Dohyun Kim & Jihun Jeung
##중간 전 프로젝트 진행상황:
-
LOAD data를 WindowsGenerator를 이용하여, Model을 만들고 학습시키려함.
-
향후 Load data에 기상청 데이터 ex) weather data를 붙여 CNN_LSTM 모델을 적용해보려 함. (normalization을 적용함, )
-
Electricity data를 일별로 총합을 구해 total_sum.csv를 만듬
-
특정 구간에서 급격히 떨어지는 부분을 빼는 등 데이터 전처리 과정이 필요함
-
PV의 경우. 제한조건 및 objective function 등 필요한 수식을 만듬.
-
PULP library를 공부 중. 이를 적용 예정.
-
Spark를 이용해 PV Data과 load data를 input으로 전기요금을 계산해볼 예정 (?)
###중간 후 프로젝트
- electricity : GIST Load data
- weather : 기상자료개방포탈 | 링크
- korea_electricity : 한국전력거래소_시간별 전력수요량(시간단위 전국 발전단 수요 데이터) | 링크
example data
| timestamp | electricity | korea_electricity | temperature | ... |
|---|---|---|---|---|
- timestamp : yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm 형식을 timestamp로 바꾸어줌.
timestamp = [0] * length #initialization
for i in range(length):
timestamp[i] = time.mktime(datetime.datetime.strptime(weather_df['timestamp'][i], '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M').timetuple())
weather_df['timestamp'] = timestamp
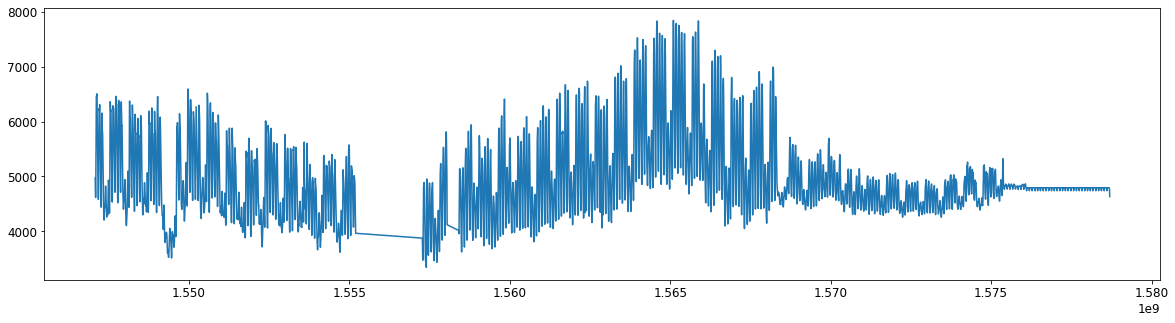
- low pass filter
#figure size
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [20, 5]
#filter variable
b, a = signal.butter(1, 0.3)
y = signal.filtfilt(b, a, xn)
plt.figure
plt.subplot(1,1,1)
plt.plot(t, xn, 'b')
plt.plot(t, y, 'r') #lfilter
plt.legend(('noisy signal','filtfilt'), loc='best')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
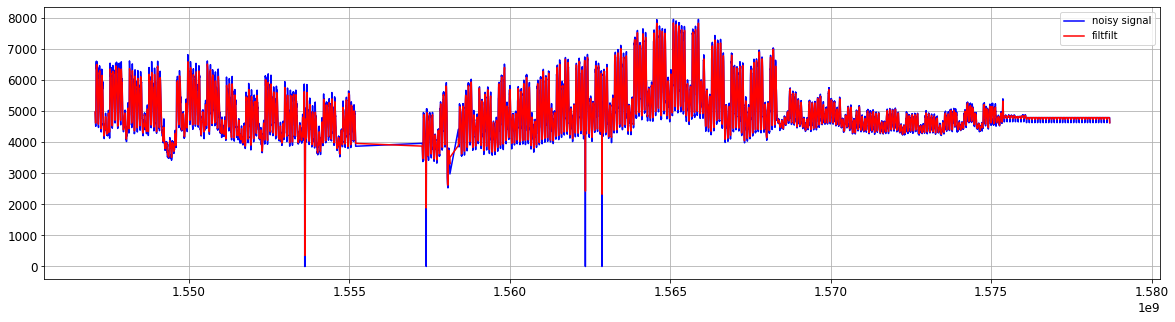 Figure. low pass filter
Figure. low pass filter
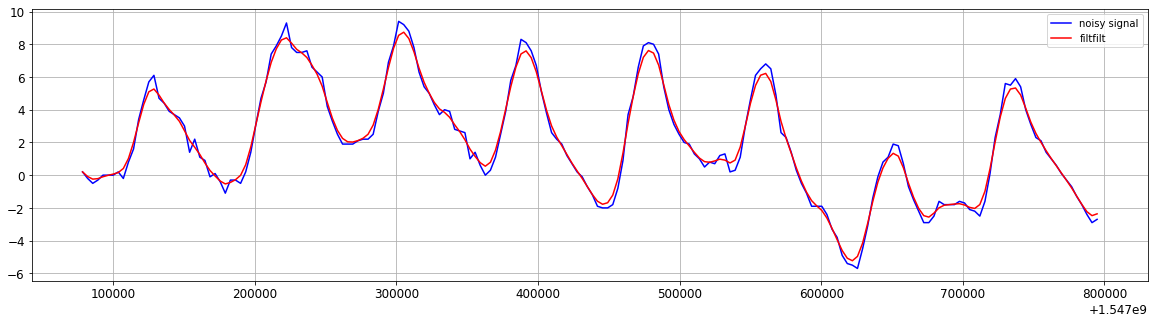 Figure. low pass filter (zoom-in)
Figure. low pass filter (zoom-in)
- trim outlier (electricity < 2000)
#remove outlier data (the sequence of removal is important to keep the consistency of index)
df_data2 = df_data
df_data2 = df_data2.drop(list(range(3739,3742)), axis=0)
df_data2 = df_data2.drop(list(range(3595,3598)), axis=0)
df_data2 = df_data2.drop(list(range(2472,2499)), axis=0)
df_data2 = df_data2.drop(list(range(2288,2291)), axis=0)
df_data2 = df_data2.drop(list(range(1813,1820)), axis=0)
- correlation
>>> corr = df_data.corr(method='pearson')
>>> print(corr)
timestamp electricity ... 지면온도(°C) korea_electricity
timestamp 1.000000 -0.011660 ... 0.127391 -0.055148
electricity -0.011660 1.000000 ... 0.454906 0.633428
