To start the local development server, install Gatsby
and then all other dependencies. This should serve up the app on
localhost:8000.
npm install -g gatsby-cli # Install Gatsby globally
npm install # Install dependencies
npm run dev # Run the development serverThe app separates its source and content – so you usually shouldn't have to dig into the JavaScript source to change things. The following points of customization are available:
| Location | Description |
|---|---|
meta.json |
General config settings, title, description etc. |
theme.sass |
Color theme. |
binder/requirements.txt |
Python requirements to install. |
chapters |
The chapters, one Markdown file per chapter. |
slides |
The slides, one Markdown file per slide deck. |
static |
Static assets like images, will be copied to the root. |
The following meta settings are available. Note that you have to re-start Gatsby to see the changes if you're editing it while the server is running.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
courseId |
Unique ID of the course. Will be used when saving completed exercises to the browser's local storage. |
title |
The title of the course. |
slogan |
Course slogan, displayed in the page title on the front page. |
description |
Course description. Used for site meta and in footer. |
bio |
Author bio. Used in the footer. |
siteUrl |
URL of the deployed site (without trailing slash). |
twitter |
Author twitter handle, used in Twitter cards meta. |
fonts |
Google Fonts to load. Should be the font part of the URL in the embed string, e.g. Lato:400,400i,700,700i. |
testTemplate |
Template used to validate the answers. ${solution} will be replaced with the user code and ${test} with the contents of the test file. |
juniper.repo |
Repo to build on Binder in user/repo format. Usually the same as this repo. |
juniper.branch |
Branch to build. Ideally not master, so the image is not rebuilt every time you push. |
juniper.lang |
Code language for syntax highlighting. |
juniper.kernelType |
The name of the kernel to use. |
juniper.debug |
Logs additional debugging info to the console. |
showProfileImage |
Whether to show the profile image in the footer. If true, a file static/profile.jpg needs to be available. |
footerLinks |
List of objects with "text" and "url" to display as links in the footer. |
theme |
Currently only used for the progressive web app, e.g. as the theme color on mobile. For the UI theme, edit theme.sass. |
All files added to /static will become available at the root of the deployed
site. So /static/image.jpg can be referenced in your course as /image.jpg.
The following assets need to be available and can be customized:
| File | Description |
|---|---|
icon.png |
Custom favicon. |
logo.svg |
The course logo. |
profile.jpg |
Photo or profile image. |
social.jpg |
Social image, displayed in Twitter and Facebook cards. |
icon_check.svg |
"Check" icon displayed on "Mark as completed" button. |
icon_slides.svg |
Icon displayed in the corner of a slides exercise. |
Chapters are placed in /chapters and are Markdown files
consisting of <exercise> components. They'll be turned into pages, e.g.
/chapter1. In their frontmatter block at the top of the file, they need to
specify type: chapter, as well as the following meta:
---
title: The chapter title
description: The chapter description
prev: /chapter1 # exact path to previous chapter or null to not show a link
next: /chapter3 # exact path to next chapter or null to not show a link
id: 2 # unique identifier for chapter
type: chapter # important: this creates a standalone page from the chapter
---
Slides are placed in /slides and are markdown files consisting of
slide content, separated by ---. They need to specify the following
frontmatter block at the top of the file:
---
type: slides
---
The first and last slide use a special layout and will display the headline
in the center of the slide. Speaker notes (in this case, the script) can be
added at the end of a slide, prefixed by Notes:. They'll then be shown on the
right next to the slides. Here's an example slides file:
---
type: slides
---
# Processing pipelines
Notes: This is a slide deck about processing pipelines.
---
# Next slide
- Some bullet points here
- And another bullet point
<img src="/image.jpg" alt="An image located in /static" />When using custom elements, make sure to place a newline between the opening/closing tags and the children. Otherwise, Markdown content may not render correctly.
Container of a single exercise.
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
id |
number / string | Unique exercise ID within chapter. |
title |
string | Exercise title. |
type |
string | Optional type. "slides" makes container wider and adds icon. |
| children | - | The contents of the exercise. |
<exercise id="1" title="Introduction to spaCy">
Content goes here...
