diff --git a/2.0_how_to_use_mtl.md b/2.0_how_to_use_mtl.md
index 7e0754a4..b9d29df1 100644
--- a/2.0_how_to_use_mtl.md
+++ b/2.0_how_to_use_mtl.md
@@ -64,7 +64,7 @@ Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. If you're watching this video, you want to kn
[ ](https://bcove.video/3A3sBiG)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. How do five key variables drive care quality? _Modeling to Learn_ emphasizes the dynamics of care over time, which can be accurately simplified to the key time-based variables that drive care quality. But be careful, the important principle is that these variables operate together over time to define an episode of care. That means care quality cannot be improved without understanding how these variables influence one another. If you want to see what Lindsey's talking about, navigate to the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf) and review each care problem—care coordination, medication management, psychotherapy, team care, and team flow. Our partners across VA describe how challenging it is to review data in one information system and then in another and end up unsure how to reconcile them, especially when you think that they indicate a different course of action. Folks are extremely busy and any new data resources must really add value to be worth learning. Let's see if these _Modeling to Learn_ variables meet the commonsense test of value added. Well, what do you think the five time-based variables are that make up an evidence-based episode of care? All outpatient care is defined by whether you can get an appointment when you need help. We focus on this all the time in VA. But then, and this is critical, you must be able to be seen again to complete a therapeutic course of care adequate to meet your need. Clinicians told us that a week was the way they think clinically. So, in _Modeling to Learn_, teams make their clinic selections to obtain an estimate of their local new patient start rate in patients per week and their appointment supply in appointments per week. Then we define evidence-based engagement as the new patient wait time in weeks, time between visits and weeks, and the engagement duration over time, again in weeks. This is a simplified definition of an evidence-based episode of care that is accurate for time. Why is it wise to focus on the dynamics of care over time? That's why _Modeling to Learn_ Blue is useful. So watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. How do five key variables drive care quality? _Modeling to Learn_ emphasizes the dynamics of care over time, which can be accurately simplified to the key time-based variables that drive care quality. But be careful, the important principle is that these variables operate together over time to define an episode of care. That means care quality cannot be improved without understanding how these variables influence one another. If you want to see what Lindsey's talking about, navigate to the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf) and review each care problem—care coordination, medication management, psychotherapy, team care, and team flow. Our partners across VA describe how challenging it is to review data in one information system and then in another and end up unsure how to reconcile them, especially when you think that they indicate a different course of action. Folks are extremely busy and any new data resources must really add value to be worth learning. Let's see if these _Modeling to Learn_ variables meet the commonsense test of value added. Well, what do you think the five time-based variables are that make up an evidence-based episode of care? All outpatient care is defined by whether you can get an appointment when you need help. We focus on this all the time in VA. But then, and this is critical, you must be able to be seen again to complete a therapeutic course of care adequate to meet your need. Clinicians told us that a week was the way they think clinically. So, in _Modeling to Learn_, teams make their clinic selections to obtain an estimate of their local new patient start rate in patients per week and their appointment supply in appointments per week. Then we define evidence-based engagement as the new patient wait time in weeks, time between visits and weeks, and the engagement duration over time, again in weeks. This is a simplified definition of an evidence-based episode of care that is accurate for time. Why is it wise to focus on the dynamics of care over time? That's why _Modeling to Learn Blue_ is useful. So watch that video to find out.
## How does _Modeling to Learn_ help improve medication management?
@@ -96,7 +96,7 @@ Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. How does an appointment backlog extend the we
[
](https://bcove.video/3A3sBiG)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. How do five key variables drive care quality? _Modeling to Learn_ emphasizes the dynamics of care over time, which can be accurately simplified to the key time-based variables that drive care quality. But be careful, the important principle is that these variables operate together over time to define an episode of care. That means care quality cannot be improved without understanding how these variables influence one another. If you want to see what Lindsey's talking about, navigate to the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf) and review each care problem—care coordination, medication management, psychotherapy, team care, and team flow. Our partners across VA describe how challenging it is to review data in one information system and then in another and end up unsure how to reconcile them, especially when you think that they indicate a different course of action. Folks are extremely busy and any new data resources must really add value to be worth learning. Let's see if these _Modeling to Learn_ variables meet the commonsense test of value added. Well, what do you think the five time-based variables are that make up an evidence-based episode of care? All outpatient care is defined by whether you can get an appointment when you need help. We focus on this all the time in VA. But then, and this is critical, you must be able to be seen again to complete a therapeutic course of care adequate to meet your need. Clinicians told us that a week was the way they think clinically. So, in _Modeling to Learn_, teams make their clinic selections to obtain an estimate of their local new patient start rate in patients per week and their appointment supply in appointments per week. Then we define evidence-based engagement as the new patient wait time in weeks, time between visits and weeks, and the engagement duration over time, again in weeks. This is a simplified definition of an evidence-based episode of care that is accurate for time. Why is it wise to focus on the dynamics of care over time? That's why _Modeling to Learn_ Blue is useful. So watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. How do five key variables drive care quality? _Modeling to Learn_ emphasizes the dynamics of care over time, which can be accurately simplified to the key time-based variables that drive care quality. But be careful, the important principle is that these variables operate together over time to define an episode of care. That means care quality cannot be improved without understanding how these variables influence one another. If you want to see what Lindsey's talking about, navigate to the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf) and review each care problem—care coordination, medication management, psychotherapy, team care, and team flow. Our partners across VA describe how challenging it is to review data in one information system and then in another and end up unsure how to reconcile them, especially when you think that they indicate a different course of action. Folks are extremely busy and any new data resources must really add value to be worth learning. Let's see if these _Modeling to Learn_ variables meet the commonsense test of value added. Well, what do you think the five time-based variables are that make up an evidence-based episode of care? All outpatient care is defined by whether you can get an appointment when you need help. We focus on this all the time in VA. But then, and this is critical, you must be able to be seen again to complete a therapeutic course of care adequate to meet your need. Clinicians told us that a week was the way they think clinically. So, in _Modeling to Learn_, teams make their clinic selections to obtain an estimate of their local new patient start rate in patients per week and their appointment supply in appointments per week. Then we define evidence-based engagement as the new patient wait time in weeks, time between visits and weeks, and the engagement duration over time, again in weeks. This is a simplified definition of an evidence-based episode of care that is accurate for time. Why is it wise to focus on the dynamics of care over time? That's why _Modeling to Learn Blue_ is useful. So watch that video to find out.
## How does _Modeling to Learn_ help improve medication management?
@@ -96,7 +96,7 @@ Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. How does an appointment backlog extend the we
[ ](https://bcove.video/3yaXy41)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. How can we better balance the needs of new and existing patients? Should we prioritize new patient start rate or weeks between visits? These trade-offs are challenging for clinicians when you know there is a whole community of patients who need help. When teams are struggling with the limits of their available time in the day to see patients, it can feel like a clinical, ethical, and even moral quandary about how to best balance patients’ needs for services with the staff resources available. Of course, staff resources are always changing. We know many teams that are excelling in providing the highest quality addiction and mental health care available. But the behavioral health workforce shortage in the US is much bigger than VA. And VAs and teams need the right tools to make sure Veterans get the care they need for recovery. Challenges balancing the new patient start rate and the weeks between visits for existing patients apply systems thinking insights that we've talked about in other _MTL_ videos, such as the physics of conserving staff time in order to ensure a clinically beneficial, realistic approach to care decisions and quality improvement that meets VA quality standards _and_ meets Veterans needs for evidence-based episodes of care. The _Modeling to Learn_ Blue Simulation User Interface available at [mtl.how/sim](https://forio.com/app/va/va-psd-sim/login.html) enables a site or team to evaluate these two balancing system stories as a function of their data for the last two years exported from _Modeling to Learn_ Red Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf). As we talked about in the _How does an appointment backlog extend the weeks between visits?_ video and _What if we keep making the same care decisions, will things get better or worse?_ video, balancing feedbacks occur in any system that has a goal, including our healthcare and clinical systems. Balancing feedbacks occur in systems that have constraints of resources, staff, and time. And as a result, the trends that occur over time tend to reset to a status quo or oscillate around the status quo. A brief _Modeling to Learn_ consult uses the site or team reviewed local data plus simulation to efficiently find local improvements that account for all these balancing trade-offs. We aim to help clinical and improvement teams find a couple empowering clinical heuristics, or rules of thumb, that are more effective for ensuring evidence-based care to get more Veterans better. When we partner with a VA or a team, we aim to find the lightest lift we can, like increase groups by 10% or adjust the return-to-clinic order for three weeks for these presenting concerns. And we often find something small that has a big payoff for Veterans. Do you want to be empowered to leverage the feedback, flow, and volume of your local care system? Watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. How can we better balance the needs of new and existing patients? Should we prioritize new patient start rate or weeks between visits? These trade-offs are challenging for clinicians when you know there is a whole community of patients who need help. When teams are struggling with the limits of their available time in the day to see patients, it can feel like a clinical, ethical, and even moral quandary about how to best balance patients’ needs for services with the staff resources available. Of course, staff resources are always changing. We know many teams that are excelling in providing the highest quality addiction and mental health care available. But the behavioral health workforce shortage in the US is much bigger than VA. And VAs and teams need the right tools to make sure Veterans get the care they need for recovery. Challenges balancing the new patient start rate and the weeks between visits for existing patients apply systems thinking insights that we've talked about in other _MTL_ videos, such as the physics of conserving staff time in order to ensure a clinically beneficial, realistic approach to care decisions and quality improvement that meets VA quality standards _and_ meets Veterans needs for evidence-based episodes of care. The _Modeling to Learn Blue_ Simulation User Interface available at [mtl.how/sim](https://forio.com/app/va/va-psd-sim/login.html) enables a site or team to evaluate these two balancing system stories as a function of their data for the last two years exported from _Modeling to Learn Red_ Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf). As we talked about in the _How does an appointment backlog extend the weeks between visits?_ video and _What if we keep making the same care decisions, will things get better or worse?_ video, balancing feedbacks occur in any system that has a goal, including our healthcare and clinical systems. Balancing feedbacks occur in systems that have constraints of resources, staff, and time. And as a result, the trends that occur over time tend to reset to a status quo or oscillate around the status quo. A brief _Modeling to Learn_ consult uses the site or team reviewed local data plus simulation to efficiently find local improvements that account for all these balancing trade-offs. We aim to help clinical and improvement teams find a couple empowering clinical heuristics, or rules of thumb, that are more effective for ensuring evidence-based care to get more Veterans better. When we partner with a VA or a team, we aim to find the lightest lift we can, like increase groups by 10% or adjust the return-to-clinic order for three weeks for these presenting concerns. And we often find something small that has a big payoff for Veterans. Do you want to be empowered to leverage the feedback, flow, and volume of your local care system? Watch that video to find out.
## How can we leverage the feedback, rates, and volume of our local care system?
diff --git a/3.0_technical_documentation.md b/3.0_technical_documentation.md
index a179c0ac..9062f13f 100644
--- a/3.0_technical_documentation.md
+++ b/3.0_technical_documentation.md
@@ -6,11 +6,11 @@
- [CPT Code Cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/cptcode_cheatsheet.png)
-### _MTL_ 3.7 Data Cheatsheet
+### _MTL 3.7_ Data Cheatsheet
- [Data Cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/mtl_how_3.7_data_cheatsheet.png)
-### _MTL_ 3.7 Sim UI Cheatsheet
+### _MTL 3.7_ Sim UI Cheatsheet
- [Sim UI Cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/mtl_how_3.7_sim_ui_cheatsheet.png)
@@ -45,13 +45,15 @@ Follow the instructions below to create an account or team in the Sim UI. Once t
- If you are creating a team or the first person to register from your Facility Team, the following pop-up window will appear (with your VISN, Facility, and Clinic pre-populated).
- Enter your Facility Team name in the pop-up window (immediately after the pre-populated information).
-
- - Click the Submit button. The submitted team name is saved even though the dropdown field remains unchanged.
- **Notes:** You must only use lowercase letters. You must use the underscore character (_) instead of spaces.
](https://bcove.video/3yaXy41)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. How can we better balance the needs of new and existing patients? Should we prioritize new patient start rate or weeks between visits? These trade-offs are challenging for clinicians when you know there is a whole community of patients who need help. When teams are struggling with the limits of their available time in the day to see patients, it can feel like a clinical, ethical, and even moral quandary about how to best balance patients’ needs for services with the staff resources available. Of course, staff resources are always changing. We know many teams that are excelling in providing the highest quality addiction and mental health care available. But the behavioral health workforce shortage in the US is much bigger than VA. And VAs and teams need the right tools to make sure Veterans get the care they need for recovery. Challenges balancing the new patient start rate and the weeks between visits for existing patients apply systems thinking insights that we've talked about in other _MTL_ videos, such as the physics of conserving staff time in order to ensure a clinically beneficial, realistic approach to care decisions and quality improvement that meets VA quality standards _and_ meets Veterans needs for evidence-based episodes of care. The _Modeling to Learn_ Blue Simulation User Interface available at [mtl.how/sim](https://forio.com/app/va/va-psd-sim/login.html) enables a site or team to evaluate these two balancing system stories as a function of their data for the last two years exported from _Modeling to Learn_ Red Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf). As we talked about in the _How does an appointment backlog extend the weeks between visits?_ video and _What if we keep making the same care decisions, will things get better or worse?_ video, balancing feedbacks occur in any system that has a goal, including our healthcare and clinical systems. Balancing feedbacks occur in systems that have constraints of resources, staff, and time. And as a result, the trends that occur over time tend to reset to a status quo or oscillate around the status quo. A brief _Modeling to Learn_ consult uses the site or team reviewed local data plus simulation to efficiently find local improvements that account for all these balancing trade-offs. We aim to help clinical and improvement teams find a couple empowering clinical heuristics, or rules of thumb, that are more effective for ensuring evidence-based care to get more Veterans better. When we partner with a VA or a team, we aim to find the lightest lift we can, like increase groups by 10% or adjust the return-to-clinic order for three weeks for these presenting concerns. And we often find something small that has a big payoff for Veterans. Do you want to be empowered to leverage the feedback, flow, and volume of your local care system? Watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. How can we better balance the needs of new and existing patients? Should we prioritize new patient start rate or weeks between visits? These trade-offs are challenging for clinicians when you know there is a whole community of patients who need help. When teams are struggling with the limits of their available time in the day to see patients, it can feel like a clinical, ethical, and even moral quandary about how to best balance patients’ needs for services with the staff resources available. Of course, staff resources are always changing. We know many teams that are excelling in providing the highest quality addiction and mental health care available. But the behavioral health workforce shortage in the US is much bigger than VA. And VAs and teams need the right tools to make sure Veterans get the care they need for recovery. Challenges balancing the new patient start rate and the weeks between visits for existing patients apply systems thinking insights that we've talked about in other _MTL_ videos, such as the physics of conserving staff time in order to ensure a clinically beneficial, realistic approach to care decisions and quality improvement that meets VA quality standards _and_ meets Veterans needs for evidence-based episodes of care. The _Modeling to Learn Blue_ Simulation User Interface available at [mtl.how/sim](https://forio.com/app/va/va-psd-sim/login.html) enables a site or team to evaluate these two balancing system stories as a function of their data for the last two years exported from _Modeling to Learn Red_ Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf). As we talked about in the _How does an appointment backlog extend the weeks between visits?_ video and _What if we keep making the same care decisions, will things get better or worse?_ video, balancing feedbacks occur in any system that has a goal, including our healthcare and clinical systems. Balancing feedbacks occur in systems that have constraints of resources, staff, and time. And as a result, the trends that occur over time tend to reset to a status quo or oscillate around the status quo. A brief _Modeling to Learn_ consult uses the site or team reviewed local data plus simulation to efficiently find local improvements that account for all these balancing trade-offs. We aim to help clinical and improvement teams find a couple empowering clinical heuristics, or rules of thumb, that are more effective for ensuring evidence-based care to get more Veterans better. When we partner with a VA or a team, we aim to find the lightest lift we can, like increase groups by 10% or adjust the return-to-clinic order for three weeks for these presenting concerns. And we often find something small that has a big payoff for Veterans. Do you want to be empowered to leverage the feedback, flow, and volume of your local care system? Watch that video to find out.
## How can we leverage the feedback, rates, and volume of our local care system?
diff --git a/3.0_technical_documentation.md b/3.0_technical_documentation.md
index a179c0ac..9062f13f 100644
--- a/3.0_technical_documentation.md
+++ b/3.0_technical_documentation.md
@@ -6,11 +6,11 @@
- [CPT Code Cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/cptcode_cheatsheet.png)
-### _MTL_ 3.7 Data Cheatsheet
+### _MTL 3.7_ Data Cheatsheet
- [Data Cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/mtl_how_3.7_data_cheatsheet.png)
-### _MTL_ 3.7 Sim UI Cheatsheet
+### _MTL 3.7_ Sim UI Cheatsheet
- [Sim UI Cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/mtl_how_3.7_sim_ui_cheatsheet.png)
@@ -45,13 +45,15 @@ Follow the instructions below to create an account or team in the Sim UI. Once t
- If you are creating a team or the first person to register from your Facility Team, the following pop-up window will appear (with your VISN, Facility, and Clinic pre-populated).
- Enter your Facility Team name in the pop-up window (immediately after the pre-populated information).
-
- - Click the Submit button. The submitted team name is saved even though the dropdown field remains unchanged.
- **Notes:** You must only use lowercase letters. You must use the underscore character (_) instead of spaces.
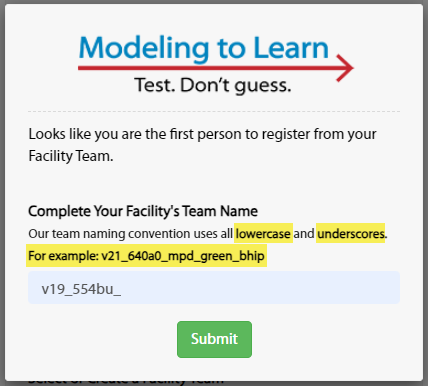 + - Click the Submit button. Even though the dropdown field remains unchanged on the form, the submitted team name is saved, as confirmed by the green text as shown in this example:
+
+
+ - Click the Submit button. Even though the dropdown field remains unchanged on the form, the submitted team name is saved, as confirmed by the green text as shown in this example:
+
+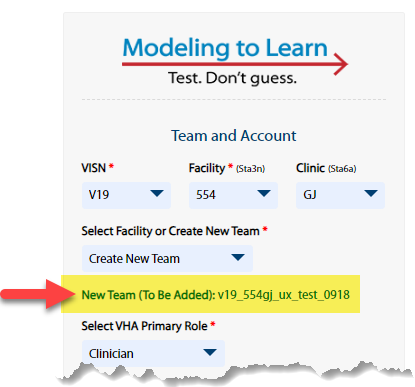 +
- **5 - Select VHA Primary Role**: Select your primary VHA role from the dropdown menu. Choices are: Clinician, Data Subject Matter Expert, Leader/Manager, Quality Improvement, Researcher/Evaluator, Systems Modeler, and Other.
- **6 - First Name**: Enter your first name.
@@ -75,9 +77,9 @@ Follow the instructions below to create an account or team in the Sim UI. Once t
- If the information is not correct, close the pop-up window and make adjustements to the registration form where needed.
- If the information is correct, click the green Submit button.
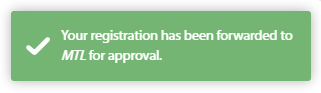
-The following message will appear for a few seconds in the upper right-hand corner of your browser window:
+A success page will appear :
-
+
- **5 - Select VHA Primary Role**: Select your primary VHA role from the dropdown menu. Choices are: Clinician, Data Subject Matter Expert, Leader/Manager, Quality Improvement, Researcher/Evaluator, Systems Modeler, and Other.
- **6 - First Name**: Enter your first name.
@@ -75,9 +77,9 @@ Follow the instructions below to create an account or team in the Sim UI. Once t
- If the information is not correct, close the pop-up window and make adjustements to the registration form where needed.
- If the information is correct, click the green Submit button.
-The following message will appear for a few seconds in the upper right-hand corner of your browser window:
+A success page will appear :
- +
+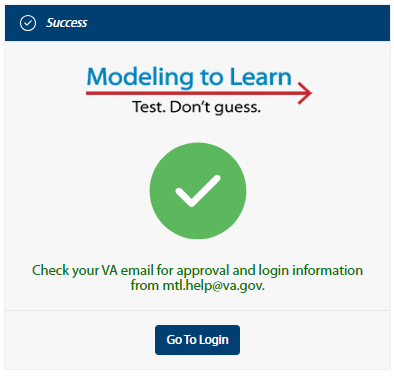 7. After your registration request is reviewed and approved, an approval email will be sent to your VA address that contains login information for accessing the _MTL_ Sim UI.
@@ -91,23 +93,24 @@ You must already have an account set up to log into the Sim UI. If you do not ha
7. After your registration request is reviewed and approved, an approval email will be sent to your VA address that contains login information for accessing the _MTL_ Sim UI.
@@ -91,23 +93,24 @@ You must already have an account set up to log into the Sim UI. If you do not ha
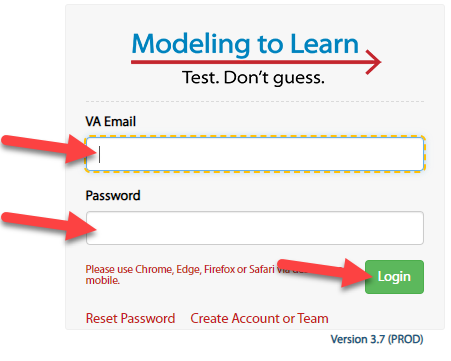 -2. A Please select a World pop-up will appear. The Sim will load teams and, once you select a team, you will be directed to that team's Home page.
+2. A Please select a World pop-up will appear. The Sim will load teams and, **once you select a team, you will be directed to that team's Home page.**
- **Note:** The login dropdown only shows worlds in which you are a team lead or participant (not an Administrator).
-- **Note:** If you have the Administrator role in any team and have been added into "administrator_login" in Epicenter, you will be allowed to login using the "administrator_login" choice. Upon logging in, Administrators are directed to the [Administrator Dashboard](#sim_ui_administrator_dashboard).
-
+- **Note:** If you have the Administrator role in any team and have been added into "administrator_login" in Epicenter, you will be allowed to login using the "administrator_login" choice. Upon logging in, Administrators are directed to the [Administrator Dashboard](#sim-ui-administrator_dashboard).
-2. A Please select a World pop-up will appear. The Sim will load teams and, once you select a team, you will be directed to that team's Home page.
+2. A Please select a World pop-up will appear. The Sim will load teams and, **once you select a team, you will be directed to that team's Home page.**
- **Note:** The login dropdown only shows worlds in which you are a team lead or participant (not an Administrator).
-- **Note:** If you have the Administrator role in any team and have been added into "administrator_login" in Epicenter, you will be allowed to login using the "administrator_login" choice. Upon logging in, Administrators are directed to the [Administrator Dashboard](#sim_ui_administrator_dashboard).
-
+- **Note:** If you have the Administrator role in any team and have been added into "administrator_login" in Epicenter, you will be allowed to login using the "administrator_login" choice. Upon logging in, Administrators are directed to the [Administrator Dashboard](#sim-ui-administrator_dashboard).
