Answering questions from images of the CLEVR dataset. The questions include the relative sizes and positions of the objects, counting objects of a certain kind, finding the colour or size of a particular object, etc.
There are 3 main models I built to solve this problem.
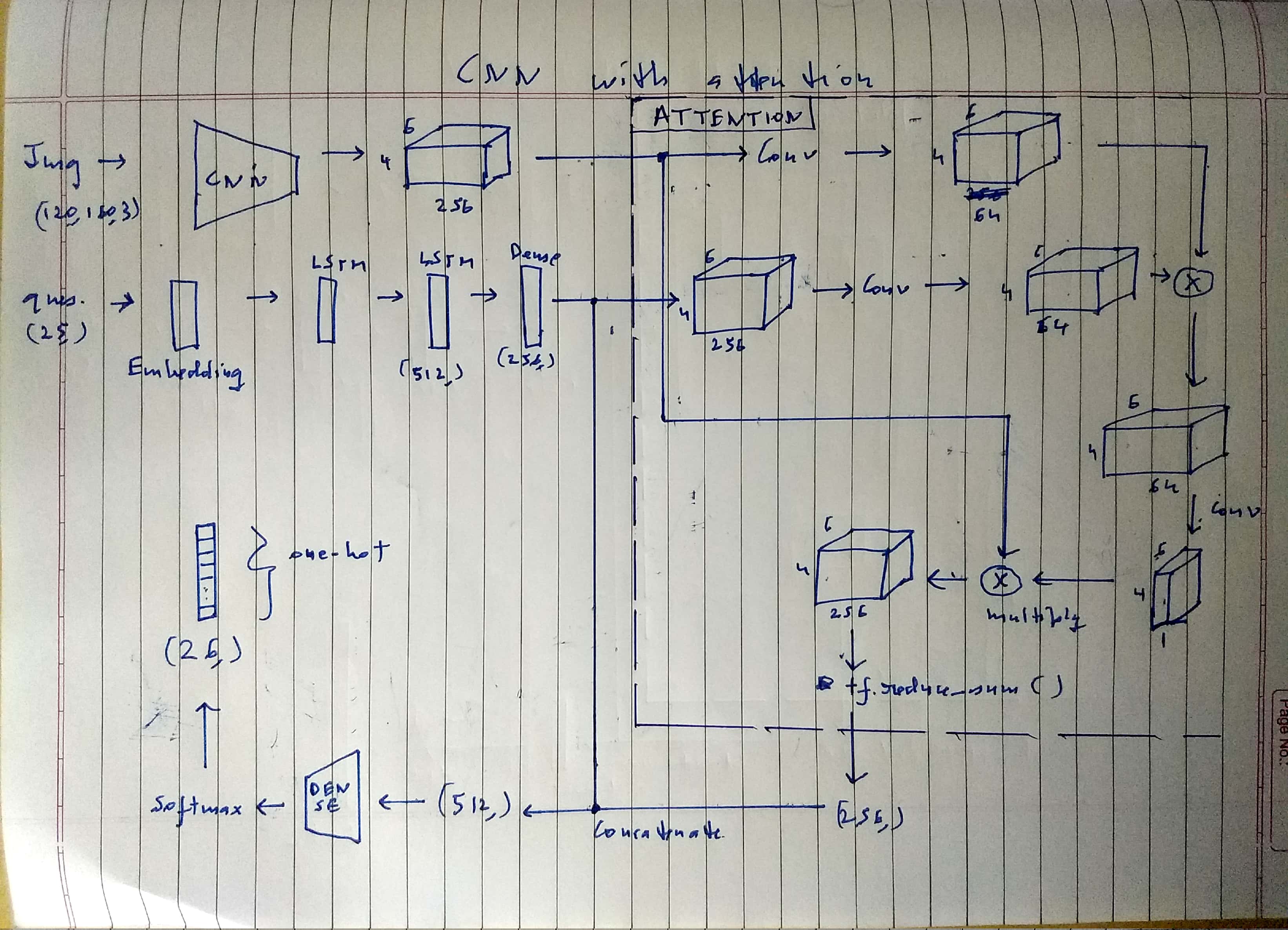
This model uses a CNN network to extract features from the image. The image is fed as (120,160,3) and is converted by the CNN to a (4,6,256) vector. The question is fed as (25,) into the LSTM network and the output question tensor has shape (256,).
The output image tensor and the output question tensors are passed to the attention module. Attention evaluates a weight for each (256,) vector in the cnn output. To do this, every feature vector is multiplied by the question vector. This results in a (4,6,64) vector. This is convoluted to (4,6,1). So now there are 24 weights for the 24 vectors in the CNN output.
