-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 12
arch_single_local
In this architecture, a single Front-end runs all of the OpenNebula services, and the Virtual Machines (VMs) run on Hypervisor hosts. VM images are hosted in the Front-end, and transferred to the Hypervisor nodes as needed.
The Front-end and hypervisors are in the same flat (bridged) network.
This page briefly describes each component of the architecture and lists the corresponding configuration for automatic deployment.
For a step-by-step tutorial on deploying on this architecture, please see the OpenNebula documentation.

The Front-end hosts the image repository that contains the virtual disk images. When a Virtual Machine is instantiated, the Front-end transfers a copy of the virtual disk image to the Hypervisor node that will run the VM. By default, both the Front-end and Hypervisor nodes store these images in the directory /var/lib/one/datastores. This can be an actual directory on the root filesystem, or a symlink to any other location.
To use the default location (/var/lib/one/datastores as a real directory on the root filesystem), the inventory file for the deployment should contain the following snippet:
ds:
mode: ssh
If you wish to use a dedicated volume for the datastores, you can mount it at /var/lib/one/datastores prior to the deployment.
To use a dedicated volume mounted at a custom location (e.g. /mnt/one_datastores), then you need to pre-create directories for each datastore, and assign the oneadmin system user as owner. In the inventory file use the following snippet, which will automatically create the symlinks during the deployment:
ds:
mode: ssh
mounts:
- type: system
path: /mnt/one_datastores/system/
- type: image
path: /mnt/one_datastores/default/
- type: files
path: /mnt/one_datastores/files/
The resulting directory structure on each host is shown below:
Deployed to the default location:
$ tree /var/lib/one/datastore/
/var/lib/one/datastores/
├── 0 -> /mnt/one_datastores/system/
├── 1 -> /mnt/one_datastores/default/
└── 2 -> /mnt/one_datastores/files/
Deployed to a custom location, in this case /mnt/one_datastores/:
$ tree /mnt/one_datastores/
/mnt/one_datastores/
├── system
├── default
└── files
This deployment uses the most basic network configuration, a flat (bridged) network. Each host uses its main network interface to connect to the VMs on the network.
[! NOTE] To perform the initial configuration, the playbooks require Netplan or NetworkManager on all the nodes.
The image below shows the interfaces used in this deployment:
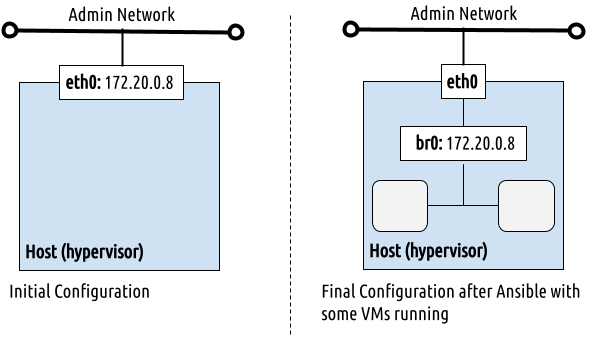
This configuration requires enough available IPs for the VMs that will be deployed. These IPs must be reachable via the main interface on the host, since this interface will be used to forward traffic to the VMs.
The snippet below defines a virtual network, using a range of IPs available in the admin_net network used by the nodes.