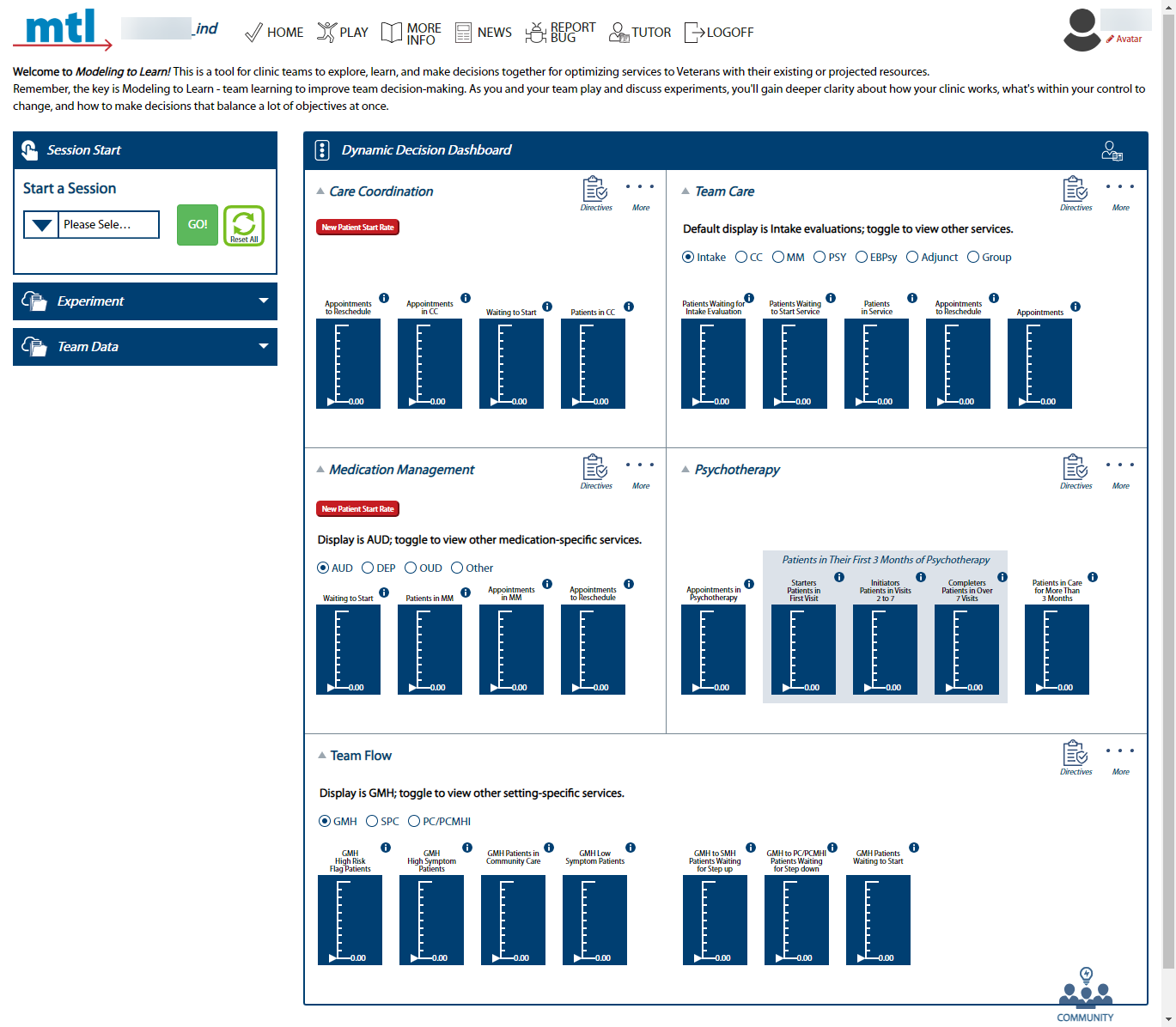
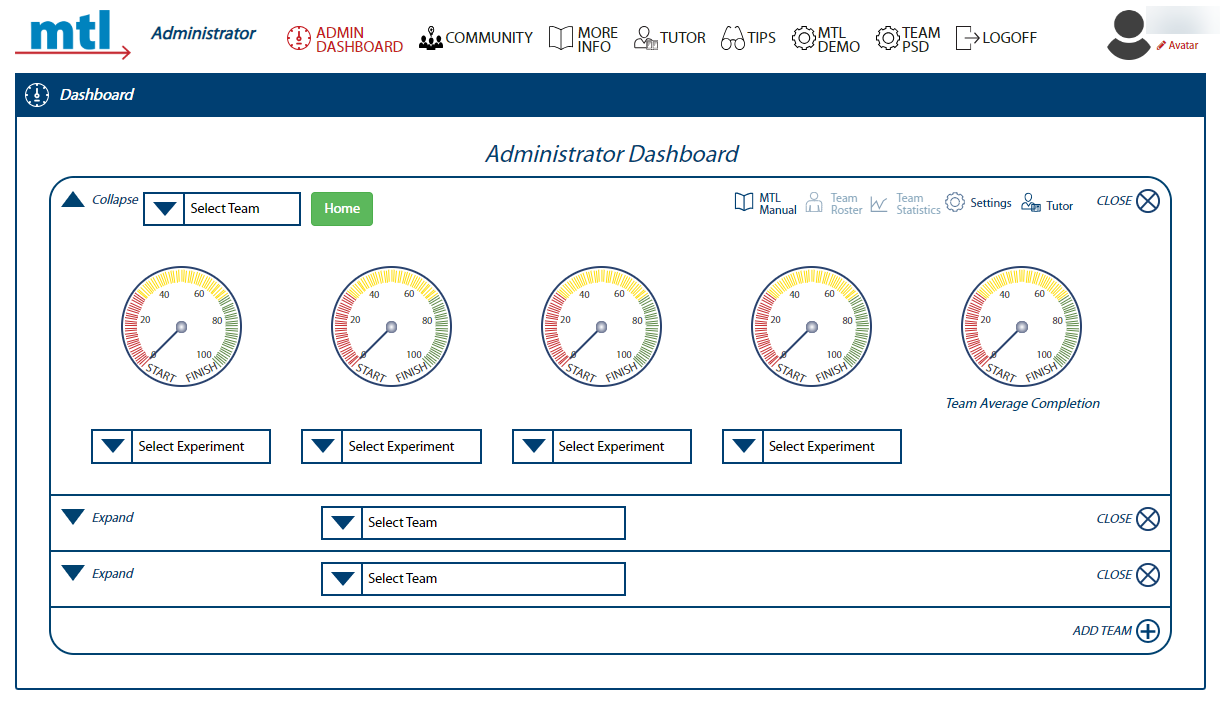
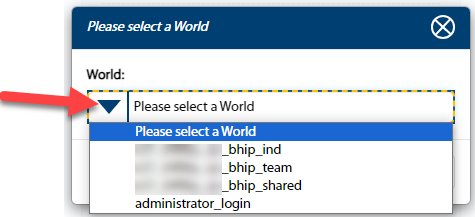 3. The screenshots below display what you will see upon logging in, depending on your role.
+- **Note:** To familiarize yourself with a team's Home page, refer to [Orient to a Team's Home Page](#orient-to-a-team's-home-page)
+
|Team Member login = team's Home page|Administrator login = Admin Dashboard |
|:---:|:---:|
|
3. The screenshots below display what you will see upon logging in, depending on your role.
+- **Note:** To familiarize yourself with a team's Home page, refer to [Orient to a Team's Home Page](#orient-to-a-team's-home-page)
+
|Team Member login = team's Home page|Administrator login = Admin Dashboard |
|:---:|:---:|
| |
| ### Make, View, and Export Team Clinic Selections for Import to Sim UI
-**Tip:** Refer to this one-page [Data Cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/mtl_how_3.7_data_cheatsheet.png) when using the Data UI and making clinic and flow selections.
+**Tip:** Refer to (or save) this one-page [Data Cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/mtl_how_3.7_data_cheatsheet.pdf) when using the Data UI and making clinic and flow selections.
The general workflow for the Data UI is that teams:
@@ -145,7 +148,7 @@ The general workflow for the Data UI is that teams:
- Click the green Apply button to pull Patient Level Data from all clinics selected in the last two years.
-- Select clinics that your team refers to in the Team Flow Selection tab to produce data tracking patients stepped up/down for the Team (SP) Flow module.
+- Select clinics that your team refers to in the Team Flow Selection tab to produce data tracking patients stepped up/down for the Team Flow module.
- For example, if you are a GMH team, you would select SMH in the dropdown for "The clinics selected below that my team refers to are" and add the SMH clinics your team refers to in the Green column, second row.
@@ -321,39 +324,35 @@ Below is a basic orientation to the Home page of any team:
### Make, View, and Export Team Clinic Selections for Import to Sim UI
-**Tip:** Refer to this one-page [Data Cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/mtl_how_3.7_data_cheatsheet.png) when using the Data UI and making clinic and flow selections.
+**Tip:** Refer to (or save) this one-page [Data Cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/mtl_how_3.7_data_cheatsheet.pdf) when using the Data UI and making clinic and flow selections.
The general workflow for the Data UI is that teams:
@@ -145,7 +148,7 @@ The general workflow for the Data UI is that teams:
- Click the green Apply button to pull Patient Level Data from all clinics selected in the last two years.
-- Select clinics that your team refers to in the Team Flow Selection tab to produce data tracking patients stepped up/down for the Team (SP) Flow module.
+- Select clinics that your team refers to in the Team Flow Selection tab to produce data tracking patients stepped up/down for the Team Flow module.
- For example, if you are a GMH team, you would select SMH in the dropdown for "The clinics selected below that my team refers to are" and add the SMH clinics your team refers to in the Green column, second row.
@@ -321,39 +324,35 @@ Below is a basic orientation to the Home page of any team:
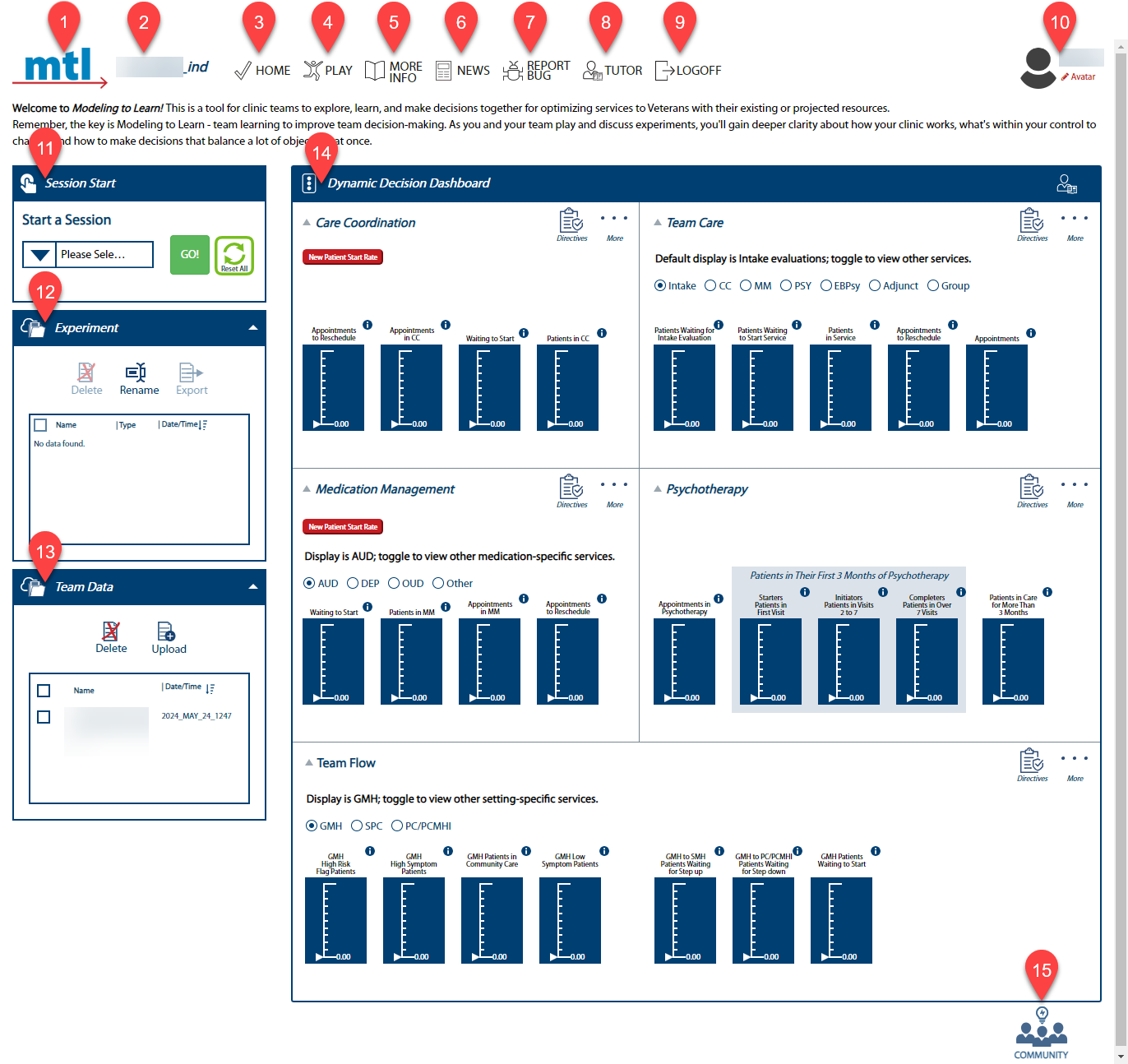 -1. **_MTL_ logo:** Click this logo on any page to return to this Home page.
-
-2. **Team Name:** The selected team name appears here. When logged into your individual world, team name = your name.
+1. **_MTL_ logo:** Click this logo to return to the Dynamic Decision Dashboard.
-3. **Home:** Click to return to this Home page.
+2. **Team Name:** The selected team name appears here with the world extension added at the end of its name. If you are logged in as an Administrator, you will see "Administrator" here.
-4. **Play:** Click to open the main Simulation User Interface (Sim UI) page.
+3. **Home:** Click to return to the Dynamic Decision Dashboard.
-5. **Team:** Click to chat with other team members. An alert will appear if you have unread chats waiting.
+4. **Play:** Click to return to the Play page.
-6. **More Info:** Click for answers to common _Modeling to Learn_ questions.
+5. **More Info:** Click for more information on how to use the Sim UI.
-7. **News:** Click for the latest news about _Modeling to Learn_. An alert will appear if you have unread news items.
+6. **News:** Click for the latest news about _Modeling to Learn_. An alert will appear if you have unread news items.
-8. **Report Bug:** Click to report a bug.
+7. **Report Bug:** Click to report a bug.
-9. **Tutor:** Click any Tutor icon for more information about the section.
+8. **Tutor:** Click any Tutor icon for an "over the shoulder" overview.
-10. **Admin Dashboard:** Click to return to the Administrator Dashboard.
+9. **Logoff:** Click to log off of the Sim UI.
-11. **Logoff:** Click to log off of the Sim UI.
+10. **Avatar:** Click to upload your profile picture.
-12. **Avatar:** Click to upload your profile picture.
+11. **Session Start window:** You can either join the simulation session in progress or start a new one. Select the team data file you wish to use from the dropdown menu, then press GO!
-13. **Session Start window:** You can either join the simulation session in progress or start a new one. Select the team data file you wish to use from the dropdown menu, then press GO!
+12. **Experiment window:** This section allows you to delete, rename, export, and sort your team's simulation experiment results.
-14. **Experiment window:** This section allows you to delete, rename, export, and sort your team's simulation experiment results.
+13. **Team Data window:** This section allows you to delete, upload, and sort team data files (which will then show in the Start a Session window). Legacy team data files are located under the _MTL_ 3.0 gray bar.
-15. **Team Data window:** This section allows you to delete, upload, and sort team data files (which will then show in the Start a Session window). Legacy team data files are located under the _MTL_ 3.0 gray bar.
+14. **Dynamic Decision Dashboard:** Use this section to navigate between the 5 modules and their associated variables.
-16. **Dynamic Decision Dashboard:** Use this section to navigate between the 5 modules and their associated variables.
-
-17. **Community:** Click to give feedback to system administrators and participate in our _MTL_ Community of Practice.
+15. **Community:** Click to give feedback to system administrators and participate in our _MTL_ Community of Practice.
### Begin a Session in the Dynamic Decision Dashboard
@@ -361,7 +360,7 @@ Below is a basic orientation to the Home page of any team:
Beginning a session in the Dynamic Decision Dashboard (DDD) allows users to look at the stocks and flows across all five modules and helps determine which module(s) to focus on.
-1. Navigate to the selected team's Home page. If you aren't sure how, see [Navigate to the Home Page of Any Team](#navigate-to-the-home=page-of-any-team).
+1. Navigate to the selected team's Home page. If you aren't sure how, see [Navigate to the Home Page of Any Team](#navigate-to-the-home-page-of-any-team).
2. Select the desired team data file from the Please Select Team Data dropdown and click GO! A Learning Mode pop-up will appear.
@@ -377,7 +376,7 @@ Beginning a session in the Dynamic Decision Dashboard (DDD) allows users to look
- Existing Patients Return-to-Clinic Visit Interval (EPRVI) = learning mode "0".
- New Patient Start Rate (NPSR) = learning mode "1".
-- Refer to the Care Coordination (CCParams) or Medication Management (MMParams) tab of the Team Data Table at mtl.how/data, for data regarding the team’s New Patient Start Rates and Return-to-Clinic Intervals.
+- Refer to the Care Coordination (CCParams) or Medication Management (MMParams) tab of the Team Data Table at mtl.how/data, for data regarding the team’s New Patient Start Rates and Return-to-Clinic Visit Intervals.
#### Upload Team Data Files from the Home Page
@@ -433,25 +432,27 @@ Below is an orientation to the Dynamic Decision Dashboard.
- **1 - Feedback Loops**: Interactive diagrams that aid in visualizing how different variables in a system are causally interrelated. Clicking here will open a pop-up window that shows an associated loop diagram along with Causal Loop Dynamics selections.
-- **2 - Decision Meters**: A quick method to visualize the relevance or significance of different aspects within a group.
+- **2 - Flow**: Visualized in Sankey form, these diagrams help visualize the rate of flow into and out of stocks. A stock is a state of care in which patients can accumulate over time. Sankey is a type of flow diagram where the width of the arrows is proportional to the flow quantity.
+
+- **3 - Decision Meters**: A quick method to visualize the relevance or significance of different aspects within a group.
-- **3 - Episodes of Care**: Graphically shows evidence-based episode of care intervals to get a bird's eye view of how long the length of engagement will be.
+- **4 - Episodes of Care**: Graphically shows evidence-based episode of care intervals to get a bird's eye view of how long the length of engagement will be.
-- **4 - Play**: Enter the main Sim UI page to see the system story and run experiments.
+- **5 - Play**: Enter the main Sim UI page to see the system story and run experiments.
-- **5 - Team Data**: A quick link to the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface that will open in a new browser tab.
+- **6 - Team Data**: A quick link to the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface that will open in a new browser tab.
-- **6 - SAIL Data**: A quick link to Strategic Analytics for Improvement and Learning Value Model (SAIL), a system for summarizing hospital system performance within Veterans Health Administration (VHA). This will open in a new browser tab.
+- **7 - SAIL Data**: A quick link to Strategic Analytics for Improvement and Learning Value Model (SAIL), a system for summarizing hospital system performance within Veterans Health Administration (VHA). This will open in a new browser tab.
-5. **Services Radio Buttons**: Select desired service radio button to see stock values for specific services in Team Care (Intake, Care Coordination, Medication Management, Psychotherapy, Evidence-based Psychotherapy, Adjunctive Services, Group Therapy).
+5. **Learning Mode Labels**: Indicates which Learning Mode the data prioritizes. Click these buttons to change the learning modes directly from the DDD; the system will re-initialize based on the new learning mode selected. Existing Patients Return-to-Clinic Visit Interval (EPRVI) = learning mode "0" and New Patient Start Rate (NPSR) = learning mode "1".
-6. **Learning Mode Labels**: Indicates which Learning Mode the data prioritizes. Click these buttons to change the learning modes directly from the DDD; the system will re-initialize based on the new learning mode selected. Existing Patients Return-to-Clinic Visit Interval (EPRVI) = learning mode "0" and New Patient Start Rate (NPSR) = learning mode "1".
+6. **Team Care Services Radio Buttons**: Select desired service radio button to see stock values for specific services in Team Care (Intake, Care Coordination, Medication Management, Psychotherapy, Evidence-based Psychotherapy, Adjunctive Services, Group Therapy). The default display is Intake evaluations.
-7. **Meds Needed Radio Buttons**: Select desired meds needed radio button to see stock values for medication-specific services (Alcohol Use Disorder, Depression, Opioid Use Disorder, and Other).
+7. **Medication Management Services Radio Buttons**: Select desired service radio button to see stock values for medication-specific services in Medication Management (Alcohol Use Disorder, Depression, Opioid Use Disorder, and Other). The defaut display is Alcolol Use Disorder.
-8. **"i" icon**: Click these to read the definition of each stock label.
+8. **"i" icon**: Click "i" icons to read the definition of each stock label.
-9. **Setting Radio Buttons**: Select desired setting radio button to see stock values for setting-specific services in Team Flow (General Mental Health, Specialty Mental Health, Primary Care/Primary Care Mental Health Integration).
+9. **Team Flow Services Radio Buttons**: Select desired service radio button to see stock values for setting-specific services in Team Flow (General Mental Health, Specialty Mental Health, Primary Care/Primary Care Mental Health Integration). The default display is General Mental Health.
10. **Community**: Click here to participate by sharing an idea, letting the team know what you like, asking a question, or joining our community.
@@ -497,7 +498,7 @@ Each story has its own unique feedback loop that shows named balancing and reinf
Decision Meters are a quick infographic-based way to identify the highest leverage points and are highly supportive of clinical decision-making; they are for "decider" users who need systems thinking insights. The meters provide a visual interface that provides real-time feedback on ranges in our primary _MTL_ units of patients/week and appointments/week. The traffic light reflects the current state results and _recommendation_ of future state results. Through dialogue with decision-makers, consultants and field users manually input values into this graphic generator so the decision meters reflect the recommendations based on the alternative scenarios/experiments run by the learner. Decision meter numbers should be reflected in the "D" box of the Q/H/F/D outputs text field within the Sim UI, usually as ranges of numbers.
-- Care Decision Meters are for _MTL_ Blue teams only.
+- Care Decision Meters are for _MTL Blue_ teams only.
- Click within each decision meter to edit. Remember to click Save if you want the values to remain!
For illustrative purposes, the Medication Management Decisions window is used as an example below to orient you to general Decisions pop-up window features.
@@ -524,7 +525,7 @@ For illustrative purposes, the Medication Management Decisions window is used as
##### Episodes of Care
-Timely access to high-quality care includes improved understanding of dynamic tradeoffs in the return-to-clinic visit interval and engagement durations. The Episodes of Care pop-up is used to graphically show evidence-based episode of care intervals to get a bird's eye view of how long the length of engagement will be. Available within the Medication Management, Psychotherapy, and Team Care modules, this pop-up integrates engagement duration and Return-to-Clinic Visit Interval (RVI) for both Medication Management and Psychotherapy.
+Timely access to high-quality care includes improved understanding of dynamic tradeoffs in the Return-to-Clinic Visit Interval (RVI) and engagement durations. The Episodes of Care pop-up is used to graphically show evidence-based episode of care intervals to get a bird's eye view of how long the length of engagement will be. Available within the Medication Management, Psychotherapy, and Team Care modules, this pop-up integrates engagement duration and RVI for both Medication Management and Psychotherapy.
The following screenshot will orient you to general features of this pop-up.
@@ -562,7 +563,7 @@ This section explains how to enter and save an experiment in the Sim UI.
- **Note:** For CC and MM, select your Learning Mode before hitting Play.
- - Refer to the Care Coordination (CCParams) or Medication Management (MMParams) tab of the Team Data Table at mtl.how/data, for data regarding the team’s New Patient Start Rates and Return-to-Clinic Intervals.