year 0.278708 -0.041752 ... -0.173866 0.098974
month 0.840054 0.007057 ... 0.229869 -0.117772
date -0.001209 0.054572 ... -0.002976 0.047094
day -0.008416 -0.006461 ... -0.007596 -0.368987
time 0.002965 0.295113 ... 0.164734 0.321971
temperature 0.192824 0.380005 ... 0.921429 -0.064204
강수량(mm) 0.021677 0.045517 ... 0.031095 0.002487
풍속(m/s) -0.070830 0.230423 ... 0.196186 0.192416
풍향(16방위) -0.164018 0.165331 ... 0.238157 0.113418
습도(%) 0.176682 -0.071612 ... 0.007366 -0.176961
증기압(hPa) 0.197663 0.378798 ... 0.718443 -0.016517
이슬점온도(°C) 0.241461 0.280366 ... 0.728326 -0.120461
현지기압(hPa) 0.053933 -0.242467 ... -0.687093 0.092686
해면기압(hPa) 0.044979 -0.248686 ... -0.701145 0.093071
전운량(10분위) 0.032239 0.101038 ... 0.118865 0.055340
시정(10m) 0.148792 0.132798 ... 0.163565 0.055807
지면온도(°C) 0.127391 0.454906 ... 1.000000 0.019157
korea_electricity -0.055148 0.633428 ... 0.019157 1.000000
- feature significance
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from matplotlib import pyplot
# split into input and output
X = df_data.iloc[:, 1:] #timestamp
y = df_data.iloc[:, 0]
# fit random forest model
model = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=500, random_state=1)
model.fit(X, y)
# show importance scores
names = df_data.columns.values[1:]
for name, score in zip(names, model.feature_importances_):
print(name, score)
print('------------------------------------------------------')
electricity 4.8691318645328e-07
year 0.1641875308458571
month 0.8298849282469517
date 0.005836185661765732
day 4.891873361976034e-05
time 2.1977916794647093e-06
temperature 6.764042455895493e-07
강수량(mm) 2.687023373225491e-08
풍속(m/s) 2.711072603142201e-07
풍향(16방위) 1.3002849610985465e-07
습도(%) 5.492011958910649e-07
증기압(hPa) 3.6728833845211496e-06
이슬점온도(°C) 3.936398224801228e-06
현지기압(hPa) 1.4493666814833007e-05
해면기압(hPa) 1.099987486407661e-05
전운량(10분위) 8.007781093506881e-07
시정(10m) 9.965253005783227e-07
지면온도(°C) 3.428553540672571e-07
korea_electricity 2.855213455813887e-06
- LSTNET은 skipGRU, CNN-GRU, attention을 이용한 postskipGRU, 그리고 autoregression을 합쳐진 모델임. (Reference[2] 참고)

loss function= MSE,optimizer=Adam,learning rate=0.001으로 설정
- 7 day * 24 day/hour의 timeseries 데이터(
Input_window = 7)로 다음날 (sliding_width = 1) 24 hour를 예측(label_width = 1)하는 모델을 만듬.