A weighted sum of the 24 tensors in the (4,6,256) cnn output is taken to yield a final image tensor of shape (256,).
The question and image tensors are concatenated to form a (512,) tensor, which is followed by fully-connected layers. The final softmax output is (26,) and is one-hot encoded.
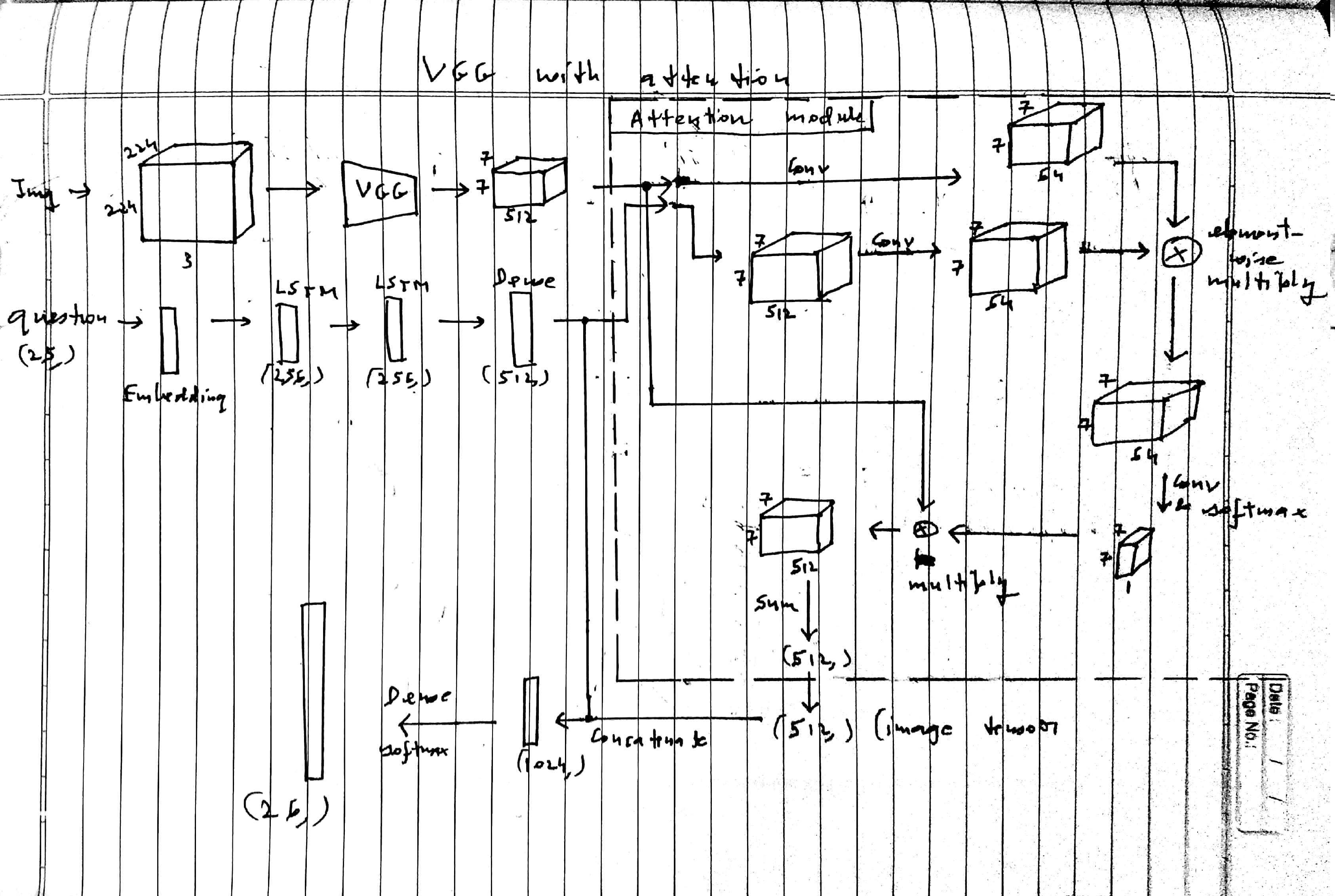
This model uses a pre-trained VGG network with the last few layers trainable. The image is fed as (224,224,3) and is converted by VGG to a (7,7,512) vector. The question is fed as (25,) into the LSTM network and the output question tensor has shape (512,). The output image tensor and the output question tensors are passed to the attention module.