+ - Refer to the Care Coordination (CCParams) or Medication Management (MMParams) tab of the Team Data Table at mtl.how/data, for data regarding the team’s New Patient Start Rates and Return-to-Clinic Visit Intervals.
3. To run a simulation for any module within the dashboard, select Play found within each module's More menu.
@@ -582,7 +583,7 @@ This section explains how to enter and save an experiment in the Sim UI.
#### Orient to the Sim UI
-**Tip:** Save this [Sim UI cheatsheet](https://github.com/lzim/mtl/blob/master/blue/session05/s05_learner/mtl_how_3.7_sim_ui_cheatsheet.pdf) to use when running an experiment.
+**Tip:** Save this [Sim UI cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/mtl_how_3.7_sim_ui_cheatsheet.pdf) to use when running an experiment.
Below is an orientation to the Play Page of the Sim UI.
@@ -606,40 +607,6 @@ Below is an orientation to the Play Page of the Sim UI.
- **9**: Text: Enter Q/H/F/Ds. Click on expand icon in blue bar for full functions.
-### Manage Discussions in Team
-
-- The Team button in the top navigation is for texting and maintaining private discussion threads with one or more individuals and open discussion threads with teams.
-- A person can chat with one or more people using the Team function by inputting the end user name (usually the va.gov email address) of the person or people they want to address.
-- A person can chat with an entire team at once, provided they are a registered end user in that team.
-
-#### Set up a Private Conversation
-
-1. Click "Team" to open the chat pop-up.
-
-
-1. **_MTL_ logo:** Click this logo on any page to return to this Home page.
-
-2. **Team Name:** The selected team name appears here. When logged into your individual world, team name = your name.
+1. **_MTL_ logo:** Click this logo to return to the Dynamic Decision Dashboard.
-3. **Home:** Click to return to this Home page.
+2. **Team Name:** The selected team name appears here with the world extension added at the end of its name. If you are logged in as an Administrator, you will see "Administrator" here.
-4. **Play:** Click to open the main Simulation User Interface (Sim UI) page.
+3. **Home:** Click to return to the Dynamic Decision Dashboard.
-5. **Team:** Click to chat with other team members. An alert will appear if you have unread chats waiting.
+4. **Play:** Click to return to the Play page.
-6. **More Info:** Click for answers to common _Modeling to Learn_ questions.
+5. **More Info:** Click for more information on how to use the Sim UI.
-7. **News:** Click for the latest news about _Modeling to Learn_. An alert will appear if you have unread news items.
+6. **News:** Click for the latest news about _Modeling to Learn_. An alert will appear if you have unread news items.
-8. **Report Bug:** Click to report a bug.
+7. **Report Bug:** Click to report a bug.
-9. **Tutor:** Click any Tutor icon for more information about the section.
+8. **Tutor:** Click any Tutor icon for an "over the shoulder" overview.
-10. **Admin Dashboard:** Click to return to the Administrator Dashboard.
+9. **Logoff:** Click to log off of the Sim UI.
-11. **Logoff:** Click to log off of the Sim UI.
+10. **Avatar:** Click to upload your profile picture.
-12. **Avatar:** Click to upload your profile picture.
+11. **Session Start window:** You can either join the simulation session in progress or start a new one. Select the team data file you wish to use from the dropdown menu, then press GO!
-13. **Session Start window:** You can either join the simulation session in progress or start a new one. Select the team data file you wish to use from the dropdown menu, then press GO!
+12. **Experiment window:** This section allows you to delete, rename, export, and sort your team's simulation experiment results.
-14. **Experiment window:** This section allows you to delete, rename, export, and sort your team's simulation experiment results.
+13. **Team Data window:** This section allows you to delete, upload, and sort team data files (which will then show in the Start a Session window). Legacy team data files are located under the _MTL_ 3.0 gray bar.
-15. **Team Data window:** This section allows you to delete, upload, and sort team data files (which will then show in the Start a Session window). Legacy team data files are located under the _MTL_ 3.0 gray bar.
+14. **Dynamic Decision Dashboard:** Use this section to navigate between the 5 modules and their associated variables.
-16. **Dynamic Decision Dashboard:** Use this section to navigate between the 5 modules and their associated variables.
-
-17. **Community:** Click to give feedback to system administrators and participate in our _MTL_ Community of Practice.
+15. **Community:** Click to give feedback to system administrators and participate in our _MTL_ Community of Practice.
### Begin a Session in the Dynamic Decision Dashboard
@@ -361,7 +360,7 @@ Below is a basic orientation to the Home page of any team:
Beginning a session in the Dynamic Decision Dashboard (DDD) allows users to look at the stocks and flows across all five modules and helps determine which module(s) to focus on.
-1. Navigate to the selected team's Home page. If you aren't sure how, see [Navigate to the Home Page of Any Team](#navigate-to-the-home=page-of-any-team).
+1. Navigate to the selected team's Home page. If you aren't sure how, see [Navigate to the Home Page of Any Team](#navigate-to-the-home-page-of-any-team).
2. Select the desired team data file from the Please Select Team Data dropdown and click GO! A Learning Mode pop-up will appear.
@@ -377,7 +376,7 @@ Beginning a session in the Dynamic Decision Dashboard (DDD) allows users to look
- Existing Patients Return-to-Clinic Visit Interval (EPRVI) = learning mode "0".
- New Patient Start Rate (NPSR) = learning mode "1".
-- Refer to the Care Coordination (CCParams) or Medication Management (MMParams) tab of the Team Data Table at mtl.how/data, for data regarding the team’s New Patient Start Rates and Return-to-Clinic Intervals.
+- Refer to the Care Coordination (CCParams) or Medication Management (MMParams) tab of the Team Data Table at mtl.how/data, for data regarding the team’s New Patient Start Rates and Return-to-Clinic Visit Intervals.
#### Upload Team Data Files from the Home Page
@@ -433,25 +432,27 @@ Below is an orientation to the Dynamic Decision Dashboard.
- **1 - Feedback Loops**: Interactive diagrams that aid in visualizing how different variables in a system are causally interrelated. Clicking here will open a pop-up window that shows an associated loop diagram along with Causal Loop Dynamics selections.
-- **2 - Decision Meters**: A quick method to visualize the relevance or significance of different aspects within a group.
+- **2 - Flow**: Visualized in Sankey form, these diagrams help visualize the rate of flow into and out of stocks. A stock is a state of care in which patients can accumulate over time. Sankey is a type of flow diagram where the width of the arrows is proportional to the flow quantity.
+
+- **3 - Decision Meters**: A quick method to visualize the relevance or significance of different aspects within a group.
-- **3 - Episodes of Care**: Graphically shows evidence-based episode of care intervals to get a bird's eye view of how long the length of engagement will be.
+- **4 - Episodes of Care**: Graphically shows evidence-based episode of care intervals to get a bird's eye view of how long the length of engagement will be.
-- **4 - Play**: Enter the main Sim UI page to see the system story and run experiments.
+- **5 - Play**: Enter the main Sim UI page to see the system story and run experiments.
-- **5 - Team Data**: A quick link to the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface that will open in a new browser tab.
+- **6 - Team Data**: A quick link to the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface that will open in a new browser tab.
-- **6 - SAIL Data**: A quick link to Strategic Analytics for Improvement and Learning Value Model (SAIL), a system for summarizing hospital system performance within Veterans Health Administration (VHA). This will open in a new browser tab.
+- **7 - SAIL Data**: A quick link to Strategic Analytics for Improvement and Learning Value Model (SAIL), a system for summarizing hospital system performance within Veterans Health Administration (VHA). This will open in a new browser tab.
-5. **Services Radio Buttons**: Select desired service radio button to see stock values for specific services in Team Care (Intake, Care Coordination, Medication Management, Psychotherapy, Evidence-based Psychotherapy, Adjunctive Services, Group Therapy).
+5. **Learning Mode Labels**: Indicates which Learning Mode the data prioritizes. Click these buttons to change the learning modes directly from the DDD; the system will re-initialize based on the new learning mode selected. Existing Patients Return-to-Clinic Visit Interval (EPRVI) = learning mode "0" and New Patient Start Rate (NPSR) = learning mode "1".
-6. **Learning Mode Labels**: Indicates which Learning Mode the data prioritizes. Click these buttons to change the learning modes directly from the DDD; the system will re-initialize based on the new learning mode selected. Existing Patients Return-to-Clinic Visit Interval (EPRVI) = learning mode "0" and New Patient Start Rate (NPSR) = learning mode "1".
+6. **Team Care Services Radio Buttons**: Select desired service radio button to see stock values for specific services in Team Care (Intake, Care Coordination, Medication Management, Psychotherapy, Evidence-based Psychotherapy, Adjunctive Services, Group Therapy). The default display is Intake evaluations.
-7. **Meds Needed Radio Buttons**: Select desired meds needed radio button to see stock values for medication-specific services (Alcohol Use Disorder, Depression, Opioid Use Disorder, and Other).
+7. **Medication Management Services Radio Buttons**: Select desired service radio button to see stock values for medication-specific services in Medication Management (Alcohol Use Disorder, Depression, Opioid Use Disorder, and Other). The defaut display is Alcolol Use Disorder.
-8. **"i" icon**: Click these to read the definition of each stock label.
+8. **"i" icon**: Click "i" icons to read the definition of each stock label.
-9. **Setting Radio Buttons**: Select desired setting radio button to see stock values for setting-specific services in Team Flow (General Mental Health, Specialty Mental Health, Primary Care/Primary Care Mental Health Integration).
+9. **Team Flow Services Radio Buttons**: Select desired service radio button to see stock values for setting-specific services in Team Flow (General Mental Health, Specialty Mental Health, Primary Care/Primary Care Mental Health Integration). The default display is General Mental Health.
10. **Community**: Click here to participate by sharing an idea, letting the team know what you like, asking a question, or joining our community.
@@ -497,7 +498,7 @@ Each story has its own unique feedback loop that shows named balancing and reinf
Decision Meters are a quick infographic-based way to identify the highest leverage points and are highly supportive of clinical decision-making; they are for "decider" users who need systems thinking insights. The meters provide a visual interface that provides real-time feedback on ranges in our primary _MTL_ units of patients/week and appointments/week. The traffic light reflects the current state results and _recommendation_ of future state results. Through dialogue with decision-makers, consultants and field users manually input values into this graphic generator so the decision meters reflect the recommendations based on the alternative scenarios/experiments run by the learner. Decision meter numbers should be reflected in the "D" box of the Q/H/F/D outputs text field within the Sim UI, usually as ranges of numbers.
-- Care Decision Meters are for _MTL_ Blue teams only.
+- Care Decision Meters are for _MTL Blue_ teams only.
- Click within each decision meter to edit. Remember to click Save if you want the values to remain!
For illustrative purposes, the Medication Management Decisions window is used as an example below to orient you to general Decisions pop-up window features.
@@ -524,7 +525,7 @@ For illustrative purposes, the Medication Management Decisions window is used as
##### Episodes of Care
-Timely access to high-quality care includes improved understanding of dynamic tradeoffs in the return-to-clinic visit interval and engagement durations. The Episodes of Care pop-up is used to graphically show evidence-based episode of care intervals to get a bird's eye view of how long the length of engagement will be. Available within the Medication Management, Psychotherapy, and Team Care modules, this pop-up integrates engagement duration and Return-to-Clinic Visit Interval (RVI) for both Medication Management and Psychotherapy.
+Timely access to high-quality care includes improved understanding of dynamic tradeoffs in the Return-to-Clinic Visit Interval (RVI) and engagement durations. The Episodes of Care pop-up is used to graphically show evidence-based episode of care intervals to get a bird's eye view of how long the length of engagement will be. Available within the Medication Management, Psychotherapy, and Team Care modules, this pop-up integrates engagement duration and RVI for both Medication Management and Psychotherapy.
The following screenshot will orient you to general features of this pop-up.
@@ -562,7 +563,7 @@ This section explains how to enter and save an experiment in the Sim UI.
- **Note:** For CC and MM, select your Learning Mode before hitting Play.
- - Refer to the Care Coordination (CCParams) or Medication Management (MMParams) tab of the Team Data Table at mtl.how/data, for data regarding the team’s New Patient Start Rates and Return-to-Clinic Intervals.
+ - Refer to the Care Coordination (CCParams) or Medication Management (MMParams) tab of the Team Data Table at mtl.how/data, for data regarding the team’s New Patient Start Rates and Return-to-Clinic Visit Intervals.
3. To run a simulation for any module within the dashboard, select Play found within each module's More menu.
@@ -582,7 +583,7 @@ This section explains how to enter and save an experiment in the Sim UI.
#### Orient to the Sim UI
-**Tip:** Save this [Sim UI cheatsheet](https://github.com/lzim/mtl/blob/master/blue/session05/s05_learner/mtl_how_3.7_sim_ui_cheatsheet.pdf) to use when running an experiment.
+**Tip:** Save this [Sim UI cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/mtl_how_3.7_sim_ui_cheatsheet.pdf) to use when running an experiment.
Below is an orientation to the Play Page of the Sim UI.
@@ -606,40 +607,6 @@ Below is an orientation to the Play Page of the Sim UI.
- **9**: Text: Enter Q/H/F/Ds. Click on expand icon in blue bar for full functions.
-### Manage Discussions in Team
-
-- The Team button in the top navigation is for texting and maintaining private discussion threads with one or more individuals and open discussion threads with teams.
-- A person can chat with one or more people using the Team function by inputting the end user name (usually the va.gov email address) of the person or people they want to address.
-- A person can chat with an entire team at once, provided they are a registered end user in that team.
-
-#### Set up a Private Conversation
-
-1. Click "Team" to open the chat pop-up.
-
- -
-2. Click Chat in the left-hand navigation to private-text an individual. The latest conversation will appear in the Chat Log, followed the next recent. The discussion thread appears in the Conversation window.
-
-
-
-2. Click Chat in the left-hand navigation to private-text an individual. The latest conversation will appear in the Chat Log, followed the next recent. The discussion thread appears in the Conversation window.
-
- -
-3. To continue a conversation, type a new message in the message line at the bottom of the window. Click the Send icon to post the chat.
-
-
-
-3. To continue a conversation, type a new message in the message line at the bottom of the window. Click the Send icon to post the chat.
-
- -
-4. To start a conversation with one or more new people, click the New icon and enter their user name and click Add. Type a new message and click Send.
-
-
-
-4. To start a conversation with one or more new people, click the New icon and enter their user name and click Add. Type a new message and click Send.
-
- -
-#### Set up an Open Team Discussion
-
-1. Click on the Team icon in the left-hand navigation. **Note how the icon has a red circle indicating there are 2 chats waiting.**
-
-
-
-#### Set up an Open Team Discussion
-
-1. Click on the Team icon in the left-hand navigation. **Note how the icon has a red circle indicating there are 2 chats waiting.**
-
- -
-2. The Teams listing will contain a list of all teams the individual is a registered end user (see blue-green highlight). A boldface team indicates a chat is waiting. **Note the listing contains _ind teams. These are teams where users are assigned an individual world with which to experiment. However, any discussions held in this thread will be visible by all registered users from their different worlds.** To have a private chat with an individual, see [Set up a Private Conversation](#set-up-a-private-conversation).
-
-
-
-2. The Teams listing will contain a list of all teams the individual is a registered end user (see blue-green highlight). A boldface team indicates a chat is waiting. **Note the listing contains _ind teams. These are teams where users are assigned an individual world with which to experiment. However, any discussions held in this thread will be visible by all registered users from their different worlds.** To have a private chat with an individual, see [Set up a Private Conversation](#set-up-a-private-conversation).
-
- -
### Resize a Window for Side-by-Side Viewing
- An administrator may need to show two items on the screen side-by-side for comparison. Field users may also want to view two items on the screen for comparison or reference.
@@ -673,7 +640,7 @@ Below is an orientation to the Play Page of the Sim UI.
-
### Resize a Window for Side-by-Side Viewing
- An administrator may need to show two items on the screen side-by-side for comparison. Field users may also want to view two items on the screen for comparison or reference.
@@ -673,7 +640,7 @@ Below is an orientation to the Play Page of the Sim UI.
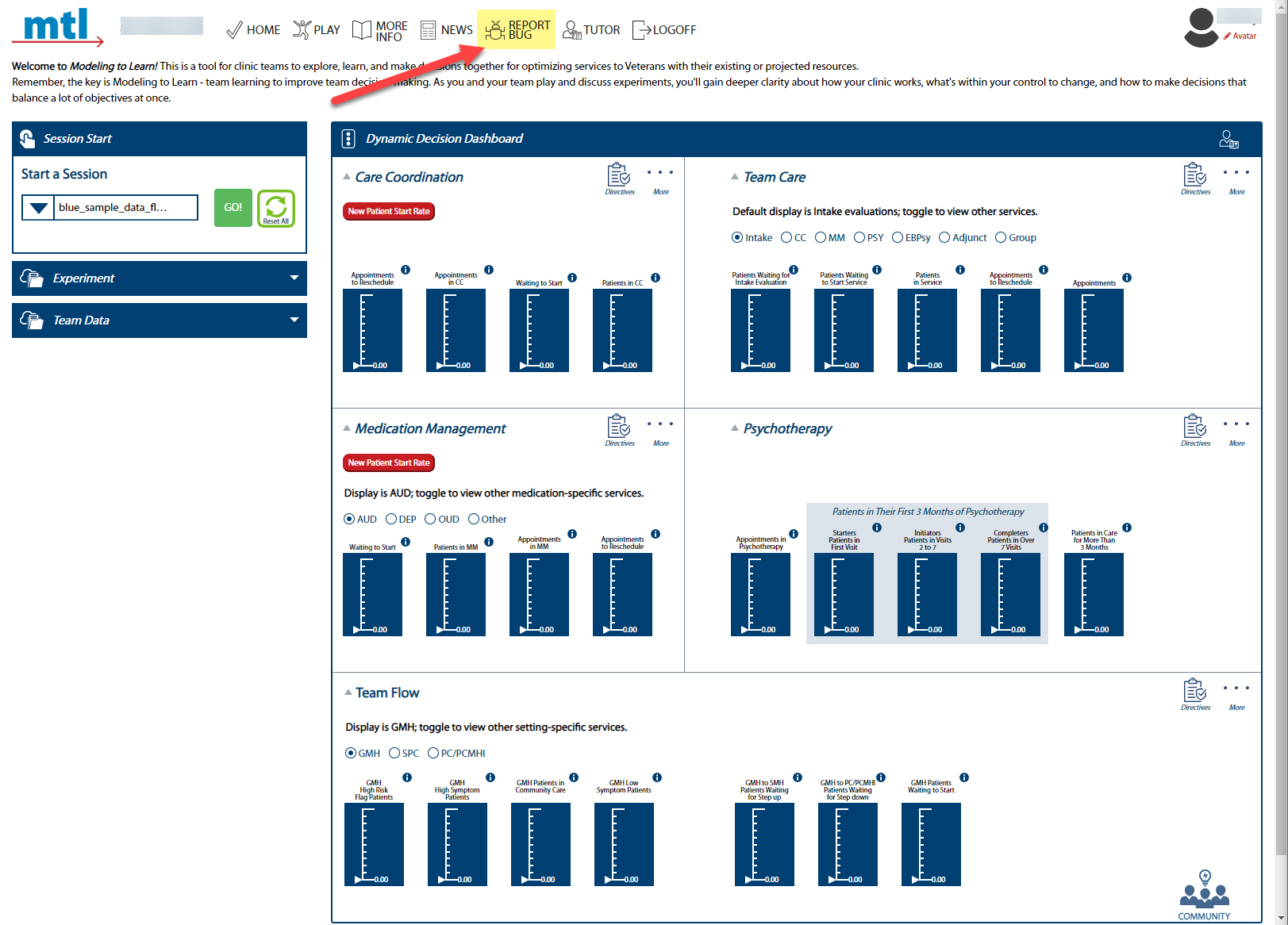 -2. Describe the issue in the field provided (please be detailed as possible). **Do not include PII or other Site identifiable information. Instead, use generic language such as “_MTL_ Blue live team on Mondays at 9am.”** If you have a screenshot you want to share, click the checkbox.
+2. Describe the issue in the field provided (please be detailed as possible). **Do not include PII or other Site identifiable information. Instead, use generic language such as “_MTL Blue_ live team on Mondays at 9am.”** If you have a screenshot you want to share, click the checkbox.
-2. Describe the issue in the field provided (please be detailed as possible). **Do not include PII or other Site identifiable information. Instead, use generic language such as “_MTL_ Blue live team on Mondays at 9am.”** If you have a screenshot you want to share, click the checkbox.
+2. Describe the issue in the field provided (please be detailed as possible). **Do not include PII or other Site identifiable information. Instead, use generic language such as “_MTL Blue_ live team on Mondays at 9am.”** If you have a screenshot you want to share, click the checkbox.
 @@ -695,7 +662,7 @@ Below is an orientation to the Play Page of the Sim UI.
@@ -695,7 +662,7 @@ Below is an orientation to the Play Page of the Sim UI.