- LSTNET으로 GIST 전력 사용량, 대한민국 전력 사용량 그리고 기온의 각각 모델을 만들고, 각각 예측모델의 output을 concat시켜 GIST 전력사용량을 예측하는 ensemble 모델로 train함.
keras tuner는 TensorFlow 프로그램에 대한 최적의 하이퍼파라미터 세트를 선택하는 데 도움을 주는 라이브러리이다.BayesianOptimizer은 gaussian process으로 적합한 hyperparameter tuning한다.max_trials=80으로,objective='val_loss'으로 설정하여 loss value가 가장 낮은 hyperparameter를 선정하였다.
2018년 11월 1일 데이터 링크
#import libarary
from pulp import *
import tensorflow as tf
import pandas as pd
#load model
reconstructed_model = keras.models.load_model("/EnerGist_2021.07/LSTNet/elec_batch_129_453.h5", custom_objects = {'rse':rse,'PostSkipTrans': PostSkipTrans, 'PreSkipTrans':PreSkipTrans,'PreARTrans':PreARTrans, 'PostARTrans':PostARTrans} )
#predict
prediction_result = model_predict(reconstructed_model, 2018_11_01_data)
- 부하량 예측 발전 모델과 비슷하게 모델을 만들었다. 다른 점은 input data에 temperature 데이터와 지스트 태양광 발전량 예측을 가지고 ensemble model을 만들었다는 점이다.
2018년 11월 1일 데이터 링크
#import libarary
from pulp import *
import tensorflow as tf
import pandas as pd
#load model
reconstructed_model = keras.models.load_model("/model_address", custom_objects = {'rse':rse,'PostSkipTrans': PostSkipTrans, 'PreSkipTrans':PreSkipTrans,'PreARTrans':PreARTrans, 'PostARTrans':PostARTrans} )
#predict
prediction_result = model_predict(reconstructed_model, 2018_11_01_data)
Library pulp로 cost를 최소화해주는 BESS schedule을 찾아주는 linear optimization을 구현하였음. optimization(season, electricity_data, PV_data)으로 사용가능하다. argument는 24시간 동안 사용한 electricity 값(e.g. electricity_t)과 PV 값(e.g. PV_t), 그리고 계절(e.g. 'summer')이다. 함수의 출력값은 total_cost와 시간별 bess_value이다.
>>> PV_t=[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0.6,11.8,58.5,125.2,196.1,235.7,308.1,68.8,48,25,1.5,0,0,0,0,0,0]
>>> electricity_t=[4972.86446897, 4827.32813707, 4714.39951693, 4640.4637654 ,
4619.08798299, 4696.02395711, 4934.15191917, 5358.15019654,
5870.89139808, 6269.93405485, 6444.9726441 , 6461.49278899,
6454.26552802, 6488.01214138, 6506.49025023, 6471.5219868 ,
6409.99699496, 6273.83475456, 6020.27016168, 5780.28216133,
5637.47629486, 5505.49176825, 5340.39785949, 5166.06439475 ] #define electricity
>>> total_cost, bess_value = optimization('summer', electricity_t, PV_t)
>>> print(total_cost)
11904816.96244172
>>> print(bess_value)
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 193.2964, 250.0, 0.0, 250.0, 59.50512, 180.68505, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
''sh python optimization.py