-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 58
Performance Tuning
— Courtesy of Ricky Ho’s Pragmatic Programmer blog.
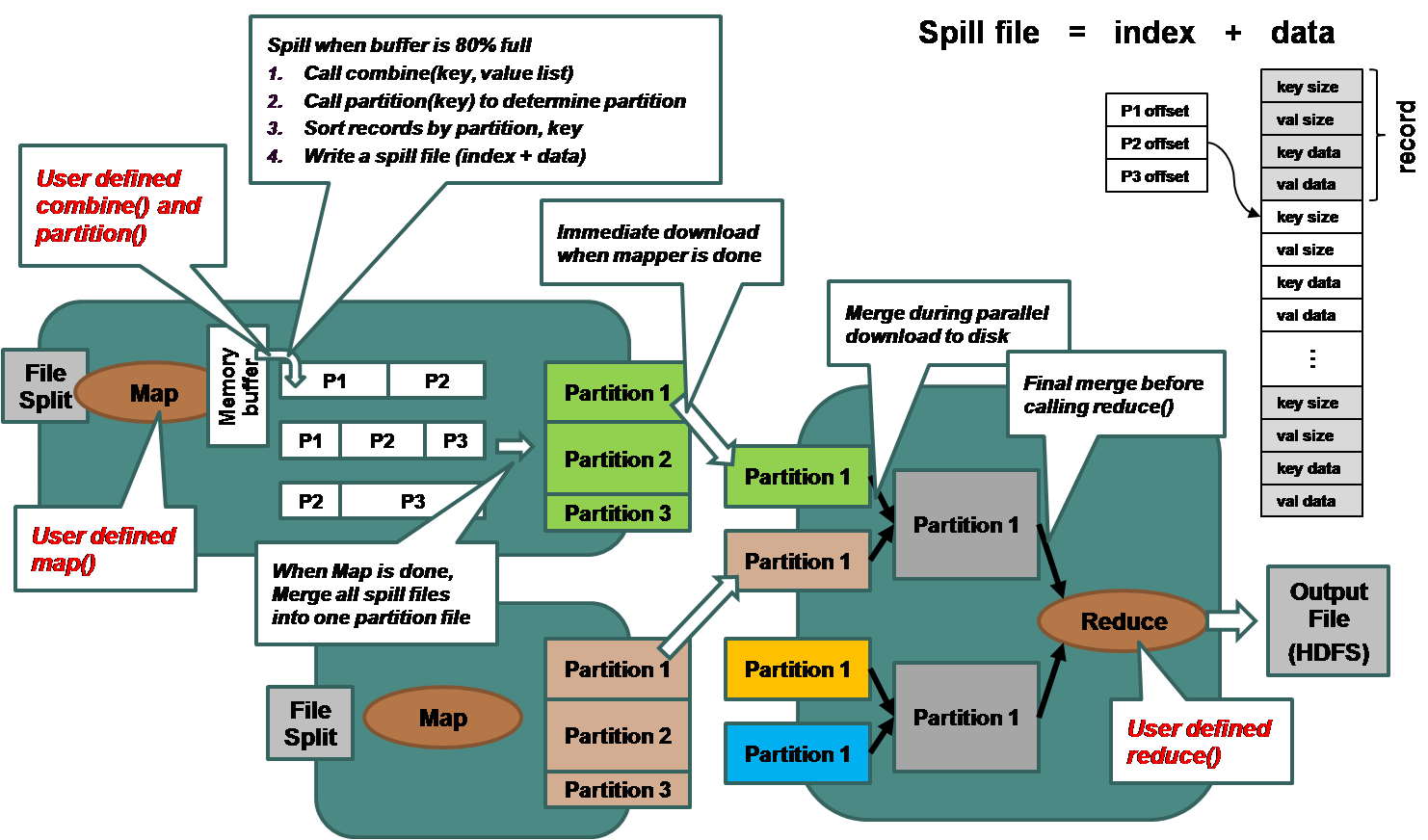
Hadoop is a complex piece of software with a variegation of components including a distributed file system, a distributed computing framework with job trackers, data nodes, and numerous simultaneously running JVM instances. With any complex software environment, there are tunings that can be employed to ensure both efficient use of space (network bandwidth, hard drive, memory, etc.) and time (object creation, combiners, in-memory combiners, etc.). This section presents various tricks to Hadoop/Faunus that can be used to tune a Faunus job sequences and Faunus MapReduce extensions.

-
Use sequence files for repeated analyses: The Hadoop sequence file is the most optimal file format for Faunus. If repeated analysis is going to be done on a graph, then it is beneficial to first generate a sequence file representation of that graph in HDFS. This file can then serve as the input for repeated analyses. Generating a sequence file is as simple as running the identity step
g.V()with the followingfaunus.properties.
faunus.graph.output.format.class=org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.SequenceFileOutputFormat- Avoid text-based representations of graphs: The GraphSON representation of a graph is easy to read/write, but very inefficient. DBpedia as a GraphSON file is 23gigs and 18gigs as a sequence file. If possible, avoid using verbose text-based formats.
- Reduce the size of the graph early in a job chain: A Faunus graph is typically multi-relational in that there are numerous types of edges in the graph. In many situations, all that information is not necessary for the graph derivation or statistic. As such, use filtering steps early on in the expression to reduce the graph down to the requisite information needed for the computation. Below, because only battled and father edges are used for the traversal, all other edges are filtered out prior to doing the traversal.
g.E.has('label','battled','father').keep.V.as('x').in('battled').in('father').linkOut('x','enemy-father')- Make use of repeated map steps: When a chain of map-steps are issued, Faunus will process that chain in-memory and thus, there is no I/O within the chain. As such, it is best to organize the traversal (if possible) with all the maps front-loading the traversal/query.
-
A vertex must be storable in main memory: The atomic unit of Faunus is a vertex. A
FaunusVertexis composed of the vertex’s properties, its incoming edges, its outgoing edges, the properties of those edges, and the path information of the traversal up to the elements. A vertex (and any working data structure) must be able to fit in main memory. As such, this is the limit of what can be processed by Faunus. Be sure to make use ofmapred.child.java.optsif more memory is required for the largest vertex being processed (e.g.-Xmx512m).
- Avoid long, non-filtering path-enabled traversals: When the history of a traversal is not needed, then the only information propagated between elements is the number of counter at the current element (as a long). When history is required, then an array of an array of element ids is propagated. With complex graph structures and with the breadth-first nature of Gremlin/Faunus, this can lead to a combinatorial explosion.
There are numerous Hadoop specific tunings. Below is a collection of blog posts that discuss tips and tricks for Hadoop.