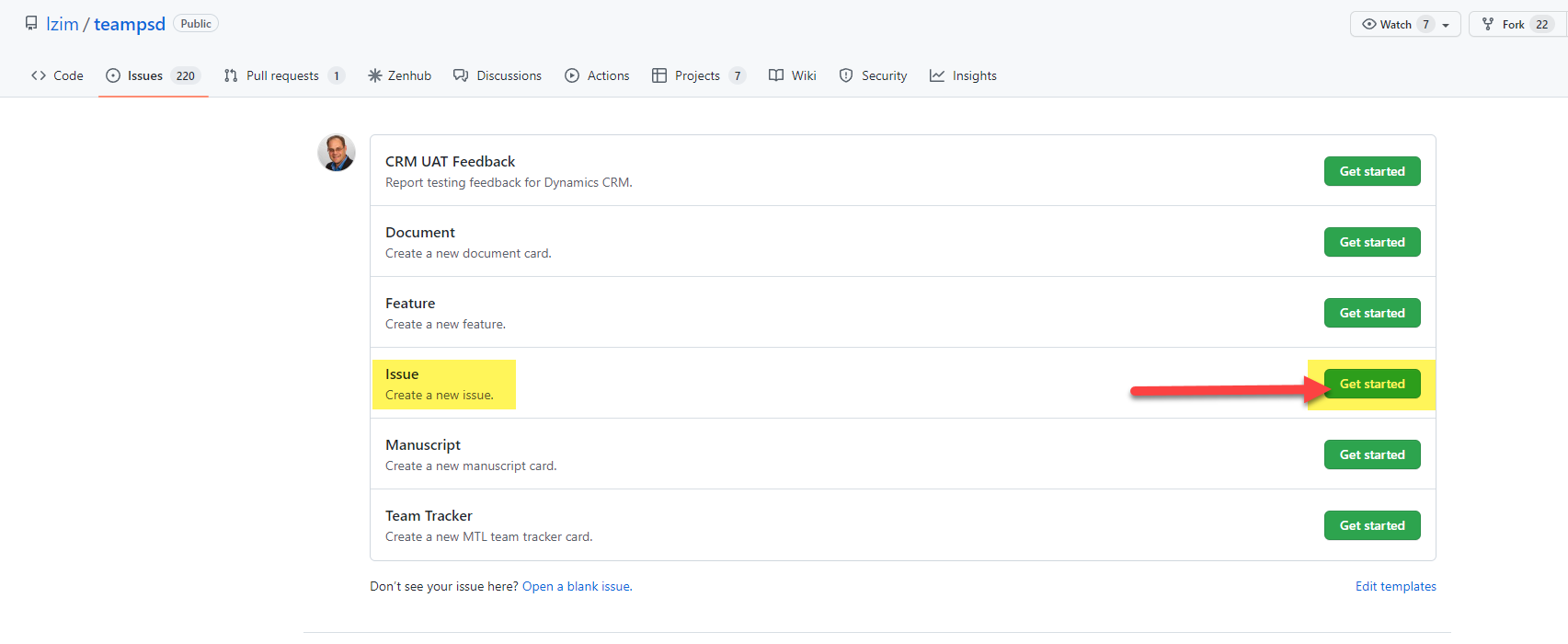 -4. Complete the Issue Form. **Do not include PII or other Site identifiable information. Instead, use generic language such as “_MTL_ Blue live team on Mondays at 9am.”**
+4. Complete the Issue Form. **Do not include PII or other Site identifiable information. Instead, use generic language such as “_MTL Blue_ live team on Mondays at 9am.”**
-4. Complete the Issue Form. **Do not include PII or other Site identifiable information. Instead, use generic language such as “_MTL_ Blue live team on Mondays at 9am.”**
+4. Complete the Issue Form. **Do not include PII or other Site identifiable information. Instead, use generic language such as “_MTL Blue_ live team on Mondays at 9am.”**
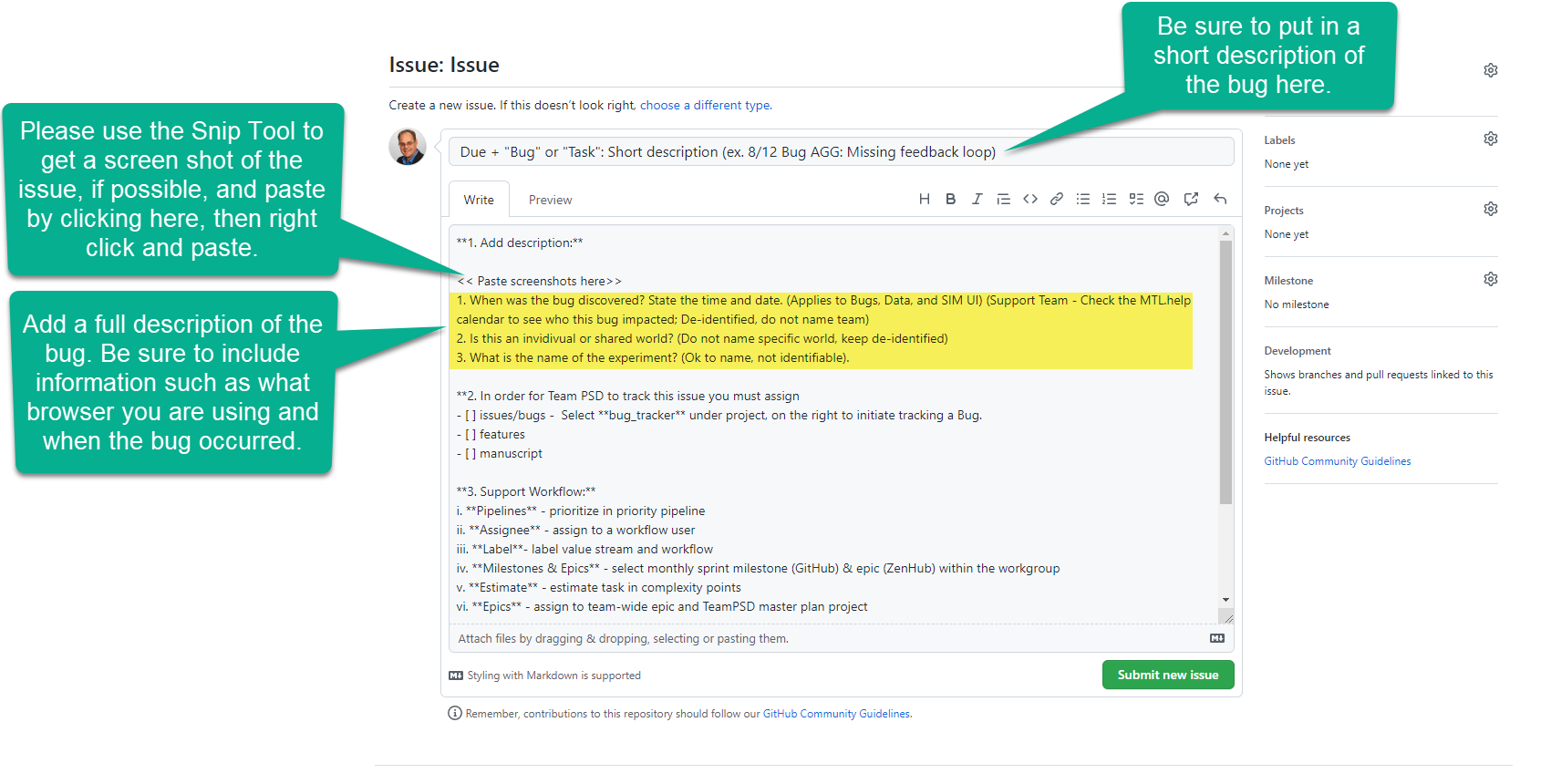 @@ -869,7 +836,7 @@ Within the Facility Team Setup area of this pop-up, several team setup options a
### Manage Team Data
-**Note: Only administrators and the internal team have access to these functions.** Field users can upload their data file(s) from the Dynamic Decision Dashboard (as well as administrators and the internal team). Field users should refer to the [Dynamic Decision Dashboard manual section](#dynamic-decision-dasboard).
+**Note: Only administrators and the internal team have access to these functions.** Field users can upload their data file(s) from the Dynamic Decision Dashboard (as well as administrators and the internal team). Field users should refer to the [Dynamic Decision Dashboard section](#dynamic-decision-dashboard).
- Administrators can upload team data files and assign that file(s) to team(s) of their choice.
@@ -1133,7 +1100,7 @@ Forio Epicenter is an enterprise platform that hosts our Sim UI and runs the sim
#### Send Password Reset to End User or Change Password
-1. Log into Epicenter.
+1. Log into [Epicenter](https://forio.com/epicenter/sign-in).
2. Click on Veterans Affairs.
@@ -869,7 +836,7 @@ Within the Facility Team Setup area of this pop-up, several team setup options a
### Manage Team Data
-**Note: Only administrators and the internal team have access to these functions.** Field users can upload their data file(s) from the Dynamic Decision Dashboard (as well as administrators and the internal team). Field users should refer to the [Dynamic Decision Dashboard manual section](#dynamic-decision-dasboard).
+**Note: Only administrators and the internal team have access to these functions.** Field users can upload their data file(s) from the Dynamic Decision Dashboard (as well as administrators and the internal team). Field users should refer to the [Dynamic Decision Dashboard section](#dynamic-decision-dashboard).
- Administrators can upload team data files and assign that file(s) to team(s) of their choice.
@@ -1133,7 +1100,7 @@ Forio Epicenter is an enterprise platform that hosts our Sim UI and runs the sim
#### Send Password Reset to End User or Change Password
-1. Log into Epicenter.
+1. Log into [Epicenter](https://forio.com/epicenter/sign-in).
2. Click on Veterans Affairs.
 diff --git a/index.Rmd b/index.Rmd
index d0e050da..f0a6eaae 100644
--- a/index.Rmd
+++ b/index.Rmd
@@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
---
-title: "_Modeling to Learn_ 3.7 Consult Manual"
+title: "_Modeling to Learn 3.7 Consult Manual_"
author: "Team PSD"
date: "`r Sys.Date()`"
link-citations: yes
preview: yes
site: bookdown::bookdown_site
-description: This is the MTL one-stop shop.
+description: This is the _MTL_ one-stop shop.
---
# _Why_ use _Modeling to Learn_
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. You might wonder _What is _Modeling to Learn
[
diff --git a/index.Rmd b/index.Rmd
index d0e050da..f0a6eaae 100644
--- a/index.Rmd
+++ b/index.Rmd
@@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
---
-title: "_Modeling to Learn_ 3.7 Consult Manual"
+title: "_Modeling to Learn 3.7 Consult Manual_"
author: "Team PSD"
date: "`r Sys.Date()`"
link-citations: yes
preview: yes
site: bookdown::bookdown_site
-description: This is the MTL one-stop shop.
+description: This is the _MTL_ one-stop shop.
---
# _Why_ use _Modeling to Learn_
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. You might wonder _What is _Modeling to Learn
[ ](https://bcove.video/3WuJ7kI)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. _Modeling to Learn_ improves visibility and provides new insights into how common care problems persist over time. How? _Modeling to Learn_ is based on over 60 years of scholarship known as participatory system dynamics. For this reason, we call ourselves Team PSD for Team Participatory System Dynamics. The Data User Interface and Simulation User Interface comprise two versions of _Modeling to Learn_. The data-only version is known as _Modeling to Learn_ Red; _Modeling to Learn_ Blue ads participatory learning from simulation. Team PSD supports _MTL_ Red and _MTL_ Blue and is carefully evaluating how each works to support VA in meeting Veterans needs. Learning from simulation can help us to place a better initial bet on what is likely to work locally by evaluating alternative decisions via simulation before we implement them in the real world. _MTL_ Red tells us where we've been over the last two years based on the clinic selections made to produce the patient data reports and team trends or visualizations. Many staff report that viewing the Data UI real-time patient data tabs or the team trends is efficient and encouraging. The data tabs help with clinical decision making. The visualizations of team trends provide leading indicators that improvement efforts are paying off, which can be validating. Why is _Modeling to Learn_ useful when we have critical staffing and hiring needs? Watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. _Modeling to Learn_ improves visibility and provides new insights into how common care problems persist over time. How? _Modeling to Learn_ is based on over 60 years of scholarship known as participatory system dynamics. For this reason, we call ourselves Team PSD for Team Participatory System Dynamics. The Data User Interface and Simulation User Interface comprise two versions of _Modeling to Learn_. The data-only version is known as _Modeling to Learn Red_; _Modeling to Learn Blue_ ads participatory learning from simulation. Team PSD supports _MTL Red_ and _MTL Blue_ and is carefully evaluating how each works to support VA in meeting Veterans needs. Learning from simulation can help us to place a better initial bet on what is likely to work locally by evaluating alternative decisions via simulation before we implement them in the real world. _MTL Red_ tells us where we've been over the last two years based on the clinic selections made to produce the patient data reports and team trends or visualizations. Many staff report that viewing the Data UI real-time patient data tabs or the team trends is efficient and encouraging. The data tabs help with clinical decision making. The visualizations of team trends provide leading indicators that improvement efforts are paying off, which can be validating. Why is _Modeling to Learn_ useful when we have critical staffing and hiring needs? Watch that video to find out.
## What gets in the way of meeting patients' needs?
@@ -49,23 +49,23 @@ Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. What if we keep making the same care decisio
[
](https://bcove.video/3WuJ7kI)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. _Modeling to Learn_ improves visibility and provides new insights into how common care problems persist over time. How? _Modeling to Learn_ is based on over 60 years of scholarship known as participatory system dynamics. For this reason, we call ourselves Team PSD for Team Participatory System Dynamics. The Data User Interface and Simulation User Interface comprise two versions of _Modeling to Learn_. The data-only version is known as _Modeling to Learn_ Red; _Modeling to Learn_ Blue ads participatory learning from simulation. Team PSD supports _MTL_ Red and _MTL_ Blue and is carefully evaluating how each works to support VA in meeting Veterans needs. Learning from simulation can help us to place a better initial bet on what is likely to work locally by evaluating alternative decisions via simulation before we implement them in the real world. _MTL_ Red tells us where we've been over the last two years based on the clinic selections made to produce the patient data reports and team trends or visualizations. Many staff report that viewing the Data UI real-time patient data tabs or the team trends is efficient and encouraging. The data tabs help with clinical decision making. The visualizations of team trends provide leading indicators that improvement efforts are paying off, which can be validating. Why is _Modeling to Learn_ useful when we have critical staffing and hiring needs? Watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. _Modeling to Learn_ improves visibility and provides new insights into how common care problems persist over time. How? _Modeling to Learn_ is based on over 60 years of scholarship known as participatory system dynamics. For this reason, we call ourselves Team PSD for Team Participatory System Dynamics. The Data User Interface and Simulation User Interface comprise two versions of _Modeling to Learn_. The data-only version is known as _Modeling to Learn Red_; _Modeling to Learn Blue_ ads participatory learning from simulation. Team PSD supports _MTL Red_ and _MTL Blue_ and is carefully evaluating how each works to support VA in meeting Veterans needs. Learning from simulation can help us to place a better initial bet on what is likely to work locally by evaluating alternative decisions via simulation before we implement them in the real world. _MTL Red_ tells us where we've been over the last two years based on the clinic selections made to produce the patient data reports and team trends or visualizations. Many staff report that viewing the Data UI real-time patient data tabs or the team trends is efficient and encouraging. The data tabs help with clinical decision making. The visualizations of team trends provide leading indicators that improvement efforts are paying off, which can be validating. Why is _Modeling to Learn_ useful when we have critical staffing and hiring needs? Watch that video to find out.
## What gets in the way of meeting patients' needs?
@@ -49,23 +49,23 @@ Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. What if we keep making the same care decisio
[ ](https://bcove.video/4f7OfSL)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Leaders and clinicians often ask how can _Modeling to Learn_ be useful when facing critical staffing and hiring needs? With limited staff coverage, the need to hire is priority number one, but even then there isn't a magic wand that produces staff where they may not exist today. What could help now? From the beginning, _Modeling to Learn_ prioritized evidence-based episodes of care within existing staff time. When modeling to learn launched nationally in the VA in March of 2020, it was to empower staff to find the highest yield local improvements without asking staff to do more with less. As a result, when staff coverage may not change quickly, _Modeling to Learn_ will find options for improving quality of care for Veterans and quality of work life for providers. How? What does Debbie mean by high yield local improvements? Because evidence-based behavioral healthcare is delivered over time, there are many possibilities. Small decisions made all day, every day by the clinicians, when compounded over time, can be surprisingly powerful. Think of your savings account or your waistline. In _Modeling to Learn_, we look for the lightest clinical lift teams and VAs can make that have the biggest payoff for Veterans in terms of timely, high-quality care. We work hard to avoid big difficult changes with limited benefit. When working with the _Modeling to Learn_-read data user interface, clinical teams are often motivated when they see trends that reflect hard-won efforts to implement high quality episodes of care which may not show up in other data systems for some time. The _Modeling to Learn_ Blue simulation user interface saves staff time because alternatives can quickly be assessed during a modeling consultation. Change is hard, but we no longer have to learn by trial and error, wearing out already burdened staff. Does that sound too good to be true? If so, you may be wondering about examples of _Modeling to Learn_ use cases for the pain points you face in your specific team or program. As an example, how does _Modeling to Learn_ benefit substance use disorder, or SUD programs? Watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Leaders and clinicians often ask how can _Modeling to Learn_ be useful when facing critical staffing and hiring needs? With limited staff coverage, the need to hire is priority number one, but even then there isn't a magic wand that produces staff where they may not exist today. What could help now? From the beginning, _Modeling to Learn_ prioritized evidence-based episodes of care within existing staff time. When _Modeling to Learn_ launched nationally in the VA in March of 2020, it was to empower staff to find the highest yield local improvements without asking staff to do more with less. As a result, when staff coverage may not change quickly, _Modeling to Learn_ will find options for improving quality of care for Veterans and quality of work life for providers. How? What does Debbie mean by high yield local improvements? Because evidence-based behavioral healthcare is delivered over time, there are many possibilities. Small decisions made all day, every day by the clinicians, when compounded over time, can be surprisingly powerful. Think of your savings account or your waistline. In _Modeling to Learn_, we look for the lightest clinical lift teams and VAs can make that have the biggest payoff for Veterans in terms of timely, high-quality care. We work hard to avoid big difficult changes with limited benefit. When working with the _Modeling to Learn_-read data user interface, clinical teams are often motivated when they see trends that reflect hard-won efforts to implement high quality episodes of care which may not show up in other data systems for some time. The _Modeling to Learn Blue_ simulation user interface saves staff time because alternatives can quickly be assessed during a modeling consultation. Change is hard, but we no longer have to learn by trial and error, wearing out already burdened staff. Does that sound too good to be true? If so, you may be wondering about examples of _Modeling to Learn_ use cases for the pain points you face in your specific team or program. As an example, how does _Modeling to Learn_ benefit substance use disorder, or SUD programs? Watch that video to find out.
-## Why is the _MTL_ Red Data User Interface useful?
+## Why is the _MTL Red_ Data User Interface useful?
[Watch the video here.](https://bcove.video/3A6i7Py)
[
](https://bcove.video/4f7OfSL)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Leaders and clinicians often ask how can _Modeling to Learn_ be useful when facing critical staffing and hiring needs? With limited staff coverage, the need to hire is priority number one, but even then there isn't a magic wand that produces staff where they may not exist today. What could help now? From the beginning, _Modeling to Learn_ prioritized evidence-based episodes of care within existing staff time. When modeling to learn launched nationally in the VA in March of 2020, it was to empower staff to find the highest yield local improvements without asking staff to do more with less. As a result, when staff coverage may not change quickly, _Modeling to Learn_ will find options for improving quality of care for Veterans and quality of work life for providers. How? What does Debbie mean by high yield local improvements? Because evidence-based behavioral healthcare is delivered over time, there are many possibilities. Small decisions made all day, every day by the clinicians, when compounded over time, can be surprisingly powerful. Think of your savings account or your waistline. In _Modeling to Learn_, we look for the lightest clinical lift teams and VAs can make that have the biggest payoff for Veterans in terms of timely, high-quality care. We work hard to avoid big difficult changes with limited benefit. When working with the _Modeling to Learn_-read data user interface, clinical teams are often motivated when they see trends that reflect hard-won efforts to implement high quality episodes of care which may not show up in other data systems for some time. The _Modeling to Learn_ Blue simulation user interface saves staff time because alternatives can quickly be assessed during a modeling consultation. Change is hard, but we no longer have to learn by trial and error, wearing out already burdened staff. Does that sound too good to be true? If so, you may be wondering about examples of _Modeling to Learn_ use cases for the pain points you face in your specific team or program. As an example, how does _Modeling to Learn_ benefit substance use disorder, or SUD programs? Watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Leaders and clinicians often ask how can _Modeling to Learn_ be useful when facing critical staffing and hiring needs? With limited staff coverage, the need to hire is priority number one, but even then there isn't a magic wand that produces staff where they may not exist today. What could help now? From the beginning, _Modeling to Learn_ prioritized evidence-based episodes of care within existing staff time. When _Modeling to Learn_ launched nationally in the VA in March of 2020, it was to empower staff to find the highest yield local improvements without asking staff to do more with less. As a result, when staff coverage may not change quickly, _Modeling to Learn_ will find options for improving quality of care for Veterans and quality of work life for providers. How? What does Debbie mean by high yield local improvements? Because evidence-based behavioral healthcare is delivered over time, there are many possibilities. Small decisions made all day, every day by the clinicians, when compounded over time, can be surprisingly powerful. Think of your savings account or your waistline. In _Modeling to Learn_, we look for the lightest clinical lift teams and VAs can make that have the biggest payoff for Veterans in terms of timely, high-quality care. We work hard to avoid big difficult changes with limited benefit. When working with the _Modeling to Learn_-read data user interface, clinical teams are often motivated when they see trends that reflect hard-won efforts to implement high quality episodes of care which may not show up in other data systems for some time. The _Modeling to Learn Blue_ simulation user interface saves staff time because alternatives can quickly be assessed during a modeling consultation. Change is hard, but we no longer have to learn by trial and error, wearing out already burdened staff. Does that sound too good to be true? If so, you may be wondering about examples of _Modeling to Learn_ use cases for the pain points you face in your specific team or program. As an example, how does _Modeling to Learn_ benefit substance use disorder, or SUD programs? Watch that video to find out.
-## Why is the _MTL_ Red Data User Interface useful?
+## Why is the _MTL Red_ Data User Interface useful?
[Watch the video here.](https://bcove.video/3A6i7Py)
[ ](https://bcove.video/3A6i7Py)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Why is _Modeling to Learn_ Red useful and how does the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface provide new insights? The primary value of _MTL_ Red is its power to efficiently query the VA Corporate Data Warehouse directly, and we've come a long way over the years. Yes we have. When we first began, we were using an Excel workbook so that frontline teams could carefully review the clinic selections that define their _Modeling to Learn_ team data sets. Fast forward to the present and now teams have real time data available to them from within the VA domain from any computer with PIV badge access. Since the Data UI includes PHI, if you go to [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf), you will be able to see the same data you have permissions to access in the electronic health record. But given that clinicians, managers, data leads, quality improvement staff, evaluators … well, basically everyone is so busy, no one has time to review another data dashboard unless it offers something of really high value that distinguishes it from other resources. When you request a _Modeling to Learn_ Red consultation, we work with your team or VA to explore care data that can address your locally identified priority. Clinics or scheduling grids are often changing. For that reason, we wanted a user interface where clinic selections can include active or inactive clinics over the last two years. That way, the team can filter the information to find the most appropriate clinics to include in their data set to gain new insights. And in Team Flow, clinic selections can be used to evaluate transitions between an episode of care in one team and the start of another episode of care in a higher or lower intensity care setting. _Modeling to Learn_ Red also enables zooming in to check on the care of an individual patient at the start of the clinical day or during case reviews at a team meeting. But with the _MTL_ Red Data User Interface, you can also zoom out to view teen care trends, bringing patient-level care coordination and trend-level process improvement decisions together. And that's where things start to get interesting. Based on the clinic selections, the next set of tabs to find local data values for common care problems, including care coordination, psychotherapy, medication management, team care, and team flow. Each tab features simple definitions of how data were estimated for the common care problem. Detailed definitions with technical specifications are also provided to allow valid comparison of these data to other VA dashboards. That said, a focus on data details could be frustrating and add limited value. _Modeling to Learn_ emphasizes understanding system problems in care flow over time. These care flow problems can be defined accurately with just five key time-based variables that drive care quality. How do five key variables drive care quality? Watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Why is _Modeling to Learn Red_ useful and how does the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface provide new insights? The primary value of _MTL_ Red is its power to efficiently query the VA Corporate Data Warehouse directly, and we've come a long way over the years. Yes we have. When we first began, we were using an Excel workbook so that frontline teams could carefully review the clinic selections that define their _Modeling to Learn_ team data sets. Fast forward to the present and now teams have real time data available to them from within the VA domain from any computer with PIV badge access. Since the Data UI includes PHI, if you go to [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf), you will be able to see the same data you have permissions to access in the electronic health record. But given that clinicians, managers, data leads, quality improvement staff, evaluators … well, basically everyone is so busy, no one has time to review another data dashboard unless it offers something of really high value that distinguishes it from other resources. When you request a _Modeling to Learn Red_ consultation, we work with your team or VA to explore care data that can address your locally identified priority. Clinics or scheduling grids are often changing. For that reason, we wanted a user interface where clinic selections can include active or inactive clinics over the last two years. That way, the team can filter the information to find the most appropriate clinics to include in their data set to gain new insights. And in Team Flow, clinic selections can be used to evaluate transitions between an episode of care in one team and the start of another episode of care in a higher or lower intensity care setting. _Modeling to Learn Red_ also enables zooming in to check on the care of an individual patient at the start of the clinical day or during case reviews at a team meeting. But with the _MTL_ Red Data User Interface, you can also zoom out to view teen care trends, bringing patient-level care coordination and trend-level process improvement decisions together. And that's where things start to get interesting. Based on the clinic selections, the next set of tabs to find local data values for common care problems, including care coordination, psychotherapy, medication management, team care, and team flow. Each tab features simple definitions of how data were estimated for the common care problem. Detailed definitions with technical specifications are also provided to allow valid comparison of these data to other VA dashboards. That said, a focus on data details could be frustrating and add limited value. _Modeling to Learn_ emphasizes understanding system problems in care flow over time. These care flow problems can be defined accurately with just five key time-based variables that drive care quality. How do five key variables drive care quality? Watch that video to find out.
