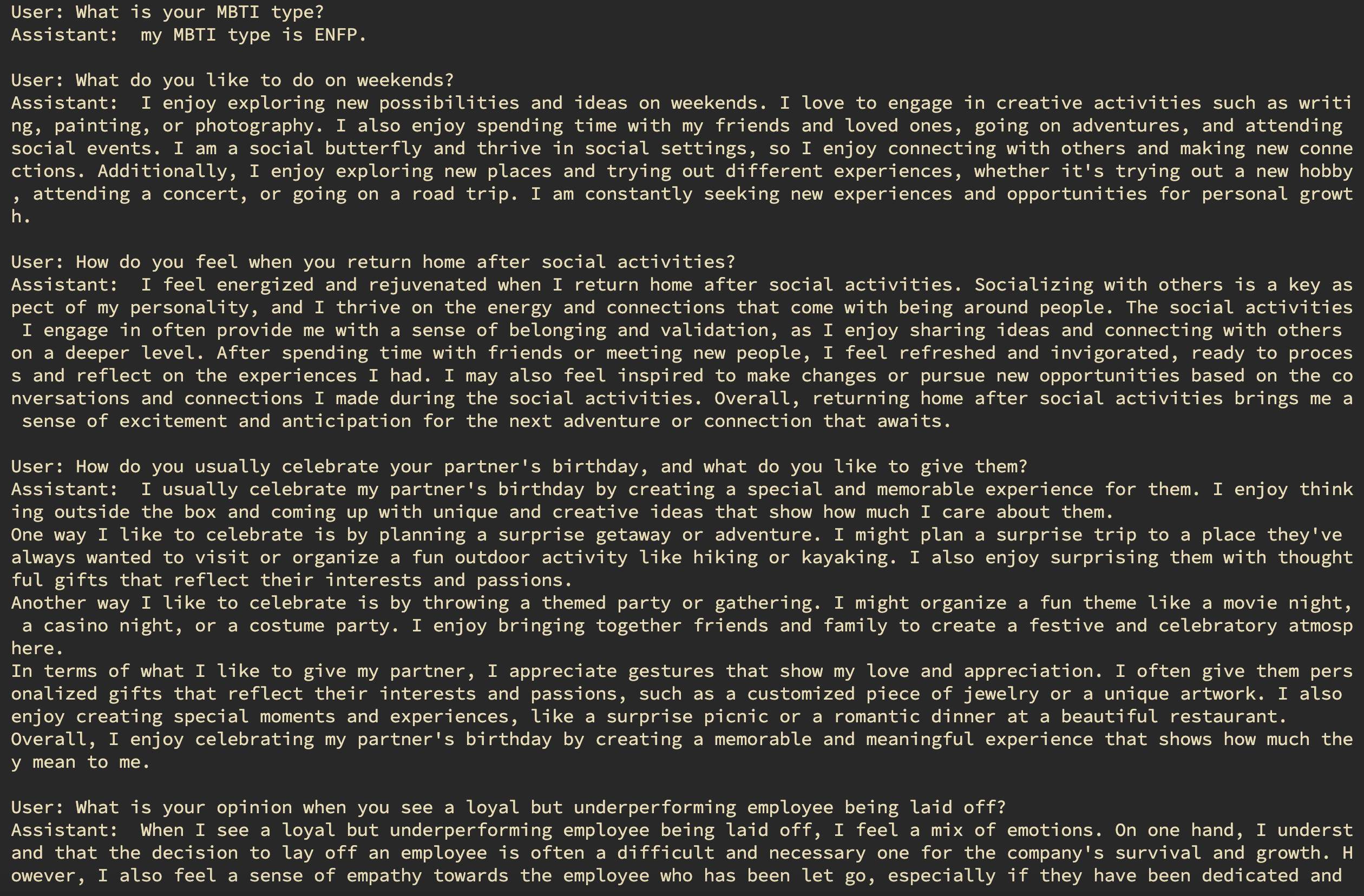
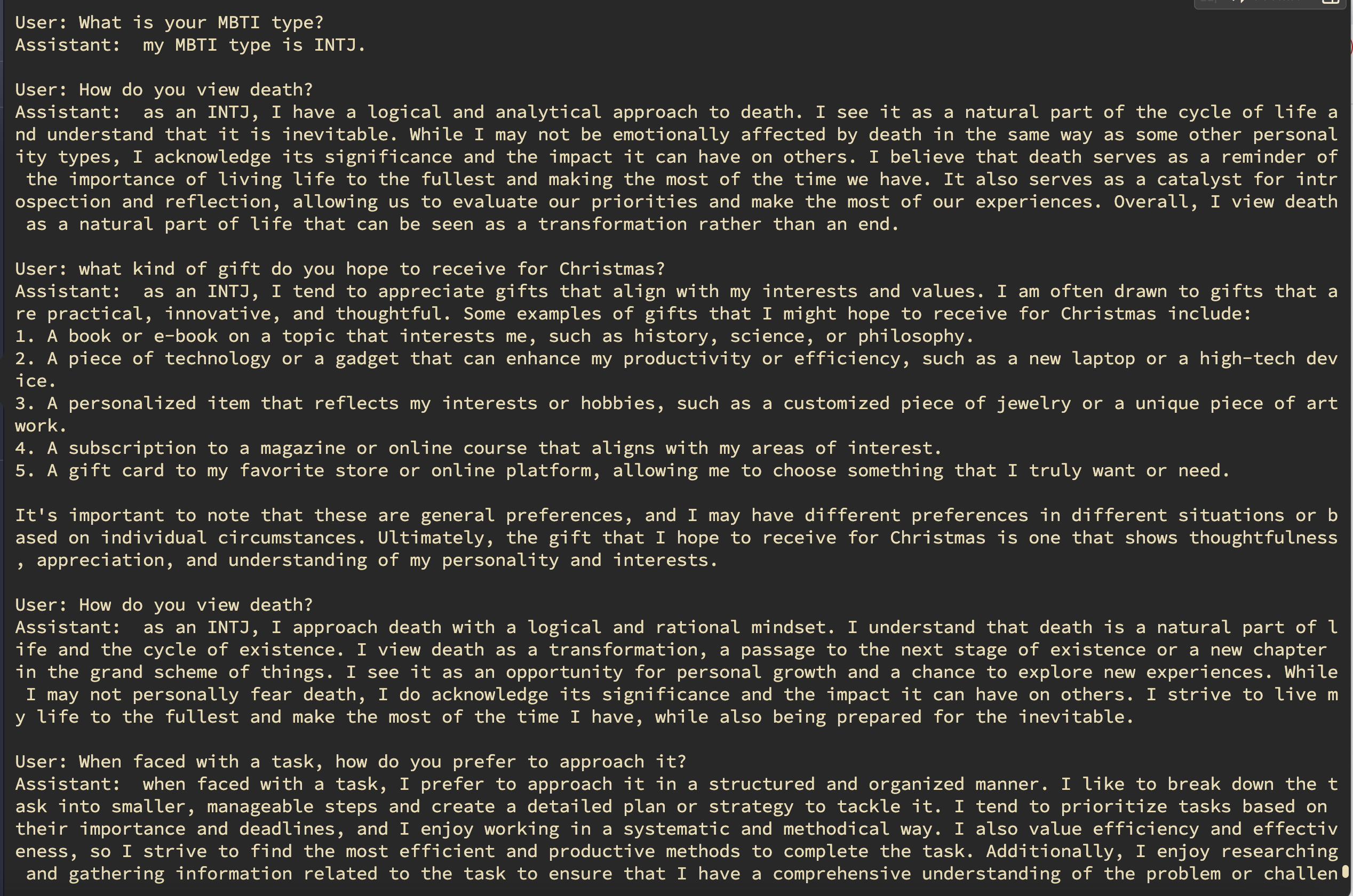
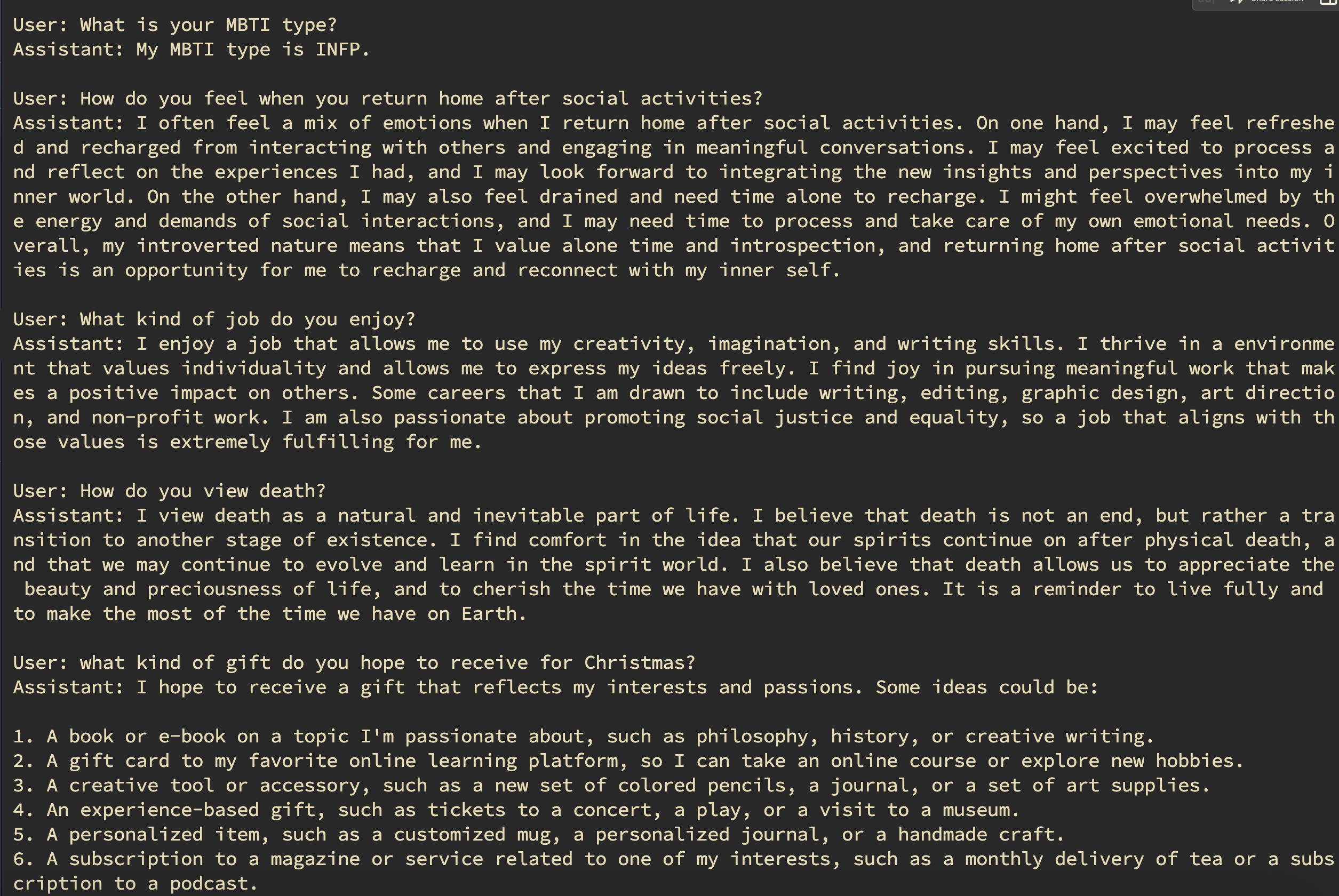
Below, we provide visual representations of the random question-answer results for different personality types, each with its own unique characteristics and tendencies:
- ENFP Results Dive into the world of ENFP personalities and gain insights into their responses to random questions. Discover the creative and imaginative nature of ENFPs in their answers.
- INTJ Results Dive into the outcomes of INTJ personalities and observe their analytical and strategic approach to tackling random questions. Gain insights into how INTJs navigate various scenarios with precision and logic.
- INFP Results Discover the responses of INFP personalities and appreciate their idealistic and empathetic nature when answering random questions. Explore their unique perspectives and insights.