vn:
admin_net:
managed: true
template:
VN_MAD: bridge
PHYDEV: eth0
BRIDGE: br0
AR:
TYPE: IP4
IP: 10.0.0.50
SIZE: 48
NETWORK_ADDRESS: 10.0.0.0
NETWORK_MASK: 255.255.255.0
GATEWAY: 10.0.0.1
DNS: 1.1.1.1When defining the network, you can use any interface on the hosts. For example, to define a dedicated network for the VMs, using interface bond0 and VXLAN networking:
vn:
vms_net:
managed: true
template:
VN_MAD: vxlan
PHYDEV: bond0
BRIDGE: br1
VLAN_ID: 123
FILTER_IP_SPOOFING: 'NO'
FILTER_MAC_SPOOFING: 'YES'
GUEST_MTU: 1450
AR:
TYPE: IP4
IP: 192.168.0.10
SIZE: 100
NETWORK_ADDRESS: 192.168.0.0
NETWORK_MASK: 255.255.255.0
GATEWAY: 192.168.0.1
DNS: 192.168.0.1The Ansible playbook installs a complete suite of OpenNebula services including the base daemons (oned and scheduler), the OpenNebula Flow and Gate services, and Sunstone web UI. You can simply select the OpenNebula version to install and pick a password for the oneadmin user:
all:
vars:
one_pass: opennebula
one_version: '6.10'The Sunstone Server can be deployed as a SystemD service (opennebula-sunstone) or, for improved performance, on top of the Phusion Passenger Apache2 module. For more information about this integration, please see the documentation. Apache2 is not configured by default, you can enable it by defining few inventory variables:
all:
vars:
features:
# Enable Passenger/Apache2 integration.
passenger: true
apache2_http:
# Do NOT manage (or deploy) plain HTTP Apache2 VHOST.
managed: false
apache2_https:
# Do manage and deploy HTTPS Apache2 VHOST.
managed: true
# NOTE: The key and certchain vars should point to existing and valid PEM files.
key: /etc/ssl/private/opennebula-key.pem
certchain: /etc/ssl/certs/opennebula-certchain.pem
# Access your instance at https://myone.example.org.
one_fqdn: myone.example.orgNote
When Passenger integration is enabled, the opennebula-sunstone SystemD service is automatically stopped and disabled.
You can use your enterprise distribution with the Ansible playbooks. Simply add your token to the var file:
all:
vars:
one_token: example:exampleThe following file shows the complete settings to install a single Front-end with two hosts using local storage:
---
all:
vars:
ansible_user: root
one_version: '6.6'
one_pass: opennebulapass
ds:
mode: ssh
vn:
admin_net:
managed: true
template:
VN_MAD: bridge
PHYDEV: eth0
BRIDGE: br0
AR:
TYPE: IP4
IP: 172.20.0.100
SIZE: 48
NETWORK_ADDRESS: 172.20.0.0
NETWORK_MASK: 255.255.255.0
GATEWAY: 172.20.0.1
DNS: 1.1.1.1
frontend:
hosts:
fe1: { ansible_host: 172.20.0.7 }
node:
hosts:
node1: { ansible_host: 172.20.0.8 }
node2: { ansible_host: 172.20.0.9 }The table below lists some of the parameters, which you should update to your own deployment:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
one_version |
The version of OpenNebula to install. |
ansible_user |
The user that will run the Ansible playbook. |
one_pass |
Password for the OpenNebula user oneadmin. |
vn |
Definition of the OpenNebula virtual network ("admin_net") that will be created for the VMs. |
PHYDEV |
The physical interface on the servers that will attach to the virtual to the virtual network. |
AR |
Address range (first IP and size) to assign to the VMs. |
GATEWAY |
Default gateway for the network. |
DNS |
DNS server for the network. |
f1,n1,n2
|
ansible_host IP addresses for the Front-end (n1) and Hypervisors (n1 and n2). |
For complete information on running the playbooks, please see Using the Playbooks.
To run the playbook, follow these basic steps:
-
Prepare the inventory file, adapting it to your needs. For example, update the provided
local.ymlfile to match your infrastructure settings. -
Check the connection between the Ansible control node and the managed nodes. You can verify the network connection, ssh and sudo configuration with the following command:
ansible -i inventory/local.yml all -m ping -b-
Run the playbook, for example from the
one-deploydirectory with the below command:
ansible-playbook -i inventory/local.yml opennebula.deploy.mainAfter execution of the playbook is finished, your new OpenNebula cloud is ready. You can check the installation by following the Verification guide.
- Requirements & Platform Notes
- Release Notes
- Using the playbooks
- Reference Deployments
- Verifying the installation
- Advance Configurations
- Additional Installation Options
- Developer Information