-## Why is the _MTL_ Blue Simulation User Interface useful?
+## Why is the _MTL Blue_ Simulation User Interface useful?
[Watch the video here.](https://bcove.video/4fnG5Gb)
[
](https://bcove.video/3A6i7Py)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Why is _Modeling to Learn_ Red useful and how does the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface provide new insights? The primary value of _MTL_ Red is its power to efficiently query the VA Corporate Data Warehouse directly, and we've come a long way over the years. Yes we have. When we first began, we were using an Excel workbook so that frontline teams could carefully review the clinic selections that define their _Modeling to Learn_ team data sets. Fast forward to the present and now teams have real time data available to them from within the VA domain from any computer with PIV badge access. Since the Data UI includes PHI, if you go to [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf), you will be able to see the same data you have permissions to access in the electronic health record. But given that clinicians, managers, data leads, quality improvement staff, evaluators … well, basically everyone is so busy, no one has time to review another data dashboard unless it offers something of really high value that distinguishes it from other resources. When you request a _Modeling to Learn_ Red consultation, we work with your team or VA to explore care data that can address your locally identified priority. Clinics or scheduling grids are often changing. For that reason, we wanted a user interface where clinic selections can include active or inactive clinics over the last two years. That way, the team can filter the information to find the most appropriate clinics to include in their data set to gain new insights. And in Team Flow, clinic selections can be used to evaluate transitions between an episode of care in one team and the start of another episode of care in a higher or lower intensity care setting. _Modeling to Learn_ Red also enables zooming in to check on the care of an individual patient at the start of the clinical day or during case reviews at a team meeting. But with the _MTL_ Red Data User Interface, you can also zoom out to view teen care trends, bringing patient-level care coordination and trend-level process improvement decisions together. And that's where things start to get interesting. Based on the clinic selections, the next set of tabs to find local data values for common care problems, including care coordination, psychotherapy, medication management, team care, and team flow. Each tab features simple definitions of how data were estimated for the common care problem. Detailed definitions with technical specifications are also provided to allow valid comparison of these data to other VA dashboards. That said, a focus on data details could be frustrating and add limited value. _Modeling to Learn_ emphasizes understanding system problems in care flow over time. These care flow problems can be defined accurately with just five key time-based variables that drive care quality. How do five key variables drive care quality? Watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Why is _Modeling to Learn Red_ useful and how does the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface provide new insights? The primary value of _MTL_ Red is its power to efficiently query the VA Corporate Data Warehouse directly, and we've come a long way over the years. Yes we have. When we first began, we were using an Excel workbook so that frontline teams could carefully review the clinic selections that define their _Modeling to Learn_ team data sets. Fast forward to the present and now teams have real time data available to them from within the VA domain from any computer with PIV badge access. Since the Data UI includes PHI, if you go to [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf), you will be able to see the same data you have permissions to access in the electronic health record. But given that clinicians, managers, data leads, quality improvement staff, evaluators … well, basically everyone is so busy, no one has time to review another data dashboard unless it offers something of really high value that distinguishes it from other resources. When you request a _Modeling to Learn Red_ consultation, we work with your team or VA to explore care data that can address your locally identified priority. Clinics or scheduling grids are often changing. For that reason, we wanted a user interface where clinic selections can include active or inactive clinics over the last two years. That way, the team can filter the information to find the most appropriate clinics to include in their data set to gain new insights. And in Team Flow, clinic selections can be used to evaluate transitions between an episode of care in one team and the start of another episode of care in a higher or lower intensity care setting. _Modeling to Learn Red_ also enables zooming in to check on the care of an individual patient at the start of the clinical day or during case reviews at a team meeting. But with the _MTL_ Red Data User Interface, you can also zoom out to view teen care trends, bringing patient-level care coordination and trend-level process improvement decisions together. And that's where things start to get interesting. Based on the clinic selections, the next set of tabs to find local data values for common care problems, including care coordination, psychotherapy, medication management, team care, and team flow. Each tab features simple definitions of how data were estimated for the common care problem. Detailed definitions with technical specifications are also provided to allow valid comparison of these data to other VA dashboards. That said, a focus on data details could be frustrating and add limited value. _Modeling to Learn_ emphasizes understanding system problems in care flow over time. These care flow problems can be defined accurately with just five key time-based variables that drive care quality. How do five key variables drive care quality? Watch that video to find out.
-## Why is the _MTL_ Blue Simulation User Interface useful?
+## Why is the _MTL Blue_ Simulation User Interface useful?
[Watch the video here.](https://bcove.video/4fnG5Gb)
[ ](https://bcove.video/4fnG5Gb)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Why is _Modeling to Learn_ Blue useful? Well, why is it wisest to focus on the dynamics of care over time? The short answer is that clinical and improvement teams cannot adjust one part of the care equation without everything else changing. In _Modeling to Learn_ Blue, we zoom out to see how care variables are locked in relationship with one another over time. The key variables that define either a poor quality or high quality episode of care must be understood together. Building from _MTL_ Red, you can export your local data set created in the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf). Then, if you navigate to [mtl.how/sim](https://forio.com/app/va/va-psd-sim/login.html), you can find the _Modeling to Learn_ Blue Simulation User Interface, which is a dynamic and interactive way to understand why problems with care coordination, medication management, psychotherapy, team care, and team flow persist over time. The Simulation User Interface is a way to see how adjustments in one part of an episode of care explain subsequent impacts in the care system. For any of the common care problems, the simulation saves you time and energy by accounting for the local new patient start rate in patients per week and the local appointment supply and appointments per week. The simulation also keeps track of the local new patient wait time in weeks, time between visits and weeks, and the engagement duration over time, again in weeks. All are calculated for you automatically in the Data User Interface, but their interdependence is accounted for in the Simulation User Interface. The _Modeling to Learn_ Blue Simulation User Interface empowers teams to avoid ineffective strategies because you very quickly learn to develop new insights that would be inefficient, if not impossible, to figure out in your head or by hand. Learning from simulation is designed to help upgrade local decision-making. Teams develop new rules of thumb and insights in which the dependent dynamics among these variables that define care are all taken into account. With a _Modeling to Learn_ consult, we come alongside with partners mid stride in their daily clinical activities who may have limited insight into what is likely to happen over the near future if they keep making the same decisions every day. With _Modeling to Learn_ Blue simulation learning, sites and teams can safely see the impact of new decisions while building new capacities for systems thinking. Why is applied systems thinking more likely to help us avoid costly mistakes? Watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Why is _Modeling to Learn Blue_ useful? Well, why is it wisest to focus on the dynamics of care over time? The short answer is that clinical and improvement teams cannot adjust one part of the care equation without everything else changing. In _Modeling to Learn Blue_, we zoom out to see how care variables are locked in relationship with one another over time. The key variables that define either a poor quality or high quality episode of care must be understood together. Building from _MTL_ Red, you can export your local data set created in the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf). Then, if you navigate to [mtl.how/sim](https://forio.com/app/va/va-psd-sim/login.html), you can find the _Modeling to Learn Blue_ Simulation User Interface, which is a dynamic and interactive way to understand why problems with care coordination, medication management, psychotherapy, team care, and team flow persist over time. The Simulation User Interface is a way to see how adjustments in one part of an episode of care explain subsequent impacts in the care system. For any of the common care problems, the simulation saves you time and energy by accounting for the local new patient start rate in patients per week and the local appointment supply and appointments per week. The simulation also keeps track of the local new patient wait time in weeks, time between visits and weeks, and the engagement duration over time, again in weeks. All are calculated for you automatically in the Data User Interface, but their interdependence is accounted for in the Simulation User Interface. The _Modeling to Learn Blue_ Simulation User Interface empowers teams to avoid ineffective strategies because you very quickly learn to develop new insights that would be inefficient, if not impossible, to figure out in your head or by hand. Learning from simulation is designed to help upgrade local decision-making. Teams develop new rules of thumb and insights in which the dependent dynamics among these variables that define care are all taken into account. With a _Modeling to Learn_ consult, we come alongside with partners mid stride in their daily clinical activities who may have limited insight into what is likely to happen over the near future if they keep making the same decisions every day. With _Modeling to Learn Blue_ simulation learning, sites and teams can safely see the impact of new decisions while building new capacities for systems thinking. Why is applied systems thinking more likely to help us avoid costly mistakes? Watch that video to find out.
## Why is applied systems thinking more likely to help us avoid costly mistakes?
](https://bcove.video/4fnG5Gb)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Why is _Modeling to Learn_ Blue useful? Well, why is it wisest to focus on the dynamics of care over time? The short answer is that clinical and improvement teams cannot adjust one part of the care equation without everything else changing. In _Modeling to Learn_ Blue, we zoom out to see how care variables are locked in relationship with one another over time. The key variables that define either a poor quality or high quality episode of care must be understood together. Building from _MTL_ Red, you can export your local data set created in the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf). Then, if you navigate to [mtl.how/sim](https://forio.com/app/va/va-psd-sim/login.html), you can find the _Modeling to Learn_ Blue Simulation User Interface, which is a dynamic and interactive way to understand why problems with care coordination, medication management, psychotherapy, team care, and team flow persist over time. The Simulation User Interface is a way to see how adjustments in one part of an episode of care explain subsequent impacts in the care system. For any of the common care problems, the simulation saves you time and energy by accounting for the local new patient start rate in patients per week and the local appointment supply and appointments per week. The simulation also keeps track of the local new patient wait time in weeks, time between visits and weeks, and the engagement duration over time, again in weeks. All are calculated for you automatically in the Data User Interface, but their interdependence is accounted for in the Simulation User Interface. The _Modeling to Learn_ Blue Simulation User Interface empowers teams to avoid ineffective strategies because you very quickly learn to develop new insights that would be inefficient, if not impossible, to figure out in your head or by hand. Learning from simulation is designed to help upgrade local decision-making. Teams develop new rules of thumb and insights in which the dependent dynamics among these variables that define care are all taken into account. With a _Modeling to Learn_ consult, we come alongside with partners mid stride in their daily clinical activities who may have limited insight into what is likely to happen over the near future if they keep making the same decisions every day. With _Modeling to Learn_ Blue simulation learning, sites and teams can safely see the impact of new decisions while building new capacities for systems thinking. Why is applied systems thinking more likely to help us avoid costly mistakes? Watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Why is _Modeling to Learn Blue_ useful? Well, why is it wisest to focus on the dynamics of care over time? The short answer is that clinical and improvement teams cannot adjust one part of the care equation without everything else changing. In _Modeling to Learn Blue_, we zoom out to see how care variables are locked in relationship with one another over time. The key variables that define either a poor quality or high quality episode of care must be understood together. Building from _MTL_ Red, you can export your local data set created in the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf). Then, if you navigate to [mtl.how/sim](https://forio.com/app/va/va-psd-sim/login.html), you can find the _Modeling to Learn Blue_ Simulation User Interface, which is a dynamic and interactive way to understand why problems with care coordination, medication management, psychotherapy, team care, and team flow persist over time. The Simulation User Interface is a way to see how adjustments in one part of an episode of care explain subsequent impacts in the care system. For any of the common care problems, the simulation saves you time and energy by accounting for the local new patient start rate in patients per week and the local appointment supply and appointments per week. The simulation also keeps track of the local new patient wait time in weeks, time between visits and weeks, and the engagement duration over time, again in weeks. All are calculated for you automatically in the Data User Interface, but their interdependence is accounted for in the Simulation User Interface. The _Modeling to Learn Blue_ Simulation User Interface empowers teams to avoid ineffective strategies because you very quickly learn to develop new insights that would be inefficient, if not impossible, to figure out in your head or by hand. Learning from simulation is designed to help upgrade local decision-making. Teams develop new rules of thumb and insights in which the dependent dynamics among these variables that define care are all taken into account. With a _Modeling to Learn_ consult, we come alongside with partners mid stride in their daily clinical activities who may have limited insight into what is likely to happen over the near future if they keep making the same decisions every day. With _Modeling to Learn Blue_ simulation learning, sites and teams can safely see the impact of new decisions while building new capacities for systems thinking. Why is applied systems thinking more likely to help us avoid costly mistakes? Watch that video to find out.
## Why is applied systems thinking more likely to help us avoid costly mistakes?
 ](https://bcove.video/3A3sBiG)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. How do five key variables drive care quality? _Modeling to Learn_ emphasizes the dynamics of care over time, which can be accurately simplified to the key time-based variables that drive care quality. But be careful, the important principle is that these variables operate together over time to define an episode of care. That means care quality cannot be improved without understanding how these variables influence one another. If you want to see what Lindsey's talking about, navigate to the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf) and review each care problem—care coordination, medication management, psychotherapy, team care, and team flow. Our partners across VA describe how challenging it is to review data in one information system and then in another and end up unsure how to reconcile them, especially when you think that they indicate a different course of action. Folks are extremely busy and any new data resources must really add value to be worth learning. Let's see if these _Modeling to Learn_ variables meet the commonsense test of value added. Well, what do you think the five time-based variables are that make up an evidence-based episode of care? All outpatient care is defined by whether you can get an appointment when you need help. We focus on this all the time in VA. But then, and this is critical, you must be able to be seen again to complete a therapeutic course of care adequate to meet your need. Clinicians told us that a week was the way they think clinically. So, in _Modeling to Learn_, teams make their clinic selections to obtain an estimate of their local new patient start rate in patients per week and their appointment supply in appointments per week. Then we define evidence-based engagement as the new patient wait time in weeks, time between visits and weeks, and the engagement duration over time, again in weeks. This is a simplified definition of an evidence-based episode of care that is accurate for time. Why is it wise to focus on the dynamics of care over time? That's why _Modeling to Learn_ Blue is useful. So watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. How do five key variables drive care quality? _Modeling to Learn_ emphasizes the dynamics of care over time, which can be accurately simplified to the key time-based variables that drive care quality. But be careful, the important principle is that these variables operate together over time to define an episode of care. That means care quality cannot be improved without understanding how these variables influence one another. If you want to see what Lindsey's talking about, navigate to the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf) and review each care problem—care coordination, medication management, psychotherapy, team care, and team flow. Our partners across VA describe how challenging it is to review data in one information system and then in another and end up unsure how to reconcile them, especially when you think that they indicate a different course of action. Folks are extremely busy and any new data resources must really add value to be worth learning. Let's see if these _Modeling to Learn_ variables meet the commonsense test of value added. Well, what do you think the five time-based variables are that make up an evidence-based episode of care? All outpatient care is defined by whether you can get an appointment when you need help. We focus on this all the time in VA. But then, and this is critical, you must be able to be seen again to complete a therapeutic course of care adequate to meet your need. Clinicians told us that a week was the way they think clinically. So, in _Modeling to Learn_, teams make their clinic selections to obtain an estimate of their local new patient start rate in patients per week and their appointment supply in appointments per week. Then we define evidence-based engagement as the new patient wait time in weeks, time between visits and weeks, and the engagement duration over time, again in weeks. This is a simplified definition of an evidence-based episode of care that is accurate for time. Why is it wise to focus on the dynamics of care over time? That's why _Modeling to Learn Blue_ is useful. So watch that video to find out.
## How does _Modeling to Learn_ help improve medication management?
@@ -96,7 +96,7 @@ Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. How does an appointment backlog extend the we
[
](https://bcove.video/3A3sBiG)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. How do five key variables drive care quality? _Modeling to Learn_ emphasizes the dynamics of care over time, which can be accurately simplified to the key time-based variables that drive care quality. But be careful, the important principle is that these variables operate together over time to define an episode of care. That means care quality cannot be improved without understanding how these variables influence one another. If you want to see what Lindsey's talking about, navigate to the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf) and review each care problem—care coordination, medication management, psychotherapy, team care, and team flow. Our partners across VA describe how challenging it is to review data in one information system and then in another and end up unsure how to reconcile them, especially when you think that they indicate a different course of action. Folks are extremely busy and any new data resources must really add value to be worth learning. Let's see if these _Modeling to Learn_ variables meet the commonsense test of value added. Well, what do you think the five time-based variables are that make up an evidence-based episode of care? All outpatient care is defined by whether you can get an appointment when you need help. We focus on this all the time in VA. But then, and this is critical, you must be able to be seen again to complete a therapeutic course of care adequate to meet your need. Clinicians told us that a week was the way they think clinically. So, in _Modeling to Learn_, teams make their clinic selections to obtain an estimate of their local new patient start rate in patients per week and their appointment supply in appointments per week. Then we define evidence-based engagement as the new patient wait time in weeks, time between visits and weeks, and the engagement duration over time, again in weeks. This is a simplified definition of an evidence-based episode of care that is accurate for time. Why is it wise to focus on the dynamics of care over time? That's why _Modeling to Learn_ Blue is useful. So watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. How do five key variables drive care quality? _Modeling to Learn_ emphasizes the dynamics of care over time, which can be accurately simplified to the key time-based variables that drive care quality. But be careful, the important principle is that these variables operate together over time to define an episode of care. That means care quality cannot be improved without understanding how these variables influence one another. If you want to see what Lindsey's talking about, navigate to the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf) and review each care problem—care coordination, medication management, psychotherapy, team care, and team flow. Our partners across VA describe how challenging it is to review data in one information system and then in another and end up unsure how to reconcile them, especially when you think that they indicate a different course of action. Folks are extremely busy and any new data resources must really add value to be worth learning. Let's see if these _Modeling to Learn_ variables meet the commonsense test of value added. Well, what do you think the five time-based variables are that make up an evidence-based episode of care? All outpatient care is defined by whether you can get an appointment when you need help. We focus on this all the time in VA. But then, and this is critical, you must be able to be seen again to complete a therapeutic course of care adequate to meet your need. Clinicians told us that a week was the way they think clinically. So, in _Modeling to Learn_, teams make their clinic selections to obtain an estimate of their local new patient start rate in patients per week and their appointment supply in appointments per week. Then we define evidence-based engagement as the new patient wait time in weeks, time between visits and weeks, and the engagement duration over time, again in weeks. This is a simplified definition of an evidence-based episode of care that is accurate for time. Why is it wise to focus on the dynamics of care over time? That's why _Modeling to Learn Blue_ is useful. So watch that video to find out.
## How does _Modeling to Learn_ help improve medication management?
@@ -96,7 +96,7 @@ Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. How does an appointment backlog extend the we
[ ](https://bcove.video/3yaXy41)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. How can we better balance the needs of new and existing patients? Should we prioritize new patient start rate or weeks between visits? These trade-offs are challenging for clinicians when you know there is a whole community of patients who need help. When teams are struggling with the limits of their available time in the day to see patients, it can feel like a clinical, ethical, and even moral quandary about how to best balance patients’ needs for services with the staff resources available. Of course, staff resources are always changing. We know many teams that are excelling in providing the highest quality addiction and mental health care available. But the behavioral health workforce shortage in the US is much bigger than VA. And VAs and teams need the right tools to make sure Veterans get the care they need for recovery. Challenges balancing the new patient start rate and the weeks between visits for existing patients apply systems thinking insights that we've talked about in other _MTL_ videos, such as the physics of conserving staff time in order to ensure a clinically beneficial, realistic approach to care decisions and quality improvement that meets VA quality standards _and_ meets Veterans needs for evidence-based episodes of care. The _Modeling to Learn_ Blue Simulation User Interface available at [mtl.how/sim](https://forio.com/app/va/va-psd-sim/login.html) enables a site or team to evaluate these two balancing system stories as a function of their data for the last two years exported from _Modeling to Learn_ Red Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf). As we talked about in the _How does an appointment backlog extend the weeks between visits?_ video and _What if we keep making the same care decisions, will things get better or worse?_ video, balancing feedbacks occur in any system that has a goal, including our healthcare and clinical systems. Balancing feedbacks occur in systems that have constraints of resources, staff, and time. And as a result, the trends that occur over time tend to reset to a status quo or oscillate around the status quo. A brief _Modeling to Learn_ consult uses the site or team reviewed local data plus simulation to efficiently find local improvements that account for all these balancing trade-offs. We aim to help clinical and improvement teams find a couple empowering clinical heuristics, or rules of thumb, that are more effective for ensuring evidence-based care to get more Veterans better. When we partner with a VA or a team, we aim to find the lightest lift we can, like increase groups by 10% or adjust the return-to-clinic order for three weeks for these presenting concerns. And we often find something small that has a big payoff for Veterans. Do you want to be empowered to leverage the feedback, flow, and volume of your local care system? Watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. How can we better balance the needs of new and existing patients? Should we prioritize new patient start rate or weeks between visits? These trade-offs are challenging for clinicians when you know there is a whole community of patients who need help. When teams are struggling with the limits of their available time in the day to see patients, it can feel like a clinical, ethical, and even moral quandary about how to best balance patients’ needs for services with the staff resources available. Of course, staff resources are always changing. We know many teams that are excelling in providing the highest quality addiction and mental health care available. But the behavioral health workforce shortage in the US is much bigger than VA. And VAs and teams need the right tools to make sure Veterans get the care they need for recovery. Challenges balancing the new patient start rate and the weeks between visits for existing patients apply systems thinking insights that we've talked about in other _MTL_ videos, such as the physics of conserving staff time in order to ensure a clinically beneficial, realistic approach to care decisions and quality improvement that meets VA quality standards _and_ meets Veterans needs for evidence-based episodes of care. The _Modeling to Learn Blue_ Simulation User Interface available at [mtl.how/sim](https://forio.com/app/va/va-psd-sim/login.html) enables a site or team to evaluate these two balancing system stories as a function of their data for the last two years exported from _Modeling to Learn Red_ Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf). As we talked about in the _How does an appointment backlog extend the weeks between visits?_ video and _What if we keep making the same care decisions, will things get better or worse?_ video, balancing feedbacks occur in any system that has a goal, including our healthcare and clinical systems. Balancing feedbacks occur in systems that have constraints of resources, staff, and time. And as a result, the trends that occur over time tend to reset to a status quo or oscillate around the status quo. A brief _Modeling to Learn_ consult uses the site or team reviewed local data plus simulation to efficiently find local improvements that account for all these balancing trade-offs. We aim to help clinical and improvement teams find a couple empowering clinical heuristics, or rules of thumb, that are more effective for ensuring evidence-based care to get more Veterans better. When we partner with a VA or a team, we aim to find the lightest lift we can, like increase groups by 10% or adjust the return-to-clinic order for three weeks for these presenting concerns. And we often find something small that has a big payoff for Veterans. Do you want to be empowered to leverage the feedback, flow, and volume of your local care system? Watch that video to find out.
## How can we leverage the feedback, rates, and volume of our local care system?
diff --git a/3.0_technical_documentation.md b/3.0_technical_documentation.md
index a179c0ac..9062f13f 100644
--- a/3.0_technical_documentation.md
+++ b/3.0_technical_documentation.md
@@ -6,11 +6,11 @@
- [CPT Code Cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/cptcode_cheatsheet.png)
-### _MTL_ 3.7 Data Cheatsheet
+### _MTL 3.7_ Data Cheatsheet
- [Data Cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/mtl_how_3.7_data_cheatsheet.png)
-### _MTL_ 3.7 Sim UI Cheatsheet
+### _MTL 3.7_ Sim UI Cheatsheet
- [Sim UI Cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/mtl_how_3.7_sim_ui_cheatsheet.png)
@@ -45,13 +45,15 @@ Follow the instructions below to create an account or team in the Sim UI. Once t
- If you are creating a team or the first person to register from your Facility Team, the following pop-up window will appear (with your VISN, Facility, and Clinic pre-populated).
- Enter your Facility Team name in the pop-up window (immediately after the pre-populated information).