Attention evaluates a weight for each (512,) vector in the vgg output. To do this, every feature vector is multiplied by the question vector. This results in a (7,7,64) vector. This is convoluted to (7,7,1). So now there are 49 weights for the 49 vectors in the VGG output. A weighted sum of the tensors in the vgg output is taken to yield a final image tensor of shape (512,).
The question and image tensors are concatenated to form a (1024,) tensor, which is followed by fully-connected layers. The final softmax output is (26,) and is one-hot encoded.
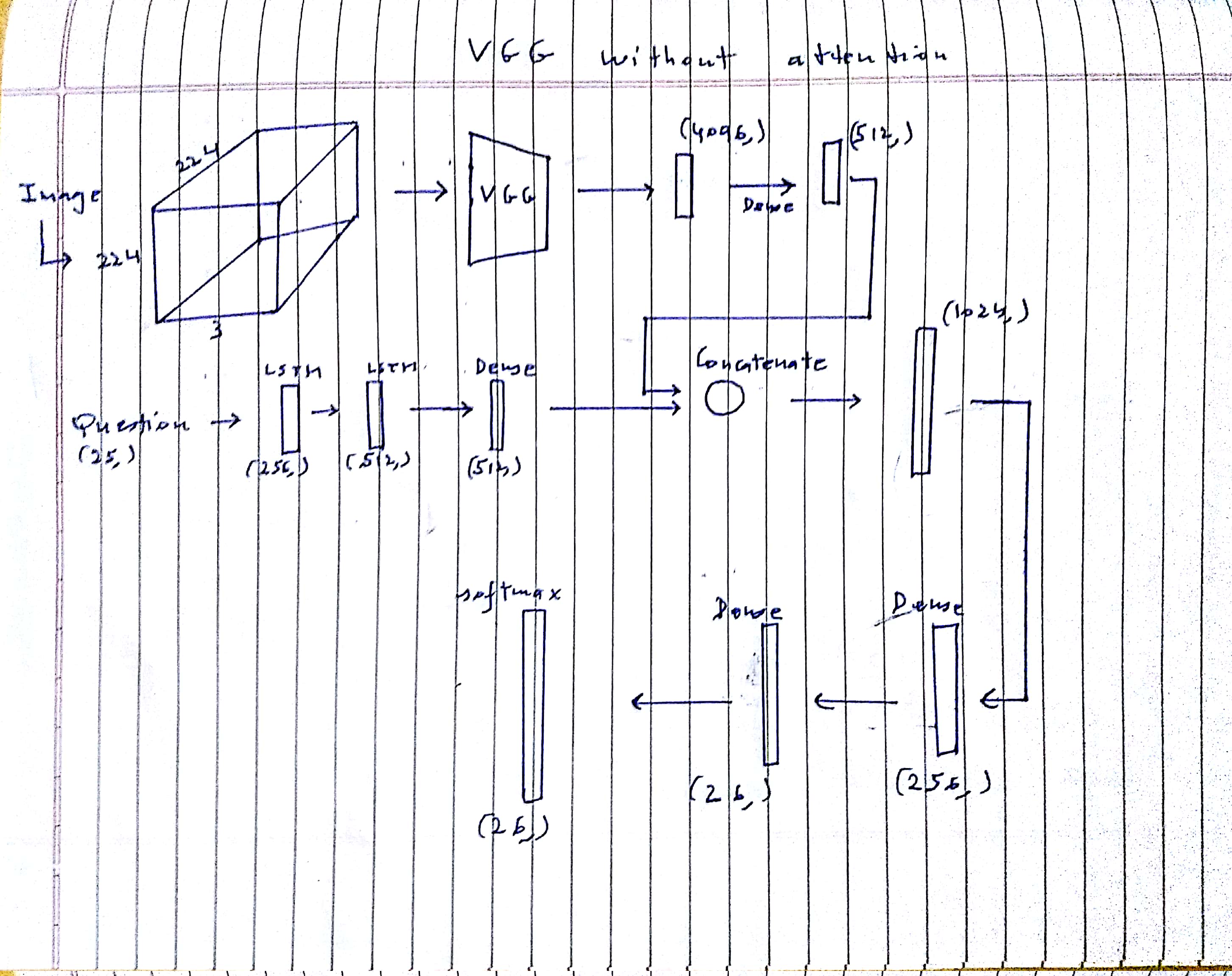
This model uses a pre-trained VGG network with the last few layers trainable. The image is fed as (224,224,3) and is converted by VGG to a (4096,) vector which is converted by a Dense layer to (512,). The question is fed as (25,) into the LSTM network and the output question tensor has shape (512,).
The output image tensor and the output question tensors are concatenated to form a (1024,) tensor, which is followed by fully-connected layers. The final softmax output is (26,) and is one-hot encoded.