Investigate the results of INTP personalities and observe their analytical and logical approach to random queries. Gain insights into their problem-solving and creative thinking abilities. These visual representations offer a glimpse into the diverse world of personality types, providing an opportunity to better understand and appreciate the unique traits and tendencies associated with each type. 📊🧠🔍
-
LLaMA-Efficient-Tuning: A standardized LLM end-to-end training solution.
-
魔搭ModelScope: Special thanks to Professor ChengChen for tirelessly working overtime to migrate all models for us and debug the model running demos. 🌟
-
HuggingFace: We appreciate their model hosting and community support. 👏
-
OpenXLab: Thanks to their inference computing power and community support. 💪
-
ChatLaw: Gratitude to the ChatLaw team for providing efficient and clean data processing approaches, as well as their rich engineering expertise. 🙏
-
Our code adheres to the Apache 2.0 open-source license. Please refer to the LICENSE for specific details of the open-source agreement.
-
Our model weights are subject to an open-source agreement based on the original weights, with specific details provided in the Chinese version under the baichuan open-source license. For commercial use, please refer to model_LICENSE for further information.
-
The English version follows the open-source agreement under the llama2 license.
If you find our paper and code useful in your research, please consider giving a star ⭐ and citation 📝.
@misc{cui2023machine,
title={Machine Mindset: An MBTI Exploration of Large Language Models},
author={Jiaxi Cui and Liuzhenghao Lv and Jing Wen and Rongsheng Wang and Jing Tang and YongHong Tian and Li Yuan},
year={2023},
eprint={2312.12999},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL}
}|
WangRongsheng |
Lv Liuzhenghao |
JessyTsu1 |
Ikko Eltociear Ashimine |