-
- - Click the Submit button. The submitted team name is saved even though the dropdown field remains unchanged.
- **Notes:** You must only use lowercase letters. You must use the underscore character (_) instead of spaces.
](https://bcove.video/3yaXy41)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. How can we better balance the needs of new and existing patients? Should we prioritize new patient start rate or weeks between visits? These trade-offs are challenging for clinicians when you know there is a whole community of patients who need help. When teams are struggling with the limits of their available time in the day to see patients, it can feel like a clinical, ethical, and even moral quandary about how to best balance patients’ needs for services with the staff resources available. Of course, staff resources are always changing. We know many teams that are excelling in providing the highest quality addiction and mental health care available. But the behavioral health workforce shortage in the US is much bigger than VA. And VAs and teams need the right tools to make sure Veterans get the care they need for recovery. Challenges balancing the new patient start rate and the weeks between visits for existing patients apply systems thinking insights that we've talked about in other _MTL_ videos, such as the physics of conserving staff time in order to ensure a clinically beneficial, realistic approach to care decisions and quality improvement that meets VA quality standards _and_ meets Veterans needs for evidence-based episodes of care. The _Modeling to Learn_ Blue Simulation User Interface available at [mtl.how/sim](https://forio.com/app/va/va-psd-sim/login.html) enables a site or team to evaluate these two balancing system stories as a function of their data for the last two years exported from _Modeling to Learn_ Red Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf). As we talked about in the _How does an appointment backlog extend the weeks between visits?_ video and _What if we keep making the same care decisions, will things get better or worse?_ video, balancing feedbacks occur in any system that has a goal, including our healthcare and clinical systems. Balancing feedbacks occur in systems that have constraints of resources, staff, and time. And as a result, the trends that occur over time tend to reset to a status quo or oscillate around the status quo. A brief _Modeling to Learn_ consult uses the site or team reviewed local data plus simulation to efficiently find local improvements that account for all these balancing trade-offs. We aim to help clinical and improvement teams find a couple empowering clinical heuristics, or rules of thumb, that are more effective for ensuring evidence-based care to get more Veterans better. When we partner with a VA or a team, we aim to find the lightest lift we can, like increase groups by 10% or adjust the return-to-clinic order for three weeks for these presenting concerns. And we often find something small that has a big payoff for Veterans. Do you want to be empowered to leverage the feedback, flow, and volume of your local care system? Watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. How can we better balance the needs of new and existing patients? Should we prioritize new patient start rate or weeks between visits? These trade-offs are challenging for clinicians when you know there is a whole community of patients who need help. When teams are struggling with the limits of their available time in the day to see patients, it can feel like a clinical, ethical, and even moral quandary about how to best balance patients’ needs for services with the staff resources available. Of course, staff resources are always changing. We know many teams that are excelling in providing the highest quality addiction and mental health care available. But the behavioral health workforce shortage in the US is much bigger than VA. And VAs and teams need the right tools to make sure Veterans get the care they need for recovery. Challenges balancing the new patient start rate and the weeks between visits for existing patients apply systems thinking insights that we've talked about in other _MTL_ videos, such as the physics of conserving staff time in order to ensure a clinically beneficial, realistic approach to care decisions and quality improvement that meets VA quality standards _and_ meets Veterans needs for evidence-based episodes of care. The _Modeling to Learn Blue_ Simulation User Interface available at [mtl.how/sim](https://forio.com/app/va/va-psd-sim/login.html) enables a site or team to evaluate these two balancing system stories as a function of their data for the last two years exported from _Modeling to Learn Red_ Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf). As we talked about in the _How does an appointment backlog extend the weeks between visits?_ video and _What if we keep making the same care decisions, will things get better or worse?_ video, balancing feedbacks occur in any system that has a goal, including our healthcare and clinical systems. Balancing feedbacks occur in systems that have constraints of resources, staff, and time. And as a result, the trends that occur over time tend to reset to a status quo or oscillate around the status quo. A brief _Modeling to Learn_ consult uses the site or team reviewed local data plus simulation to efficiently find local improvements that account for all these balancing trade-offs. We aim to help clinical and improvement teams find a couple empowering clinical heuristics, or rules of thumb, that are more effective for ensuring evidence-based care to get more Veterans better. When we partner with a VA or a team, we aim to find the lightest lift we can, like increase groups by 10% or adjust the return-to-clinic order for three weeks for these presenting concerns. And we often find something small that has a big payoff for Veterans. Do you want to be empowered to leverage the feedback, flow, and volume of your local care system? Watch that video to find out.
## How can we leverage the feedback, rates, and volume of our local care system?
diff --git a/3.0_technical_documentation.md b/3.0_technical_documentation.md
index a179c0ac..9062f13f 100644
--- a/3.0_technical_documentation.md
+++ b/3.0_technical_documentation.md
@@ -6,11 +6,11 @@
- [CPT Code Cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/cptcode_cheatsheet.png)
-### _MTL_ 3.7 Data Cheatsheet
+### _MTL 3.7_ Data Cheatsheet
- [Data Cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/mtl_how_3.7_data_cheatsheet.png)
-### _MTL_ 3.7 Sim UI Cheatsheet
+### _MTL 3.7_ Sim UI Cheatsheet
- [Sim UI Cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/mtl_how_3.7_sim_ui_cheatsheet.png)
@@ -45,13 +45,15 @@ Follow the instructions below to create an account or team in the Sim UI. Once t
- If you are creating a team or the first person to register from your Facility Team, the following pop-up window will appear (with your VISN, Facility, and Clinic pre-populated).
- Enter your Facility Team name in the pop-up window (immediately after the pre-populated information).
-
- - Click the Submit button. The submitted team name is saved even though the dropdown field remains unchanged.
- **Notes:** You must only use lowercase letters. You must use the underscore character (_) instead of spaces.
 + - Click the Submit button. Even though the dropdown field remains unchanged on the form, the submitted team name is saved, as confirmed by the green text as shown in this example:
+
+
+ - Click the Submit button. Even though the dropdown field remains unchanged on the form, the submitted team name is saved, as confirmed by the green text as shown in this example:
+
+ +
- **5 - Select VHA Primary Role**: Select your primary VHA role from the dropdown menu. Choices are: Clinician, Data Subject Matter Expert, Leader/Manager, Quality Improvement, Researcher/Evaluator, Systems Modeler, and Other.
- **6 - First Name**: Enter your first name.
@@ -75,9 +77,9 @@ Follow the instructions below to create an account or team in the Sim UI. Once t
- If the information is not correct, close the pop-up window and make adjustements to the registration form where needed.
- If the information is correct, click the green Submit button.
-The following message will appear for a few seconds in the upper right-hand corner of your browser window:
+A success page will appear :
-
+
- **5 - Select VHA Primary Role**: Select your primary VHA role from the dropdown menu. Choices are: Clinician, Data Subject Matter Expert, Leader/Manager, Quality Improvement, Researcher/Evaluator, Systems Modeler, and Other.
- **6 - First Name**: Enter your first name.
@@ -75,9 +77,9 @@ Follow the instructions below to create an account or team in the Sim UI. Once t
- If the information is not correct, close the pop-up window and make adjustements to the registration form where needed.
- If the information is correct, click the green Submit button.
-The following message will appear for a few seconds in the upper right-hand corner of your browser window:
+A success page will appear :
- +
+ 7. After your registration request is reviewed and approved, an approval email will be sent to your VA address that contains login information for accessing the _MTL_ Sim UI.
@@ -91,23 +93,24 @@ You must already have an account set up to log into the Sim UI. If you do not ha
7. After your registration request is reviewed and approved, an approval email will be sent to your VA address that contains login information for accessing the _MTL_ Sim UI.
@@ -91,23 +93,24 @@ You must already have an account set up to log into the Sim UI. If you do not ha
 -2. A Please select a World pop-up will appear. The Sim will load teams and, once you select a team, you will be directed to that team's Home page.
+2. A Please select a World pop-up will appear. The Sim will load teams and, **once you select a team, you will be directed to that team's Home page.**
- **Note:** The login dropdown only shows worlds in which you are a team lead or participant (not an Administrator).
-- **Note:** If you have the Administrator role in any team and have been added into "administrator_login" in Epicenter, you will be allowed to login using the "administrator_login" choice. Upon logging in, Administrators are directed to the [Administrator Dashboard](#sim_ui_administrator_dashboard).
-
+- **Note:** If you have the Administrator role in any team and have been added into "administrator_login" in Epicenter, you will be allowed to login using the "administrator_login" choice. Upon logging in, Administrators are directed to the [Administrator Dashboard](#sim-ui-administrator_dashboard).
-2. A Please select a World pop-up will appear. The Sim will load teams and, once you select a team, you will be directed to that team's Home page.
+2. A Please select a World pop-up will appear. The Sim will load teams and, **once you select a team, you will be directed to that team's Home page.**
- **Note:** The login dropdown only shows worlds in which you are a team lead or participant (not an Administrator).
-- **Note:** If you have the Administrator role in any team and have been added into "administrator_login" in Epicenter, you will be allowed to login using the "administrator_login" choice. Upon logging in, Administrators are directed to the [Administrator Dashboard](#sim_ui_administrator_dashboard).
-
+- **Note:** If you have the Administrator role in any team and have been added into "administrator_login" in Epicenter, you will be allowed to login using the "administrator_login" choice. Upon logging in, Administrators are directed to the [Administrator Dashboard](#sim-ui-administrator_dashboard).
 3. The screenshots below display what you will see upon logging in, depending on your role.
+- **Note:** To familiarize yourself with a team's Home page, refer to [Orient to a Team's Home Page](#orient-to-a-team's-home-page)
+
|Team Member login = team's Home page|Administrator login = Admin Dashboard |
|:---:|:---:|
|
3. The screenshots below display what you will see upon logging in, depending on your role.
+- **Note:** To familiarize yourself with a team's Home page, refer to [Orient to a Team's Home Page](#orient-to-a-team's-home-page)
+
|Team Member login = team's Home page|Administrator login = Admin Dashboard |
|:---:|:---:|
| |
| ### Make, View, and Export Team Clinic Selections for Import to Sim UI
-**Tip:** Refer to this one-page [Data Cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/mtl_how_3.7_data_cheatsheet.png) when using the Data UI and making clinic and flow selections.
+**Tip:** Refer to (or save) this one-page [Data Cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/mtl_how_3.7_data_cheatsheet.pdf) when using the Data UI and making clinic and flow selections.
The general workflow for the Data UI is that teams:
@@ -145,7 +148,7 @@ The general workflow for the Data UI is that teams:
- Click the green Apply button to pull Patient Level Data from all clinics selected in the last two years.
-- Select clinics that your team refers to in the Team Flow Selection tab to produce data tracking patients stepped up/down for the Team (SP) Flow module.
+- Select clinics that your team refers to in the Team Flow Selection tab to produce data tracking patients stepped up/down for the Team Flow module.
- For example, if you are a GMH team, you would select SMH in the dropdown for "The clinics selected below that my team refers to are" and add the SMH clinics your team refers to in the Green column, second row.
@@ -321,39 +324,35 @@ Below is a basic orientation to the Home page of any team:
### Make, View, and Export Team Clinic Selections for Import to Sim UI
-**Tip:** Refer to this one-page [Data Cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/mtl_how_3.7_data_cheatsheet.png) when using the Data UI and making clinic and flow selections.
+**Tip:** Refer to (or save) this one-page [Data Cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/mtl_how_3.7_data_cheatsheet.pdf) when using the Data UI and making clinic and flow selections.
The general workflow for the Data UI is that teams:
@@ -145,7 +148,7 @@ The general workflow for the Data UI is that teams:
- Click the green Apply button to pull Patient Level Data from all clinics selected in the last two years.
-- Select clinics that your team refers to in the Team Flow Selection tab to produce data tracking patients stepped up/down for the Team (SP) Flow module.
+- Select clinics that your team refers to in the Team Flow Selection tab to produce data tracking patients stepped up/down for the Team Flow module.
- For example, if you are a GMH team, you would select SMH in the dropdown for "The clinics selected below that my team refers to are" and add the SMH clinics your team refers to in the Green column, second row.
@@ -321,39 +324,35 @@ Below is a basic orientation to the Home page of any team:
 -1. **_MTL_ logo:** Click this logo on any page to return to this Home page.
-
-2. **Team Name:** The selected team name appears here. When logged into your individual world, team name = your name.
+1. **_MTL_ logo:** Click this logo to return to the Dynamic Decision Dashboard.
-3. **Home:** Click to return to this Home page.
+2. **Team Name:** The selected team name appears here with the world extension added at the end of its name. If you are logged in as an Administrator, you will see "Administrator" here.
-4. **Play:** Click to open the main Simulation User Interface (Sim UI) page.
+3. **Home:** Click to return to the Dynamic Decision Dashboard.
-5. **Team:** Click to chat with other team members. An alert will appear if you have unread chats waiting.
+4. **Play:** Click to return to the Play page.
-6. **More Info:** Click for answers to common _Modeling to Learn_ questions.
+5. **More Info:** Click for more information on how to use the Sim UI.
-7. **News:** Click for the latest news about _Modeling to Learn_. An alert will appear if you have unread news items.
+6. **News:** Click for the latest news about _Modeling to Learn_. An alert will appear if you have unread news items.
-8. **Report Bug:** Click to report a bug.
+7. **Report Bug:** Click to report a bug.
-9. **Tutor:** Click any Tutor icon for more information about the section.
+8. **Tutor:** Click any Tutor icon for an "over the shoulder" overview.
-10. **Admin Dashboard:** Click to return to the Administrator Dashboard.
+9. **Logoff:** Click to log off of the Sim UI.
-11. **Logoff:** Click to log off of the Sim UI.
+10. **Avatar:** Click to upload your profile picture.
-12. **Avatar:** Click to upload your profile picture.
+11. **Session Start window:** You can either join the simulation session in progress or start a new one. Select the team data file you wish to use from the dropdown menu, then press GO!
-13. **Session Start window:** You can either join the simulation session in progress or start a new one. Select the team data file you wish to use from the dropdown menu, then press GO!
+12. **Experiment window:** This section allows you to delete, rename, export, and sort your team's simulation experiment results.
-14. **Experiment window:** This section allows you to delete, rename, export, and sort your team's simulation experiment results.
+13. **Team Data window:** This section allows you to delete, upload, and sort team data files (which will then show in the Start a Session window). Legacy team data files are located under the _MTL_ 3.0 gray bar.
-15. **Team Data window:** This section allows you to delete, upload, and sort team data files (which will then show in the Start a Session window). Legacy team data files are located under the _MTL_ 3.0 gray bar.
+14. **Dynamic Decision Dashboard:** Use this section to navigate between the 5 modules and their associated variables.
-16. **Dynamic Decision Dashboard:** Use this section to navigate between the 5 modules and their associated variables.
-
-17. **Community:** Click to give feedback to system administrators and participate in our _MTL_ Community of Practice.
+15. **Community:** Click to give feedback to system administrators and participate in our _MTL_ Community of Practice.
### Begin a Session in the Dynamic Decision Dashboard
@@ -361,7 +360,7 @@ Below is a basic orientation to the Home page of any team:
Beginning a session in the Dynamic Decision Dashboard (DDD) allows users to look at the stocks and flows across all five modules and helps determine which module(s) to focus on.
-1. Navigate to the selected team's Home page. If you aren't sure how, see [Navigate to the Home Page of Any Team](#navigate-to-the-home=page-of-any-team).
+1. Navigate to the selected team's Home page. If you aren't sure how, see [Navigate to the Home Page of Any Team](#navigate-to-the-home-page-of-any-team).
2. Select the desired team data file from the Please Select Team Data dropdown and click GO! A Learning Mode pop-up will appear.
@@ -377,7 +376,7 @@ Beginning a session in the Dynamic Decision Dashboard (DDD) allows users to look
- Existing Patients Return-to-Clinic Visit Interval (EPRVI) = learning mode "0".
- New Patient Start Rate (NPSR) = learning mode "1".
-- Refer to the Care Coordination (CCParams) or Medication Management (MMParams) tab of the Team Data Table at mtl.how/data, for data regarding the team’s New Patient Start Rates and Return-to-Clinic Intervals.
+- Refer to the Care Coordination (CCParams) or Medication Management (MMParams) tab of the Team Data Table at mtl.how/data, for data regarding the team’s New Patient Start Rates and Return-to-Clinic Visit Intervals.
#### Upload Team Data Files from the Home Page
@@ -433,25 +432,27 @@ Below is an orientation to the Dynamic Decision Dashboard.
- **1 - Feedback Loops**: Interactive diagrams that aid in visualizing how different variables in a system are causally interrelated. Clicking here will open a pop-up window that shows an associated loop diagram along with Causal Loop Dynamics selections.
-- **2 - Decision Meters**: A quick method to visualize the relevance or significance of different aspects within a group.
+- **2 - Flow**: Visualized in Sankey form, these diagrams help visualize the rate of flow into and out of stocks. A stock is a state of care in which patients can accumulate over time. Sankey is a type of flow diagram where the width of the arrows is proportional to the flow quantity.
+
+- **3 - Decision Meters**: A quick method to visualize the relevance or significance of different aspects within a group.
-- **3 - Episodes of Care**: Graphically shows evidence-based episode of care intervals to get a bird's eye view of how long the length of engagement will be.
+- **4 - Episodes of Care**: Graphically shows evidence-based episode of care intervals to get a bird's eye view of how long the length of engagement will be.
-- **4 - Play**: Enter the main Sim UI page to see the system story and run experiments.
+- **5 - Play**: Enter the main Sim UI page to see the system story and run experiments.
-- **5 - Team Data**: A quick link to the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface that will open in a new browser tab.
+- **6 - Team Data**: A quick link to the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface that will open in a new browser tab.
-- **6 - SAIL Data**: A quick link to Strategic Analytics for Improvement and Learning Value Model (SAIL), a system for summarizing hospital system performance within Veterans Health Administration (VHA). This will open in a new browser tab.
+- **7 - SAIL Data**: A quick link to Strategic Analytics for Improvement and Learning Value Model (SAIL), a system for summarizing hospital system performance within Veterans Health Administration (VHA). This will open in a new browser tab.
-5. **Services Radio Buttons**: Select desired service radio button to see stock values for specific services in Team Care (Intake, Care Coordination, Medication Management, Psychotherapy, Evidence-based Psychotherapy, Adjunctive Services, Group Therapy).
+5. **Learning Mode Labels**: Indicates which Learning Mode the data prioritizes. Click these buttons to change the learning modes directly from the DDD; the system will re-initialize based on the new learning mode selected. Existing Patients Return-to-Clinic Visit Interval (EPRVI) = learning mode "0" and New Patient Start Rate (NPSR) = learning mode "1".
-6. **Learning Mode Labels**: Indicates which Learning Mode the data prioritizes. Click these buttons to change the learning modes directly from the DDD; the system will re-initialize based on the new learning mode selected. Existing Patients Return-to-Clinic Visit Interval (EPRVI) = learning mode "0" and New Patient Start Rate (NPSR) = learning mode "1".
+6. **Team Care Services Radio Buttons**: Select desired service radio button to see stock values for specific services in Team Care (Intake, Care Coordination, Medication Management, Psychotherapy, Evidence-based Psychotherapy, Adjunctive Services, Group Therapy). The default display is Intake evaluations.
-7. **Meds Needed Radio Buttons**: Select desired meds needed radio button to see stock values for medication-specific services (Alcohol Use Disorder, Depression, Opioid Use Disorder, and Other).
+7. **Medication Management Services Radio Buttons**: Select desired service radio button to see stock values for medication-specific services in Medication Management (Alcohol Use Disorder, Depression, Opioid Use Disorder, and Other). The defaut display is Alcolol Use Disorder.
-8. **"i" icon**: Click these to read the definition of each stock label.
+8. **"i" icon**: Click "i" icons to read the definition of each stock label.
-9. **Setting Radio Buttons**: Select desired setting radio button to see stock values for setting-specific services in Team Flow (General Mental Health, Specialty Mental Health, Primary Care/Primary Care Mental Health Integration).
+9. **Team Flow Services Radio Buttons**: Select desired service radio button to see stock values for setting-specific services in Team Flow (General Mental Health, Specialty Mental Health, Primary Care/Primary Care Mental Health Integration). The default display is General Mental Health.
10. **Community**: Click here to participate by sharing an idea, letting the team know what you like, asking a question, or joining our community.
@@ -497,7 +498,7 @@ Each story has its own unique feedback loop that shows named balancing and reinf
Decision Meters are a quick infographic-based way to identify the highest leverage points and are highly supportive of clinical decision-making; they are for "decider" users who need systems thinking insights. The meters provide a visual interface that provides real-time feedback on ranges in our primary _MTL_ units of patients/week and appointments/week. The traffic light reflects the current state results and _recommendation_ of future state results. Through dialogue with decision-makers, consultants and field users manually input values into this graphic generator so the decision meters reflect the recommendations based on the alternative scenarios/experiments run by the learner. Decision meter numbers should be reflected in the "D" box of the Q/H/F/D outputs text field within the Sim UI, usually as ranges of numbers.
-- Care Decision Meters are for _MTL_ Blue teams only.
+- Care Decision Meters are for _MTL Blue_ teams only.
- Click within each decision meter to edit. Remember to click Save if you want the values to remain!
For illustrative purposes, the Medication Management Decisions window is used as an example below to orient you to general Decisions pop-up window features.
@@ -524,7 +525,7 @@ For illustrative purposes, the Medication Management Decisions window is used as
##### Episodes of Care
-Timely access to high-quality care includes improved understanding of dynamic tradeoffs in the return-to-clinic visit interval and engagement durations. The Episodes of Care pop-up is used to graphically show evidence-based episode of care intervals to get a bird's eye view of how long the length of engagement will be. Available within the Medication Management, Psychotherapy, and Team Care modules, this pop-up integrates engagement duration and Return-to-Clinic Visit Interval (RVI) for both Medication Management and Psychotherapy.
+Timely access to high-quality care includes improved understanding of dynamic tradeoffs in the Return-to-Clinic Visit Interval (RVI) and engagement durations. The Episodes of Care pop-up is used to graphically show evidence-based episode of care intervals to get a bird's eye view of how long the length of engagement will be. Available within the Medication Management, Psychotherapy, and Team Care modules, this pop-up integrates engagement duration and RVI for both Medication Management and Psychotherapy.
The following screenshot will orient you to general features of this pop-up.
@@ -562,7 +563,7 @@ This section explains how to enter and save an experiment in the Sim UI.
- **Note:** For CC and MM, select your Learning Mode before hitting Play.
- - Refer to the Care Coordination (CCParams) or Medication Management (MMParams) tab of the Team Data Table at mtl.how/data, for data regarding the team’s New Patient Start Rates and Return-to-Clinic Intervals.
+ - Refer to the Care Coordination (CCParams) or Medication Management (MMParams) tab of the Team Data Table at mtl.how/data, for data regarding the team’s New Patient Start Rates and Return-to-Clinic Visit Intervals.
3. To run a simulation for any module within the dashboard, select Play found within each module's More menu.
@@ -582,7 +583,7 @@ This section explains how to enter and save an experiment in the Sim UI.
#### Orient to the Sim UI
-**Tip:** Save this [Sim UI cheatsheet](https://github.com/lzim/mtl/blob/master/blue/session05/s05_learner/mtl_how_3.7_sim_ui_cheatsheet.pdf) to use when running an experiment.
+**Tip:** Save this [Sim UI cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/mtl_how_3.7_sim_ui_cheatsheet.pdf) to use when running an experiment.
Below is an orientation to the Play Page of the Sim UI.
@@ -606,40 +607,6 @@ Below is an orientation to the Play Page of the Sim UI.
- **9**: Text: Enter Q/H/F/Ds. Click on expand icon in blue bar for full functions.