</exercise>| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
id |
number / string | Unique identifier of the code exercise. |
source |
string | Name of the source file (without file extension). Defaults to exc_${id} if not set. |
solution |
string | Name of the solution file (without file extension). Defaults to solution_${id} if not set. |
test |
string | Name of the test file (without file extension). Defaults to test_${id} if not set. |
| children | string | Optional hints displayed when the user clicks "Show hints". |
<codeblock id="02_03">
This is a hint!
</codeblock>Container to display slides interactively using Reveal.js and a Markdown file.
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
source |
string | Name of slides file (without file extension). |
<slides source="chapter1_01_introduction-to-spacy">
</slides>Container for multiple-choice question.
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
id |
string / number | Optional unique ID. Can be used if more than one choice question is present in one exercise. |
| children | nodes | Only <opt> components for the options. |
<choice>
<opt text="Option one">You have selected option one! This is not good.</opt>
<opt text="Option two" correct="true">Yay! </opt>
</choice>A multiple-choice option.
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
text |
string | The option text to be displayed. Supports inline HTML. |
correct |
string | "true" if the option is the correct answer. |
| children | string | The text to be displayed if the option is selected (explaining why it's correct or incorrect). |
The requirements.txt in the repository defines the
packages that are installed when building it with Binder. You can specify the
binder settings like repo, branch and kernel type in the "juniper" section of
the meta.json. I'd recommend running the very first build via the interface on
the Binder website, as this gives you a detailed build
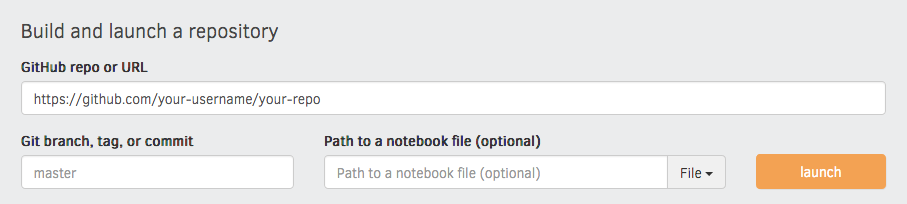
log and feedback on whether everything worked as expected. Enter your repository
URL, click "launch" and wait for it to install the dependencies and build the
image.
To validate the code when the user hits "Submit", we're currently using a
slightly hacky trick. Since the Python code is sent back to the kernel as a
string, we can manipulate it and add tests – for example, exercise
exc_01_02_01.py will be validated using test_01_02_01.py (if available). The
user code and test are combined using a string template. At the moment, the
testTemplate in the meta.json looks like this:
from wasabi import Printer
__msg__ = Printer()
__solution__ = """${solution}"""
${solution}
${test}
try:
test()
except AssertionError as e:
__msg__.fail(e)
If present, ${solution} will be replaced with the string value of the
submitted user code. In this case, we're inserting it twice: once as a string so
we can check whether the submission includes something, and once as the code, so
we can actually run it and check the objects it creates. ${test} is replaced
by the contents of the test file. It's also making
wasabi's printer available as __msg__, so
we can easily print pretty messages in the tests. Finally, the try/accept
block checks if the test function raises an AssertionError and if so, displays
the error message. This also hides the full error traceback (which can easily
leak the correct answers).
A test file could then look like this:
def test():
assert "spacy.load" in __solution__, "Are you calling spacy.load?"
assert nlp.meta["lang"] == "en", "Are you loading the correct model?"
assert nlp.meta["name"] == "core_web_sm", "Are you loading the correct model?"
assert "nlp(text)" in __solution__, "Are you processing the text correctly?"
assert "print(doc.text)" in __solution__, "Are you printing the Doc's text?"
__msg__.good(
"Well done! Now that you've practiced loading models, let's look at "
"some of their predictions."
)The string answer is available as __solution__, and the test also has access
to the solution code.
For more details on how it all works behind the scenes, see the original course repo.