-### Manage Discussions in Team
-
-- The Team button in the top navigation is for texting and maintaining private discussion threads with one or more individuals and open discussion threads with teams.
-- A person can chat with one or more people using the Team function by inputting the end user name (usually the va.gov email address) of the person or people they want to address.
-- A person can chat with an entire team at once, provided they are a registered end user in that team.
-
-#### Set up a Private Conversation
-
-1. Click "Team" to open the chat pop-up.
-
-
-1. **_MTL_ logo:** Click this logo on any page to return to this Home page.
-
-2. **Team Name:** The selected team name appears here. When logged into your individual world, team name = your name.
+1. **_MTL_ logo:** Click this logo to return to the Dynamic Decision Dashboard.
-3. **Home:** Click to return to this Home page.
+2. **Team Name:** The selected team name appears here with the world extension added at the end of its name. If you are logged in as an Administrator, you will see "Administrator" here.
-4. **Play:** Click to open the main Simulation User Interface (Sim UI) page.
+3. **Home:** Click to return to the Dynamic Decision Dashboard.
-5. **Team:** Click to chat with other team members. An alert will appear if you have unread chats waiting.
+4. **Play:** Click to return to the Play page.
-6. **More Info:** Click for answers to common _Modeling to Learn_ questions.
+5. **More Info:** Click for more information on how to use the Sim UI.
-7. **News:** Click for the latest news about _Modeling to Learn_. An alert will appear if you have unread news items.
+6. **News:** Click for the latest news about _Modeling to Learn_. An alert will appear if you have unread news items.
-8. **Report Bug:** Click to report a bug.
+7. **Report Bug:** Click to report a bug.
-9. **Tutor:** Click any Tutor icon for more information about the section.
+8. **Tutor:** Click any Tutor icon for an "over the shoulder" overview.
-10. **Admin Dashboard:** Click to return to the Administrator Dashboard.
+9. **Logoff:** Click to log off of the Sim UI.
-11. **Logoff:** Click to log off of the Sim UI.
+10. **Avatar:** Click to upload your profile picture.
-12. **Avatar:** Click to upload your profile picture.
+11. **Session Start window:** You can either join the simulation session in progress or start a new one. Select the team data file you wish to use from the dropdown menu, then press GO!
-13. **Session Start window:** You can either join the simulation session in progress or start a new one. Select the team data file you wish to use from the dropdown menu, then press GO!
+12. **Experiment window:** This section allows you to delete, rename, export, and sort your team's simulation experiment results.
-14. **Experiment window:** This section allows you to delete, rename, export, and sort your team's simulation experiment results.
+13. **Team Data window:** This section allows you to delete, upload, and sort team data files (which will then show in the Start a Session window). Legacy team data files are located under the _MTL_ 3.0 gray bar.
-15. **Team Data window:** This section allows you to delete, upload, and sort team data files (which will then show in the Start a Session window). Legacy team data files are located under the _MTL_ 3.0 gray bar.
+14. **Dynamic Decision Dashboard:** Use this section to navigate between the 5 modules and their associated variables.
-16. **Dynamic Decision Dashboard:** Use this section to navigate between the 5 modules and their associated variables.
-
-17. **Community:** Click to give feedback to system administrators and participate in our _MTL_ Community of Practice.
+15. **Community:** Click to give feedback to system administrators and participate in our _MTL_ Community of Practice.
### Begin a Session in the Dynamic Decision Dashboard
@@ -361,7 +360,7 @@ Below is a basic orientation to the Home page of any team:
Beginning a session in the Dynamic Decision Dashboard (DDD) allows users to look at the stocks and flows across all five modules and helps determine which module(s) to focus on.
-1. Navigate to the selected team's Home page. If you aren't sure how, see [Navigate to the Home Page of Any Team](#navigate-to-the-home=page-of-any-team).
+1. Navigate to the selected team's Home page. If you aren't sure how, see [Navigate to the Home Page of Any Team](#navigate-to-the-home-page-of-any-team).
2. Select the desired team data file from the Please Select Team Data dropdown and click GO! A Learning Mode pop-up will appear.
@@ -377,7 +376,7 @@ Beginning a session in the Dynamic Decision Dashboard (DDD) allows users to look
- Existing Patients Return-to-Clinic Visit Interval (EPRVI) = learning mode "0".
- New Patient Start Rate (NPSR) = learning mode "1".
-- Refer to the Care Coordination (CCParams) or Medication Management (MMParams) tab of the Team Data Table at mtl.how/data, for data regarding the team’s New Patient Start Rates and Return-to-Clinic Intervals.
+- Refer to the Care Coordination (CCParams) or Medication Management (MMParams) tab of the Team Data Table at mtl.how/data, for data regarding the team’s New Patient Start Rates and Return-to-Clinic Visit Intervals.
#### Upload Team Data Files from the Home Page
@@ -433,25 +432,27 @@ Below is an orientation to the Dynamic Decision Dashboard.
- **1 - Feedback Loops**: Interactive diagrams that aid in visualizing how different variables in a system are causally interrelated. Clicking here will open a pop-up window that shows an associated loop diagram along with Causal Loop Dynamics selections.
-- **2 - Decision Meters**: A quick method to visualize the relevance or significance of different aspects within a group.
+- **2 - Flow**: Visualized in Sankey form, these diagrams help visualize the rate of flow into and out of stocks. A stock is a state of care in which patients can accumulate over time. Sankey is a type of flow diagram where the width of the arrows is proportional to the flow quantity.
+
+- **3 - Decision Meters**: A quick method to visualize the relevance or significance of different aspects within a group.
-- **3 - Episodes of Care**: Graphically shows evidence-based episode of care intervals to get a bird's eye view of how long the length of engagement will be.
+- **4 - Episodes of Care**: Graphically shows evidence-based episode of care intervals to get a bird's eye view of how long the length of engagement will be.
-- **4 - Play**: Enter the main Sim UI page to see the system story and run experiments.
+- **5 - Play**: Enter the main Sim UI page to see the system story and run experiments.
-- **5 - Team Data**: A quick link to the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface that will open in a new browser tab.
+- **6 - Team Data**: A quick link to the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface that will open in a new browser tab.
-- **6 - SAIL Data**: A quick link to Strategic Analytics for Improvement and Learning Value Model (SAIL), a system for summarizing hospital system performance within Veterans Health Administration (VHA). This will open in a new browser tab.
+- **7 - SAIL Data**: A quick link to Strategic Analytics for Improvement and Learning Value Model (SAIL), a system for summarizing hospital system performance within Veterans Health Administration (VHA). This will open in a new browser tab.
-5. **Services Radio Buttons**: Select desired service radio button to see stock values for specific services in Team Care (Intake, Care Coordination, Medication Management, Psychotherapy, Evidence-based Psychotherapy, Adjunctive Services, Group Therapy).
+5. **Learning Mode Labels**: Indicates which Learning Mode the data prioritizes. Click these buttons to change the learning modes directly from the DDD; the system will re-initialize based on the new learning mode selected. Existing Patients Return-to-Clinic Visit Interval (EPRVI) = learning mode "0" and New Patient Start Rate (NPSR) = learning mode "1".
-6. **Learning Mode Labels**: Indicates which Learning Mode the data prioritizes. Click these buttons to change the learning modes directly from the DDD; the system will re-initialize based on the new learning mode selected. Existing Patients Return-to-Clinic Visit Interval (EPRVI) = learning mode "0" and New Patient Start Rate (NPSR) = learning mode "1".
+6. **Team Care Services Radio Buttons**: Select desired service radio button to see stock values for specific services in Team Care (Intake, Care Coordination, Medication Management, Psychotherapy, Evidence-based Psychotherapy, Adjunctive Services, Group Therapy). The default display is Intake evaluations.
-7. **Meds Needed Radio Buttons**: Select desired meds needed radio button to see stock values for medication-specific services (Alcohol Use Disorder, Depression, Opioid Use Disorder, and Other).
+7. **Medication Management Services Radio Buttons**: Select desired service radio button to see stock values for medication-specific services in Medication Management (Alcohol Use Disorder, Depression, Opioid Use Disorder, and Other). The defaut display is Alcolol Use Disorder.
-8. **"i" icon**: Click these to read the definition of each stock label.
+8. **"i" icon**: Click "i" icons to read the definition of each stock label.
-9. **Setting Radio Buttons**: Select desired setting radio button to see stock values for setting-specific services in Team Flow (General Mental Health, Specialty Mental Health, Primary Care/Primary Care Mental Health Integration).
+9. **Team Flow Services Radio Buttons**: Select desired service radio button to see stock values for setting-specific services in Team Flow (General Mental Health, Specialty Mental Health, Primary Care/Primary Care Mental Health Integration). The default display is General Mental Health.
10. **Community**: Click here to participate by sharing an idea, letting the team know what you like, asking a question, or joining our community.
@@ -497,7 +498,7 @@ Each story has its own unique feedback loop that shows named balancing and reinf
Decision Meters are a quick infographic-based way to identify the highest leverage points and are highly supportive of clinical decision-making; they are for "decider" users who need systems thinking insights. The meters provide a visual interface that provides real-time feedback on ranges in our primary _MTL_ units of patients/week and appointments/week. The traffic light reflects the current state results and _recommendation_ of future state results. Through dialogue with decision-makers, consultants and field users manually input values into this graphic generator so the decision meters reflect the recommendations based on the alternative scenarios/experiments run by the learner. Decision meter numbers should be reflected in the "D" box of the Q/H/F/D outputs text field within the Sim UI, usually as ranges of numbers.
-- Care Decision Meters are for _MTL_ Blue teams only.
+- Care Decision Meters are for _MTL Blue_ teams only.
- Click within each decision meter to edit. Remember to click Save if you want the values to remain!
For illustrative purposes, the Medication Management Decisions window is used as an example below to orient you to general Decisions pop-up window features.
@@ -524,7 +525,7 @@ For illustrative purposes, the Medication Management Decisions window is used as
##### Episodes of Care
-Timely access to high-quality care includes improved understanding of dynamic tradeoffs in the return-to-clinic visit interval and engagement durations. The Episodes of Care pop-up is used to graphically show evidence-based episode of care intervals to get a bird's eye view of how long the length of engagement will be. Available within the Medication Management, Psychotherapy, and Team Care modules, this pop-up integrates engagement duration and Return-to-Clinic Visit Interval (RVI) for both Medication Management and Psychotherapy.
+Timely access to high-quality care includes improved understanding of dynamic tradeoffs in the Return-to-Clinic Visit Interval (RVI) and engagement durations. The Episodes of Care pop-up is used to graphically show evidence-based episode of care intervals to get a bird's eye view of how long the length of engagement will be. Available within the Medication Management, Psychotherapy, and Team Care modules, this pop-up integrates engagement duration and RVI for both Medication Management and Psychotherapy.
The following screenshot will orient you to general features of this pop-up.
@@ -562,7 +563,7 @@ This section explains how to enter and save an experiment in the Sim UI.
- **Note:** For CC and MM, select your Learning Mode before hitting Play.
- - Refer to the Care Coordination (CCParams) or Medication Management (MMParams) tab of the Team Data Table at mtl.how/data, for data regarding the team’s New Patient Start Rates and Return-to-Clinic Intervals.
+ - Refer to the Care Coordination (CCParams) or Medication Management (MMParams) tab of the Team Data Table at mtl.how/data, for data regarding the team’s New Patient Start Rates and Return-to-Clinic Visit Intervals.
3. To run a simulation for any module within the dashboard, select Play found within each module's More menu.
@@ -582,7 +583,7 @@ This section explains how to enter and save an experiment in the Sim UI.
#### Orient to the Sim UI
-**Tip:** Save this [Sim UI cheatsheet](https://github.com/lzim/mtl/blob/master/blue/session05/s05_learner/mtl_how_3.7_sim_ui_cheatsheet.pdf) to use when running an experiment.
+**Tip:** Save this [Sim UI cheatsheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lzim/mtl/gh-pages/images/mtl_how_3.7_sim_ui_cheatsheet.pdf) to use when running an experiment.
Below is an orientation to the Play Page of the Sim UI.
@@ -606,40 +607,6 @@ Below is an orientation to the Play Page of the Sim UI.
- **9**: Text: Enter Q/H/F/Ds. Click on expand icon in blue bar for full functions.
-### Manage Discussions in Team
-
-- The Team button in the top navigation is for texting and maintaining private discussion threads with one or more individuals and open discussion threads with teams.
-- A person can chat with one or more people using the Team function by inputting the end user name (usually the va.gov email address) of the person or people they want to address.
-- A person can chat with an entire team at once, provided they are a registered end user in that team.
-
-#### Set up a Private Conversation
-
-1. Click "Team" to open the chat pop-up.
-
- -
-2. Click Chat in the left-hand navigation to private-text an individual. The latest conversation will appear in the Chat Log, followed the next recent. The discussion thread appears in the Conversation window.
-
-
-
-2. Click Chat in the left-hand navigation to private-text an individual. The latest conversation will appear in the Chat Log, followed the next recent. The discussion thread appears in the Conversation window.
-
- -
-3. To continue a conversation, type a new message in the message line at the bottom of the window. Click the Send icon to post the chat.
-
-
-
-3. To continue a conversation, type a new message in the message line at the bottom of the window. Click the Send icon to post the chat.
-
- -
-4. To start a conversation with one or more new people, click the New icon and enter their user name and click Add. Type a new message and click Send.
-
-
-
-4. To start a conversation with one or more new people, click the New icon and enter their user name and click Add. Type a new message and click Send.
-
- -
-#### Set up an Open Team Discussion
-
-1. Click on the Team icon in the left-hand navigation. **Note how the icon has a red circle indicating there are 2 chats waiting.**
-
-
-
-#### Set up an Open Team Discussion
-
-1. Click on the Team icon in the left-hand navigation. **Note how the icon has a red circle indicating there are 2 chats waiting.**
-
- -
-2. The Teams listing will contain a list of all teams the individual is a registered end user (see blue-green highlight). A boldface team indicates a chat is waiting. **Note the listing contains _ind teams. These are teams where users are assigned an individual world with which to experiment. However, any discussions held in this thread will be visible by all registered users from their different worlds.** To have a private chat with an individual, see [Set up a Private Conversation](#set-up-a-private-conversation).
-
-
-
-2. The Teams listing will contain a list of all teams the individual is a registered end user (see blue-green highlight). A boldface team indicates a chat is waiting. **Note the listing contains _ind teams. These are teams where users are assigned an individual world with which to experiment. However, any discussions held in this thread will be visible by all registered users from their different worlds.** To have a private chat with an individual, see [Set up a Private Conversation](#set-up-a-private-conversation).
-
- -
### Resize a Window for Side-by-Side Viewing
- An administrator may need to show two items on the screen side-by-side for comparison. Field users may also want to view two items on the screen for comparison or reference.
@@ -673,7 +640,7 @@ Below is an orientation to the Play Page of the Sim UI.
-
### Resize a Window for Side-by-Side Viewing
- An administrator may need to show two items on the screen side-by-side for comparison. Field users may also want to view two items on the screen for comparison or reference.
@@ -673,7 +640,7 @@ Below is an orientation to the Play Page of the Sim UI.
 @@ -695,7 +662,7 @@ Below is an orientation to the Play Page of the Sim UI.
@@ -695,7 +662,7 @@ Below is an orientation to the Play Page of the Sim UI.
 -4. Complete the Issue Form. **Do not include PII or other Site identifiable information. Instead, use generic language such as “_MTL_ Blue live team on Mondays at 9am.”**
+4. Complete the Issue Form. **Do not include PII or other Site identifiable information. Instead, use generic language such as “_MTL Blue_ live team on Mondays at 9am.”**
-4. Complete the Issue Form. **Do not include PII or other Site identifiable information. Instead, use generic language such as “_MTL_ Blue live team on Mondays at 9am.”**
+4. Complete the Issue Form. **Do not include PII or other Site identifiable information. Instead, use generic language such as “_MTL Blue_ live team on Mondays at 9am.”**
 @@ -869,7 +836,7 @@ Within the Facility Team Setup area of this pop-up, several team setup options a
### Manage Team Data
-**Note: Only administrators and the internal team have access to these functions.** Field users can upload their data file(s) from the Dynamic Decision Dashboard (as well as administrators and the internal team). Field users should refer to the [Dynamic Decision Dashboard manual section](#dynamic-decision-dasboard).
+**Note: Only administrators and the internal team have access to these functions.** Field users can upload their data file(s) from the Dynamic Decision Dashboard (as well as administrators and the internal team). Field users should refer to the [Dynamic Decision Dashboard section](#dynamic-decision-dashboard).
- Administrators can upload team data files and assign that file(s) to team(s) of their choice.
@@ -1133,7 +1100,7 @@ Forio Epicenter is an enterprise platform that hosts our Sim UI and runs the sim
#### Send Password Reset to End User or Change Password
-1. Log into Epicenter.
+1. Log into [Epicenter](https://forio.com/epicenter/sign-in).
2. Click on Veterans Affairs.
@@ -869,7 +836,7 @@ Within the Facility Team Setup area of this pop-up, several team setup options a
### Manage Team Data
-**Note: Only administrators and the internal team have access to these functions.** Field users can upload their data file(s) from the Dynamic Decision Dashboard (as well as administrators and the internal team). Field users should refer to the [Dynamic Decision Dashboard manual section](#dynamic-decision-dasboard).
+**Note: Only administrators and the internal team have access to these functions.** Field users can upload their data file(s) from the Dynamic Decision Dashboard (as well as administrators and the internal team). Field users should refer to the [Dynamic Decision Dashboard section](#dynamic-decision-dashboard).
- Administrators can upload team data files and assign that file(s) to team(s) of their choice.
@@ -1133,7 +1100,7 @@ Forio Epicenter is an enterprise platform that hosts our Sim UI and runs the sim
#### Send Password Reset to End User or Change Password
-1. Log into Epicenter.
+1. Log into [Epicenter](https://forio.com/epicenter/sign-in).
2. Click on Veterans Affairs.
 diff --git a/index.Rmd b/index.Rmd
index d0e050da..f0a6eaae 100644
--- a/index.Rmd
+++ b/index.Rmd
@@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
---
-title: "_Modeling to Learn_ 3.7 Consult Manual"
+title: "_Modeling to Learn 3.7 Consult Manual_"
author: "Team PSD"
date: "`r Sys.Date()`"
link-citations: yes
preview: yes
site: bookdown::bookdown_site
-description: This is the MTL one-stop shop.
+description: This is the _MTL_ one-stop shop.
---
# _Why_ use _Modeling to Learn_
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. You might wonder _What is _Modeling to Learn
[
diff --git a/index.Rmd b/index.Rmd
index d0e050da..f0a6eaae 100644
--- a/index.Rmd
+++ b/index.Rmd
@@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
---
-title: "_Modeling to Learn_ 3.7 Consult Manual"
+title: "_Modeling to Learn 3.7 Consult Manual_"
author: "Team PSD"
date: "`r Sys.Date()`"
link-citations: yes
preview: yes
site: bookdown::bookdown_site
-description: This is the MTL one-stop shop.
+description: This is the _MTL_ one-stop shop.
---
# _Why_ use _Modeling to Learn_
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. You might wonder _What is _Modeling to Learn
[ ](https://bcove.video/3WuJ7kI)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. _Modeling to Learn_ improves visibility and provides new insights into how common care problems persist over time. How? _Modeling to Learn_ is based on over 60 years of scholarship known as participatory system dynamics. For this reason, we call ourselves Team PSD for Team Participatory System Dynamics. The Data User Interface and Simulation User Interface comprise two versions of _Modeling to Learn_. The data-only version is known as _Modeling to Learn_ Red; _Modeling to Learn_ Blue ads participatory learning from simulation. Team PSD supports _MTL_ Red and _MTL_ Blue and is carefully evaluating how each works to support VA in meeting Veterans needs. Learning from simulation can help us to place a better initial bet on what is likely to work locally by evaluating alternative decisions via simulation before we implement them in the real world. _MTL_ Red tells us where we've been over the last two years based on the clinic selections made to produce the patient data reports and team trends or visualizations. Many staff report that viewing the Data UI real-time patient data tabs or the team trends is efficient and encouraging. The data tabs help with clinical decision making. The visualizations of team trends provide leading indicators that improvement efforts are paying off, which can be validating. Why is _Modeling to Learn_ useful when we have critical staffing and hiring needs? Watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. _Modeling to Learn_ improves visibility and provides new insights into how common care problems persist over time. How? _Modeling to Learn_ is based on over 60 years of scholarship known as participatory system dynamics. For this reason, we call ourselves Team PSD for Team Participatory System Dynamics. The Data User Interface and Simulation User Interface comprise two versions of _Modeling to Learn_. The data-only version is known as _Modeling to Learn Red_; _Modeling to Learn Blue_ ads participatory learning from simulation. Team PSD supports _MTL Red_ and _MTL Blue_ and is carefully evaluating how each works to support VA in meeting Veterans needs. Learning from simulation can help us to place a better initial bet on what is likely to work locally by evaluating alternative decisions via simulation before we implement them in the real world. _MTL Red_ tells us where we've been over the last two years based on the clinic selections made to produce the patient data reports and team trends or visualizations. Many staff report that viewing the Data UI real-time patient data tabs or the team trends is efficient and encouraging. The data tabs help with clinical decision making. The visualizations of team trends provide leading indicators that improvement efforts are paying off, which can be validating. Why is _Modeling to Learn_ useful when we have critical staffing and hiring needs? Watch that video to find out.
## What gets in the way of meeting patients' needs?
@@ -49,23 +49,23 @@ Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. What if we keep making the same care decisio
[
](https://bcove.video/3WuJ7kI)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. _Modeling to Learn_ improves visibility and provides new insights into how common care problems persist over time. How? _Modeling to Learn_ is based on over 60 years of scholarship known as participatory system dynamics. For this reason, we call ourselves Team PSD for Team Participatory System Dynamics. The Data User Interface and Simulation User Interface comprise two versions of _Modeling to Learn_. The data-only version is known as _Modeling to Learn_ Red; _Modeling to Learn_ Blue ads participatory learning from simulation. Team PSD supports _MTL_ Red and _MTL_ Blue and is carefully evaluating how each works to support VA in meeting Veterans needs. Learning from simulation can help us to place a better initial bet on what is likely to work locally by evaluating alternative decisions via simulation before we implement them in the real world. _MTL_ Red tells us where we've been over the last two years based on the clinic selections made to produce the patient data reports and team trends or visualizations. Many staff report that viewing the Data UI real-time patient data tabs or the team trends is efficient and encouraging. The data tabs help with clinical decision making. The visualizations of team trends provide leading indicators that improvement efforts are paying off, which can be validating. Why is _Modeling to Learn_ useful when we have critical staffing and hiring needs? Watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is David. _Modeling to Learn_ improves visibility and provides new insights into how common care problems persist over time. How? _Modeling to Learn_ is based on over 60 years of scholarship known as participatory system dynamics. For this reason, we call ourselves Team PSD for Team Participatory System Dynamics. The Data User Interface and Simulation User Interface comprise two versions of _Modeling to Learn_. The data-only version is known as _Modeling to Learn Red_; _Modeling to Learn Blue_ ads participatory learning from simulation. Team PSD supports _MTL Red_ and _MTL Blue_ and is carefully evaluating how each works to support VA in meeting Veterans needs. Learning from simulation can help us to place a better initial bet on what is likely to work locally by evaluating alternative decisions via simulation before we implement them in the real world. _MTL Red_ tells us where we've been over the last two years based on the clinic selections made to produce the patient data reports and team trends or visualizations. Many staff report that viewing the Data UI real-time patient data tabs or the team trends is efficient and encouraging. The data tabs help with clinical decision making. The visualizations of team trends provide leading indicators that improvement efforts are paying off, which can be validating. Why is _Modeling to Learn_ useful when we have critical staffing and hiring needs? Watch that video to find out.
## What gets in the way of meeting patients' needs?
@@ -49,23 +49,23 @@ Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. What if we keep making the same care decisio
[ ](https://bcove.video/4f7OfSL)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Leaders and clinicians often ask how can _Modeling to Learn_ be useful when facing critical staffing and hiring needs? With limited staff coverage, the need to hire is priority number one, but even then there isn't a magic wand that produces staff where they may not exist today. What could help now? From the beginning, _Modeling to Learn_ prioritized evidence-based episodes of care within existing staff time. When modeling to learn launched nationally in the VA in March of 2020, it was to empower staff to find the highest yield local improvements without asking staff to do more with less. As a result, when staff coverage may not change quickly, _Modeling to Learn_ will find options for improving quality of care for Veterans and quality of work life for providers. How? What does Debbie mean by high yield local improvements? Because evidence-based behavioral healthcare is delivered over time, there are many possibilities. Small decisions made all day, every day by the clinicians, when compounded over time, can be surprisingly powerful. Think of your savings account or your waistline. In _Modeling to Learn_, we look for the lightest clinical lift teams and VAs can make that have the biggest payoff for Veterans in terms of timely, high-quality care. We work hard to avoid big difficult changes with limited benefit. When working with the _Modeling to Learn_-read data user interface, clinical teams are often motivated when they see trends that reflect hard-won efforts to implement high quality episodes of care which may not show up in other data systems for some time. The _Modeling to Learn_ Blue simulation user interface saves staff time because alternatives can quickly be assessed during a modeling consultation. Change is hard, but we no longer have to learn by trial and error, wearing out already burdened staff. Does that sound too good to be true? If so, you may be wondering about examples of _Modeling to Learn_ use cases for the pain points you face in your specific team or program. As an example, how does _Modeling to Learn_ benefit substance use disorder, or SUD programs? Watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Leaders and clinicians often ask how can _Modeling to Learn_ be useful when facing critical staffing and hiring needs? With limited staff coverage, the need to hire is priority number one, but even then there isn't a magic wand that produces staff where they may not exist today. What could help now? From the beginning, _Modeling to Learn_ prioritized evidence-based episodes of care within existing staff time. When _Modeling to Learn_ launched nationally in the VA in March of 2020, it was to empower staff to find the highest yield local improvements without asking staff to do more with less. As a result, when staff coverage may not change quickly, _Modeling to Learn_ will find options for improving quality of care for Veterans and quality of work life for providers. How? What does Debbie mean by high yield local improvements? Because evidence-based behavioral healthcare is delivered over time, there are many possibilities. Small decisions made all day, every day by the clinicians, when compounded over time, can be surprisingly powerful. Think of your savings account or your waistline. In _Modeling to Learn_, we look for the lightest clinical lift teams and VAs can make that have the biggest payoff for Veterans in terms of timely, high-quality care. We work hard to avoid big difficult changes with limited benefit. When working with the _Modeling to Learn_-read data user interface, clinical teams are often motivated when they see trends that reflect hard-won efforts to implement high quality episodes of care which may not show up in other data systems for some time. The _Modeling to Learn Blue_ simulation user interface saves staff time because alternatives can quickly be assessed during a modeling consultation. Change is hard, but we no longer have to learn by trial and error, wearing out already burdened staff. Does that sound too good to be true? If so, you may be wondering about examples of _Modeling to Learn_ use cases for the pain points you face in your specific team or program. As an example, how does _Modeling to Learn_ benefit substance use disorder, or SUD programs? Watch that video to find out.
-## Why is the _MTL_ Red Data User Interface useful?
+## Why is the _MTL Red_ Data User Interface useful?
[Watch the video here.](https://bcove.video/3A6i7Py)
[
](https://bcove.video/4f7OfSL)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Leaders and clinicians often ask how can _Modeling to Learn_ be useful when facing critical staffing and hiring needs? With limited staff coverage, the need to hire is priority number one, but even then there isn't a magic wand that produces staff where they may not exist today. What could help now? From the beginning, _Modeling to Learn_ prioritized evidence-based episodes of care within existing staff time. When modeling to learn launched nationally in the VA in March of 2020, it was to empower staff to find the highest yield local improvements without asking staff to do more with less. As a result, when staff coverage may not change quickly, _Modeling to Learn_ will find options for improving quality of care for Veterans and quality of work life for providers. How? What does Debbie mean by high yield local improvements? Because evidence-based behavioral healthcare is delivered over time, there are many possibilities. Small decisions made all day, every day by the clinicians, when compounded over time, can be surprisingly powerful. Think of your savings account or your waistline. In _Modeling to Learn_, we look for the lightest clinical lift teams and VAs can make that have the biggest payoff for Veterans in terms of timely, high-quality care. We work hard to avoid big difficult changes with limited benefit. When working with the _Modeling to Learn_-read data user interface, clinical teams are often motivated when they see trends that reflect hard-won efforts to implement high quality episodes of care which may not show up in other data systems for some time. The _Modeling to Learn_ Blue simulation user interface saves staff time because alternatives can quickly be assessed during a modeling consultation. Change is hard, but we no longer have to learn by trial and error, wearing out already burdened staff. Does that sound too good to be true? If so, you may be wondering about examples of _Modeling to Learn_ use cases for the pain points you face in your specific team or program. As an example, how does _Modeling to Learn_ benefit substance use disorder, or SUD programs? Watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Leaders and clinicians often ask how can _Modeling to Learn_ be useful when facing critical staffing and hiring needs? With limited staff coverage, the need to hire is priority number one, but even then there isn't a magic wand that produces staff where they may not exist today. What could help now? From the beginning, _Modeling to Learn_ prioritized evidence-based episodes of care within existing staff time. When _Modeling to Learn_ launched nationally in the VA in March of 2020, it was to empower staff to find the highest yield local improvements without asking staff to do more with less. As a result, when staff coverage may not change quickly, _Modeling to Learn_ will find options for improving quality of care for Veterans and quality of work life for providers. How? What does Debbie mean by high yield local improvements? Because evidence-based behavioral healthcare is delivered over time, there are many possibilities. Small decisions made all day, every day by the clinicians, when compounded over time, can be surprisingly powerful. Think of your savings account or your waistline. In _Modeling to Learn_, we look for the lightest clinical lift teams and VAs can make that have the biggest payoff for Veterans in terms of timely, high-quality care. We work hard to avoid big difficult changes with limited benefit. When working with the _Modeling to Learn_-read data user interface, clinical teams are often motivated when they see trends that reflect hard-won efforts to implement high quality episodes of care which may not show up in other data systems for some time. The _Modeling to Learn Blue_ simulation user interface saves staff time because alternatives can quickly be assessed during a modeling consultation. Change is hard, but we no longer have to learn by trial and error, wearing out already burdened staff. Does that sound too good to be true? If so, you may be wondering about examples of _Modeling to Learn_ use cases for the pain points you face in your specific team or program. As an example, how does _Modeling to Learn_ benefit substance use disorder, or SUD programs? Watch that video to find out.
-## Why is the _MTL_ Red Data User Interface useful?
+## Why is the _MTL Red_ Data User Interface useful?
[Watch the video here.](https://bcove.video/3A6i7Py)
[ ](https://bcove.video/3A6i7Py)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Why is _Modeling to Learn_ Red useful and how does the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface provide new insights? The primary value of _MTL_ Red is its power to efficiently query the VA Corporate Data Warehouse directly, and we've come a long way over the years. Yes we have. When we first began, we were using an Excel workbook so that frontline teams could carefully review the clinic selections that define their _Modeling to Learn_ team data sets. Fast forward to the present and now teams have real time data available to them from within the VA domain from any computer with PIV badge access. Since the Data UI includes PHI, if you go to [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf), you will be able to see the same data you have permissions to access in the electronic health record. But given that clinicians, managers, data leads, quality improvement staff, evaluators … well, basically everyone is so busy, no one has time to review another data dashboard unless it offers something of really high value that distinguishes it from other resources. When you request a _Modeling to Learn_ Red consultation, we work with your team or VA to explore care data that can address your locally identified priority. Clinics or scheduling grids are often changing. For that reason, we wanted a user interface where clinic selections can include active or inactive clinics over the last two years. That way, the team can filter the information to find the most appropriate clinics to include in their data set to gain new insights. And in Team Flow, clinic selections can be used to evaluate transitions between an episode of care in one team and the start of another episode of care in a higher or lower intensity care setting. _Modeling to Learn_ Red also enables zooming in to check on the care of an individual patient at the start of the clinical day or during case reviews at a team meeting. But with the _MTL_ Red Data User Interface, you can also zoom out to view teen care trends, bringing patient-level care coordination and trend-level process improvement decisions together. And that's where things start to get interesting. Based on the clinic selections, the next set of tabs to find local data values for common care problems, including care coordination, psychotherapy, medication management, team care, and team flow. Each tab features simple definitions of how data were estimated for the common care problem. Detailed definitions with technical specifications are also provided to allow valid comparison of these data to other VA dashboards. That said, a focus on data details could be frustrating and add limited value. _Modeling to Learn_ emphasizes understanding system problems in care flow over time. These care flow problems can be defined accurately with just five key time-based variables that drive care quality. How do five key variables drive care quality? Watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Why is _Modeling to Learn Red_ useful and how does the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface provide new insights? The primary value of _MTL_ Red is its power to efficiently query the VA Corporate Data Warehouse directly, and we've come a long way over the years. Yes we have. When we first began, we were using an Excel workbook so that frontline teams could carefully review the clinic selections that define their _Modeling to Learn_ team data sets. Fast forward to the present and now teams have real time data available to them from within the VA domain from any computer with PIV badge access. Since the Data UI includes PHI, if you go to [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf), you will be able to see the same data you have permissions to access in the electronic health record. But given that clinicians, managers, data leads, quality improvement staff, evaluators … well, basically everyone is so busy, no one has time to review another data dashboard unless it offers something of really high value that distinguishes it from other resources. When you request a _Modeling to Learn Red_ consultation, we work with your team or VA to explore care data that can address your locally identified priority. Clinics or scheduling grids are often changing. For that reason, we wanted a user interface where clinic selections can include active or inactive clinics over the last two years. That way, the team can filter the information to find the most appropriate clinics to include in their data set to gain new insights. And in Team Flow, clinic selections can be used to evaluate transitions between an episode of care in one team and the start of another episode of care in a higher or lower intensity care setting. _Modeling to Learn Red_ also enables zooming in to check on the care of an individual patient at the start of the clinical day or during case reviews at a team meeting. But with the _MTL_ Red Data User Interface, you can also zoom out to view teen care trends, bringing patient-level care coordination and trend-level process improvement decisions together. And that's where things start to get interesting. Based on the clinic selections, the next set of tabs to find local data values for common care problems, including care coordination, psychotherapy, medication management, team care, and team flow. Each tab features simple definitions of how data were estimated for the common care problem. Detailed definitions with technical specifications are also provided to allow valid comparison of these data to other VA dashboards. That said, a focus on data details could be frustrating and add limited value. _Modeling to Learn_ emphasizes understanding system problems in care flow over time. These care flow problems can be defined accurately with just five key time-based variables that drive care quality. How do five key variables drive care quality? Watch that video to find out.
-## Why is the _MTL_ Blue Simulation User Interface useful?
+## Why is the _MTL Blue_ Simulation User Interface useful?
[Watch the video here.](https://bcove.video/4fnG5Gb)
[
](https://bcove.video/3A6i7Py)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Why is _Modeling to Learn_ Red useful and how does the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface provide new insights? The primary value of _MTL_ Red is its power to efficiently query the VA Corporate Data Warehouse directly, and we've come a long way over the years. Yes we have. When we first began, we were using an Excel workbook so that frontline teams could carefully review the clinic selections that define their _Modeling to Learn_ team data sets. Fast forward to the present and now teams have real time data available to them from within the VA domain from any computer with PIV badge access. Since the Data UI includes PHI, if you go to [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf), you will be able to see the same data you have permissions to access in the electronic health record. But given that clinicians, managers, data leads, quality improvement staff, evaluators … well, basically everyone is so busy, no one has time to review another data dashboard unless it offers something of really high value that distinguishes it from other resources. When you request a _Modeling to Learn_ Red consultation, we work with your team or VA to explore care data that can address your locally identified priority. Clinics or scheduling grids are often changing. For that reason, we wanted a user interface where clinic selections can include active or inactive clinics over the last two years. That way, the team can filter the information to find the most appropriate clinics to include in their data set to gain new insights. And in Team Flow, clinic selections can be used to evaluate transitions between an episode of care in one team and the start of another episode of care in a higher or lower intensity care setting. _Modeling to Learn_ Red also enables zooming in to check on the care of an individual patient at the start of the clinical day or during case reviews at a team meeting. But with the _MTL_ Red Data User Interface, you can also zoom out to view teen care trends, bringing patient-level care coordination and trend-level process improvement decisions together. And that's where things start to get interesting. Based on the clinic selections, the next set of tabs to find local data values for common care problems, including care coordination, psychotherapy, medication management, team care, and team flow. Each tab features simple definitions of how data were estimated for the common care problem. Detailed definitions with technical specifications are also provided to allow valid comparison of these data to other VA dashboards. That said, a focus on data details could be frustrating and add limited value. _Modeling to Learn_ emphasizes understanding system problems in care flow over time. These care flow problems can be defined accurately with just five key time-based variables that drive care quality. How do five key variables drive care quality? Watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Why is _Modeling to Learn Red_ useful and how does the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface provide new insights? The primary value of _MTL_ Red is its power to efficiently query the VA Corporate Data Warehouse directly, and we've come a long way over the years. Yes we have. When we first began, we were using an Excel workbook so that frontline teams could carefully review the clinic selections that define their _Modeling to Learn_ team data sets. Fast forward to the present and now teams have real time data available to them from within the VA domain from any computer with PIV badge access. Since the Data UI includes PHI, if you go to [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138/reports/05dd8dbd-313f-4993-b406-6feea2fdb060/ReportSection?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf), you will be able to see the same data you have permissions to access in the electronic health record. But given that clinicians, managers, data leads, quality improvement staff, evaluators … well, basically everyone is so busy, no one has time to review another data dashboard unless it offers something of really high value that distinguishes it from other resources. When you request a _Modeling to Learn Red_ consultation, we work with your team or VA to explore care data that can address your locally identified priority. Clinics or scheduling grids are often changing. For that reason, we wanted a user interface where clinic selections can include active or inactive clinics over the last two years. That way, the team can filter the information to find the most appropriate clinics to include in their data set to gain new insights. And in Team Flow, clinic selections can be used to evaluate transitions between an episode of care in one team and the start of another episode of care in a higher or lower intensity care setting. _Modeling to Learn Red_ also enables zooming in to check on the care of an individual patient at the start of the clinical day or during case reviews at a team meeting. But with the _MTL_ Red Data User Interface, you can also zoom out to view teen care trends, bringing patient-level care coordination and trend-level process improvement decisions together. And that's where things start to get interesting. Based on the clinic selections, the next set of tabs to find local data values for common care problems, including care coordination, psychotherapy, medication management, team care, and team flow. Each tab features simple definitions of how data were estimated for the common care problem. Detailed definitions with technical specifications are also provided to allow valid comparison of these data to other VA dashboards. That said, a focus on data details could be frustrating and add limited value. _Modeling to Learn_ emphasizes understanding system problems in care flow over time. These care flow problems can be defined accurately with just five key time-based variables that drive care quality. How do five key variables drive care quality? Watch that video to find out.
-## Why is the _MTL_ Blue Simulation User Interface useful?
+## Why is the _MTL Blue_ Simulation User Interface useful?
[Watch the video here.](https://bcove.video/4fnG5Gb)
[ ](https://bcove.video/4fnG5Gb)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Why is _Modeling to Learn_ Blue useful? Well, why is it wisest to focus on the dynamics of care over time? The short answer is that clinical and improvement teams cannot adjust one part of the care equation without everything else changing. In _Modeling to Learn_ Blue, we zoom out to see how care variables are locked in relationship with one another over time. The key variables that define either a poor quality or high quality episode of care must be understood together. Building from _MTL_ Red, you can export your local data set created in the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf). Then, if you navigate to [mtl.how/sim](https://forio.com/app/va/va-psd-sim/login.html), you can find the _Modeling to Learn_ Blue Simulation User Interface, which is a dynamic and interactive way to understand why problems with care coordination, medication management, psychotherapy, team care, and team flow persist over time. The Simulation User Interface is a way to see how adjustments in one part of an episode of care explain subsequent impacts in the care system. For any of the common care problems, the simulation saves you time and energy by accounting for the local new patient start rate in patients per week and the local appointment supply and appointments per week. The simulation also keeps track of the local new patient wait time in weeks, time between visits and weeks, and the engagement duration over time, again in weeks. All are calculated for you automatically in the Data User Interface, but their interdependence is accounted for in the Simulation User Interface. The _Modeling to Learn_ Blue Simulation User Interface empowers teams to avoid ineffective strategies because you very quickly learn to develop new insights that would be inefficient, if not impossible, to figure out in your head or by hand. Learning from simulation is designed to help upgrade local decision-making. Teams develop new rules of thumb and insights in which the dependent dynamics among these variables that define care are all taken into account. With a _Modeling to Learn_ consult, we come alongside with partners mid stride in their daily clinical activities who may have limited insight into what is likely to happen over the near future if they keep making the same decisions every day. With _Modeling to Learn_ Blue simulation learning, sites and teams can safely see the impact of new decisions while building new capacities for systems thinking. Why is applied systems thinking more likely to help us avoid costly mistakes? Watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Why is _Modeling to Learn Blue_ useful? Well, why is it wisest to focus on the dynamics of care over time? The short answer is that clinical and improvement teams cannot adjust one part of the care equation without everything else changing. In _Modeling to Learn Blue_, we zoom out to see how care variables are locked in relationship with one another over time. The key variables that define either a poor quality or high quality episode of care must be understood together. Building from _MTL_ Red, you can export your local data set created in the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf). Then, if you navigate to [mtl.how/sim](https://forio.com/app/va/va-psd-sim/login.html), you can find the _Modeling to Learn Blue_ Simulation User Interface, which is a dynamic and interactive way to understand why problems with care coordination, medication management, psychotherapy, team care, and team flow persist over time. The Simulation User Interface is a way to see how adjustments in one part of an episode of care explain subsequent impacts in the care system. For any of the common care problems, the simulation saves you time and energy by accounting for the local new patient start rate in patients per week and the local appointment supply and appointments per week. The simulation also keeps track of the local new patient wait time in weeks, time between visits and weeks, and the engagement duration over time, again in weeks. All are calculated for you automatically in the Data User Interface, but their interdependence is accounted for in the Simulation User Interface. The _Modeling to Learn Blue_ Simulation User Interface empowers teams to avoid ineffective strategies because you very quickly learn to develop new insights that would be inefficient, if not impossible, to figure out in your head or by hand. Learning from simulation is designed to help upgrade local decision-making. Teams develop new rules of thumb and insights in which the dependent dynamics among these variables that define care are all taken into account. With a _Modeling to Learn_ consult, we come alongside with partners mid stride in their daily clinical activities who may have limited insight into what is likely to happen over the near future if they keep making the same decisions every day. With _Modeling to Learn Blue_ simulation learning, sites and teams can safely see the impact of new decisions while building new capacities for systems thinking. Why is applied systems thinking more likely to help us avoid costly mistakes? Watch that video to find out.
## Why is applied systems thinking more likely to help us avoid costly mistakes?
](https://bcove.video/4fnG5Gb)
-Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Why is _Modeling to Learn_ Blue useful? Well, why is it wisest to focus on the dynamics of care over time? The short answer is that clinical and improvement teams cannot adjust one part of the care equation without everything else changing. In _Modeling to Learn_ Blue, we zoom out to see how care variables are locked in relationship with one another over time. The key variables that define either a poor quality or high quality episode of care must be understood together. Building from _MTL_ Red, you can export your local data set created in the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf). Then, if you navigate to [mtl.how/sim](https://forio.com/app/va/va-psd-sim/login.html), you can find the _Modeling to Learn_ Blue Simulation User Interface, which is a dynamic and interactive way to understand why problems with care coordination, medication management, psychotherapy, team care, and team flow persist over time. The Simulation User Interface is a way to see how adjustments in one part of an episode of care explain subsequent impacts in the care system. For any of the common care problems, the simulation saves you time and energy by accounting for the local new patient start rate in patients per week and the local appointment supply and appointments per week. The simulation also keeps track of the local new patient wait time in weeks, time between visits and weeks, and the engagement duration over time, again in weeks. All are calculated for you automatically in the Data User Interface, but their interdependence is accounted for in the Simulation User Interface. The _Modeling to Learn_ Blue Simulation User Interface empowers teams to avoid ineffective strategies because you very quickly learn to develop new insights that would be inefficient, if not impossible, to figure out in your head or by hand. Learning from simulation is designed to help upgrade local decision-making. Teams develop new rules of thumb and insights in which the dependent dynamics among these variables that define care are all taken into account. With a _Modeling to Learn_ consult, we come alongside with partners mid stride in their daily clinical activities who may have limited insight into what is likely to happen over the near future if they keep making the same decisions every day. With _Modeling to Learn_ Blue simulation learning, sites and teams can safely see the impact of new decisions while building new capacities for systems thinking. Why is applied systems thinking more likely to help us avoid costly mistakes? Watch that video to find out.
+Hi, I'm Lindsey and this is Debbie. Why is _Modeling to Learn Blue_ useful? Well, why is it wisest to focus on the dynamics of care over time? The short answer is that clinical and improvement teams cannot adjust one part of the care equation without everything else changing. In _Modeling to Learn Blue_, we zoom out to see how care variables are locked in relationship with one another over time. The key variables that define either a poor quality or high quality episode of care must be understood together. Building from _MTL_ Red, you can export your local data set created in the _Modeling to Learn_ Data User Interface at [mtl.how/data](https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/apps/b9686a29-6857-46c9-bdf9-043ca2b29138?ctid=e95f1b23-abaf-45ee-821d-b7ab251ab3bf). Then, if you navigate to [mtl.how/sim](https://forio.com/app/va/va-psd-sim/login.html), you can find the _Modeling to Learn Blue_ Simulation User Interface, which is a dynamic and interactive way to understand why problems with care coordination, medication management, psychotherapy, team care, and team flow persist over time. The Simulation User Interface is a way to see how adjustments in one part of an episode of care explain subsequent impacts in the care system. For any of the common care problems, the simulation saves you time and energy by accounting for the local new patient start rate in patients per week and the local appointment supply and appointments per week. The simulation also keeps track of the local new patient wait time in weeks, time between visits and weeks, and the engagement duration over time, again in weeks. All are calculated for you automatically in the Data User Interface, but their interdependence is accounted for in the Simulation User Interface. The _Modeling to Learn Blue_ Simulation User Interface empowers teams to avoid ineffective strategies because you very quickly learn to develop new insights that would be inefficient, if not impossible, to figure out in your head or by hand. Learning from simulation is designed to help upgrade local decision-making. Teams develop new rules of thumb and insights in which the dependent dynamics among these variables that define care are all taken into account. With a _Modeling to Learn_ consult, we come alongside with partners mid stride in their daily clinical activities who may have limited insight into what is likely to happen over the near future if they keep making the same decisions every day. With _Modeling to Learn Blue_ simulation learning, sites and teams can safely see the impact of new decisions while building new capacities for systems thinking. Why is applied systems thinking more likely to help us avoid costly mistakes? Watch that video to find out.
## Why is applied systems thinking more likely to help us avoid costly mistakes?